While doing any kind of work in your daily life, there have been many times when you have involuntarily wandered off. In moments like these, no matter how hard you try to focus on one thing, you may even have the feeling that something is keeping you from taking care of your work. What would you think if we told you that these distractions have a scientific explanation? Here are the scientific explanations on the subject…
Most of the involuntary distractions have a common feature: Regardless of the circumstances, the person temporarily becomes indifferent to the work he is doing. all your bond cuts out for a while.
Scientists consider this involuntary distraction a hypothetically explains. According to this hypothesis, there is a network called DMN (Default Mode Network) in the human brain, and when this network interacts with all other parts of the brain, the person begins to wander away uncontrollably. Let’s take a look at the details and more about this very interesting hypothesis.
The hypothesis is that the reason for the far dive is the activation of the waking resting mode.
When a person is indifferent or not fully focused on what is happening around them, the person’s brain goes into a state of waking rest. DMN This network, called this network, can also come into play when people think about their past or future and become introverted.
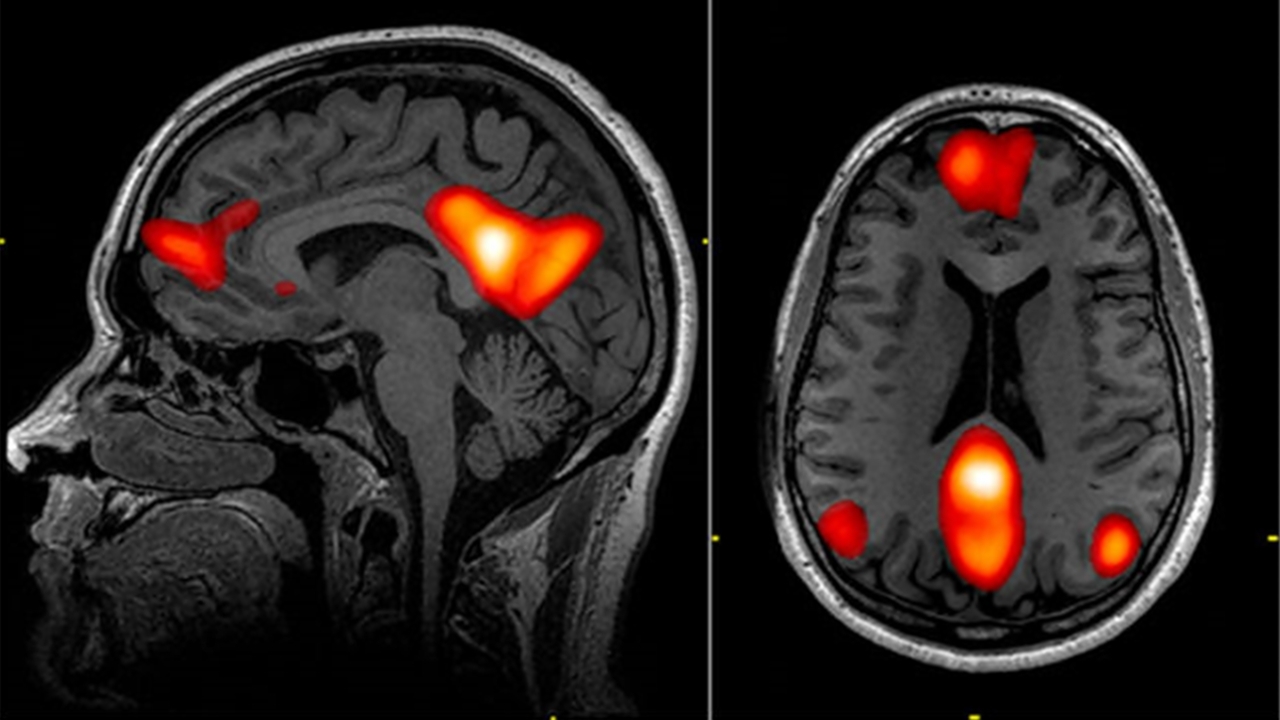
In other words, when you do not fully focus on what you are doing and give yourself away, this mode of the brain activates and unconsciously directs you to get away from the situation you are in. Another name for this mode is the situation that occurs without a conscious choice. “Default Mode”. However, it should be noted that there is no positive correlation between the DMN and the attention networks of the brain. For example, even if a person really cares about his work, this does not mean that he pays serious attention to that work. So even someone who works hard and carefully can sometimes get distracted.
Some scientists explain the reason for this situation with the dissociation hypothesis.
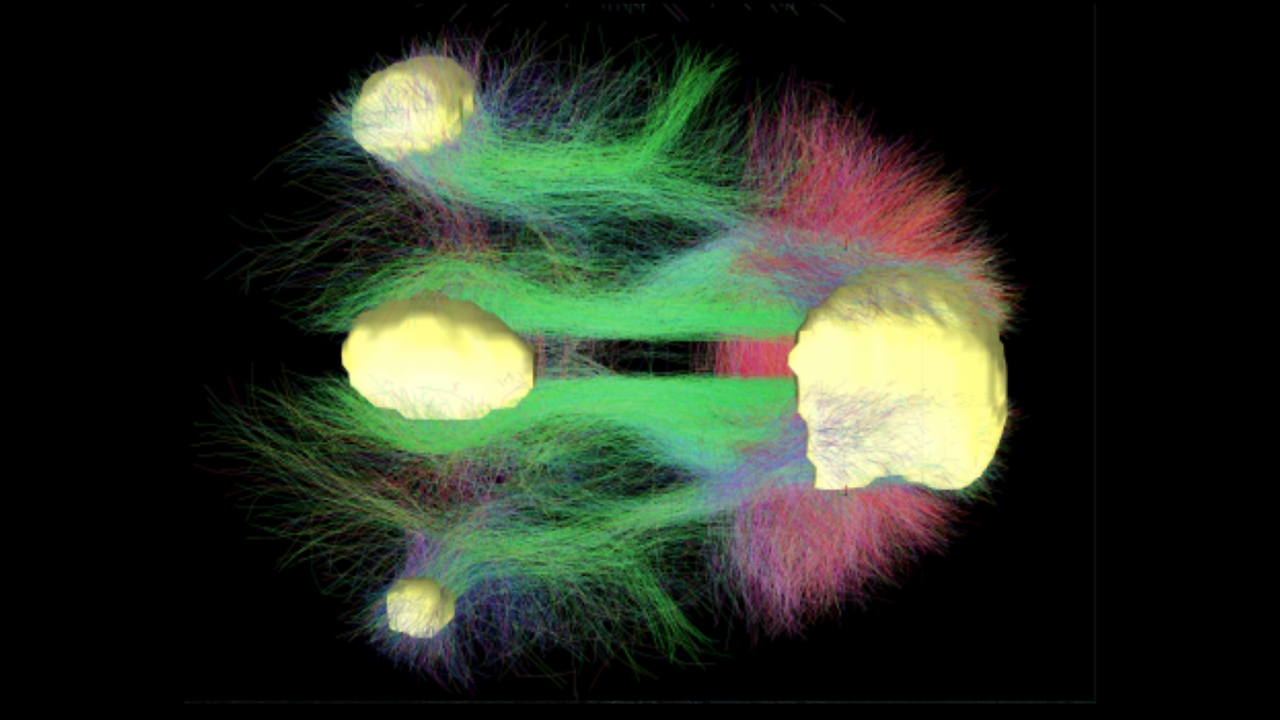
According to scientists Jonathan W. Schooler and Jonathan Smallwood, when one’s attention is detached from one’s surroundings, one becomes desensitized to outside things. This depersonalization allows one’s pupils to become completely independent of the external environment, and thus the person’s pupils one shrinks and one grows. This situation, in question, can cause people to look away and ask the question of who they are so distracted by.
Resources: Live Science, Outstanding Evidence
RELATED NEWS
