Have you ever thought about why you can instantly compare the photos shared by NASA to certain things?
Recently NASADuring Halloween, he shared images that both fascinated and gave people a little chill. Finally, we saw that a view resembling an animal face was shared. Of course, it’s not hard to think that NASA chose these specifically.
Because by doing this, the company your apophenia (Apophenia) It aims to trigger. Before you get doomsday scenarios coming to your mind, let us point out that this is no different than comparing clouds to different things. Dead star remnant that looks like a hand, to the sun that looks like a pumpkin and other photographs, you will look at them with a much different perspective when you reach the end of this content.
Before moving on to the photos, let’s explain briefly: What is apophenia?
A galaxy cluster captured by Hubble
- We will look at these more in the following parts of our content.
Apophenia, confusion between events or objects a connection that doesn’t actually exist or the state of seeing order is called. We know scientifically that the shapes formed by clouds are random. We can also take one of the clouds and make it look like a smiling face. At its most basic, this condition is called apophenia.
Apophenia was first described in 1958. German Psychiatrist Klaus Conrad It emerged as a result of his studies on schizophrenia. However, it has become clear that this is an effect on the brain and is not limited to those diagnosed with schizophrenia. But Conrad’s observations indicated that people suffering from schizophrenia attributed what they saw to a message or meaning.
So let’s explain it this way. You may compare a cloud to a moon and a star and laugh at it. But people with psychological problems may try to make sense of this or can be perceived as a message. As a result, the effort to achieve something naturally causes these people to lose control. can wear out.
Of course, this does not mean that you do not do this in daily life.
Let’s say you woke up in the morning, had a good night’s sleep, the weather was just the way you liked it, the order you placed yesterday arrived this morning, you constantly see green lights when you get in your car, and when you want to buy coffee, you come across the shop. 50 percent discount You come across. When all of this happens one by one, inevitably “I’m on my lucky dayYou make an inference like “.
Relying on this pattern Making decisions during the day, playing games of chance, or simply thinking that everything will continue like this throughout the day, includes you in apophenia.
Think about it this way:
It affects whether you get enough sleep (what time you go to bed, your nutrition, your departure time, etc.), determines what the weather will be like that day (climatic events, pollution, season, etc.), affects when your cargo will be delivered (traffic, weather conditions, distance, etc.). .), determining the duration of the green lights (countdown depending on the day-night situation, etc.) and affecting the discount that the coffee shop decides on that day (certain day of the month, sudden decision of the founder, etc.). There are countless factors,
For this very reason, we believe that events, good or bad, will continue this way. not to believe.
There are 4 types of apophenia:
- pareidolia
- gambler’s fallacy
- Clustering illusion
- Confirmation bias
These types, named according to the situations they are in, apophenia gathered under its roof. Let’s talk about all of them briefly without getting confused.
Pareidolia is often confused with apophenia.
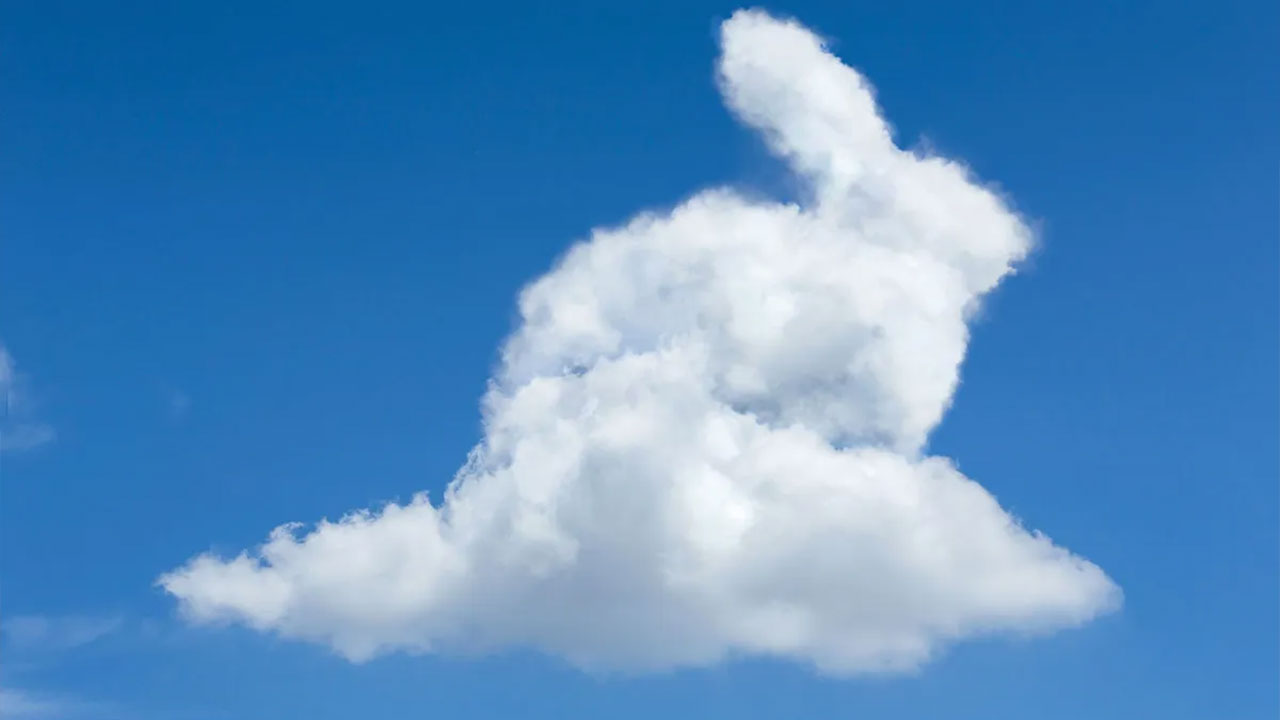

The difference is that pareidolia occurs specifically in visual stimuli. Well NASA’s Pareidolia is why we compare the images he shares to something else. You can find a similar example of this in the image above.
The gambler’s fallacy is about the future.
Because we said gamblerI don’t have itDon’t say. If in the examThere are 3 A’s, this is not a definite A, let me eliminate it immediately.If you think “, then you are making the same mistake. Imagine, in a roulette game at the Monte Carlo Casino in 1913, the ball lands on black 26 times in a row.
For example, those who play the game say “after 3 black points”will never come across black again” he thinks and plays with other options. Millions are lost as a result. However, each tour takes place independently of the previous one. Just because it comes across black 300 times doesn’t mean it won’t happen 301 times.
Let’s talk about the illusion of gathering.
Here, data plays a role. Our consciousness tries to find order in the chaos of data. This, going well for a short time Thinking that things will continue like that can also be included, thinking that the 1-week situation of share prices will continue that way.
For example Furkan Korkmaz’s Although making 3 3-pointers in the first 5 minutes of the match provides motivation, it does not mean that he can maintain this performance throughout the match. Or to think that a stock that has been declining for a week will continue or increase based on this data alone. It’s a mistake.
Biased confirmation occurs as a result of our prejudices.
If you ignore sources that claim the opposite of what you want to believe while researching something, you are doing biased verification. Also, someone you don’t know looking at your appearance An example of this is making inferences about his/her personal characteristics.
Now let’s come to these NASA photos, which we compare to many things thanks to pareidolia:
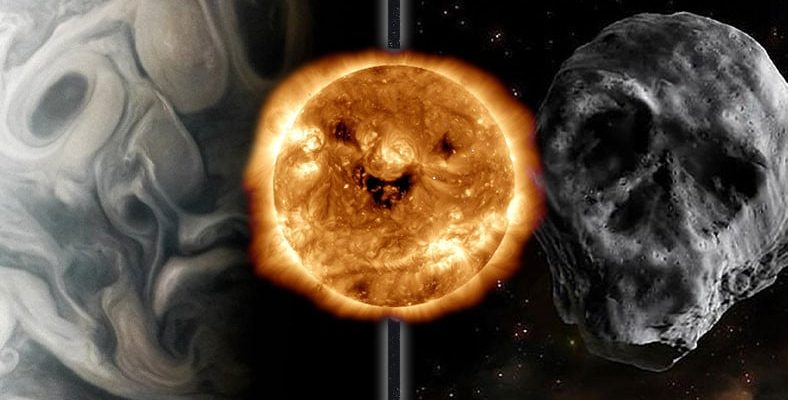
This image, which looks like it was created by Picasso, appears with the clouds of Jupiter.
Here, you can see the hand-like electromagnetic trace left behind by a dying star.
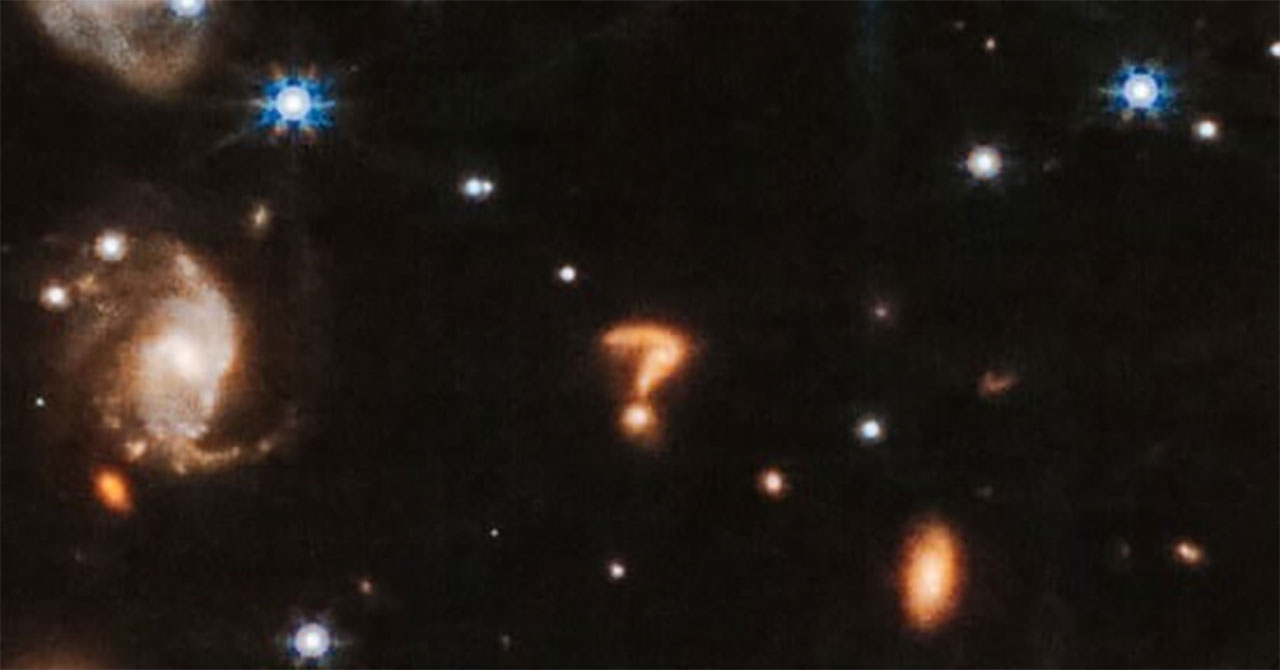
It is not yet clear what this question mark, 1,400 light years away, is.

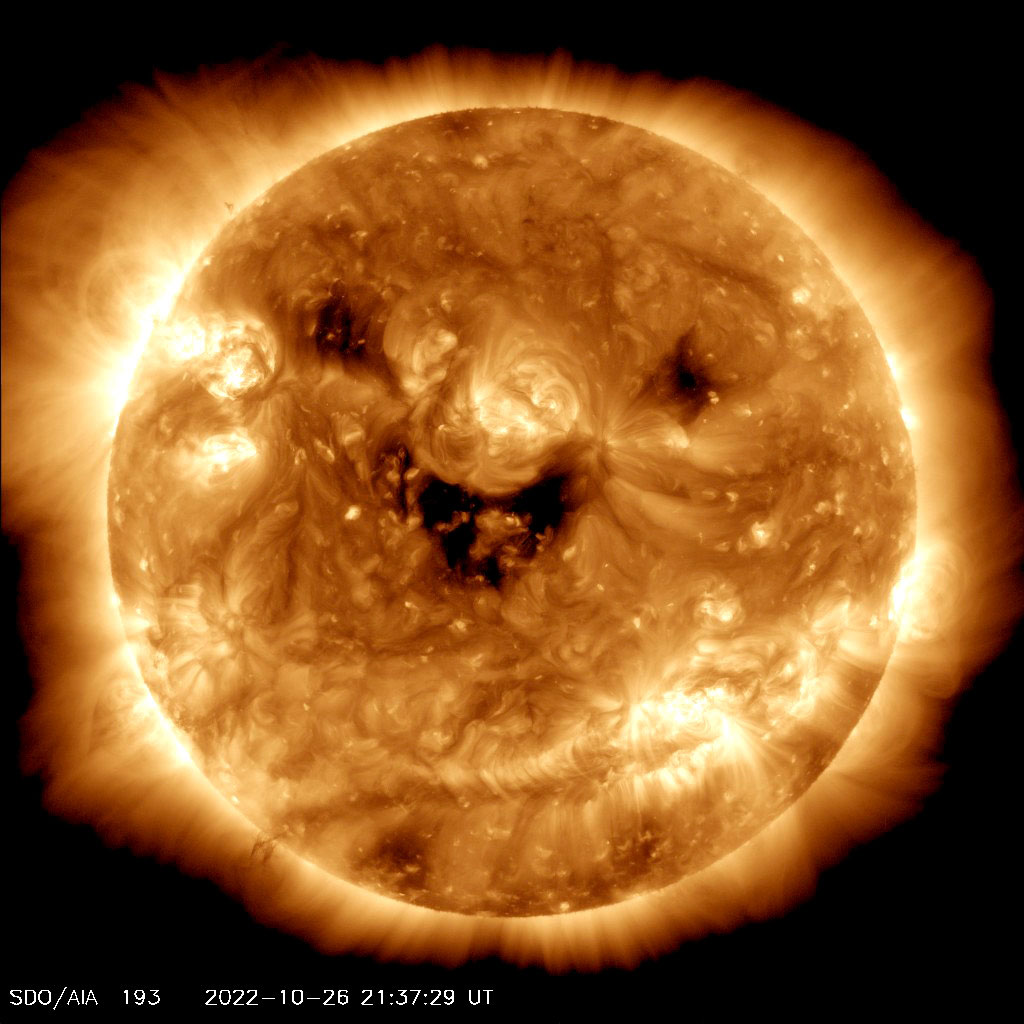
This image, shared on Halloween, actually shows active parts of the Sun.
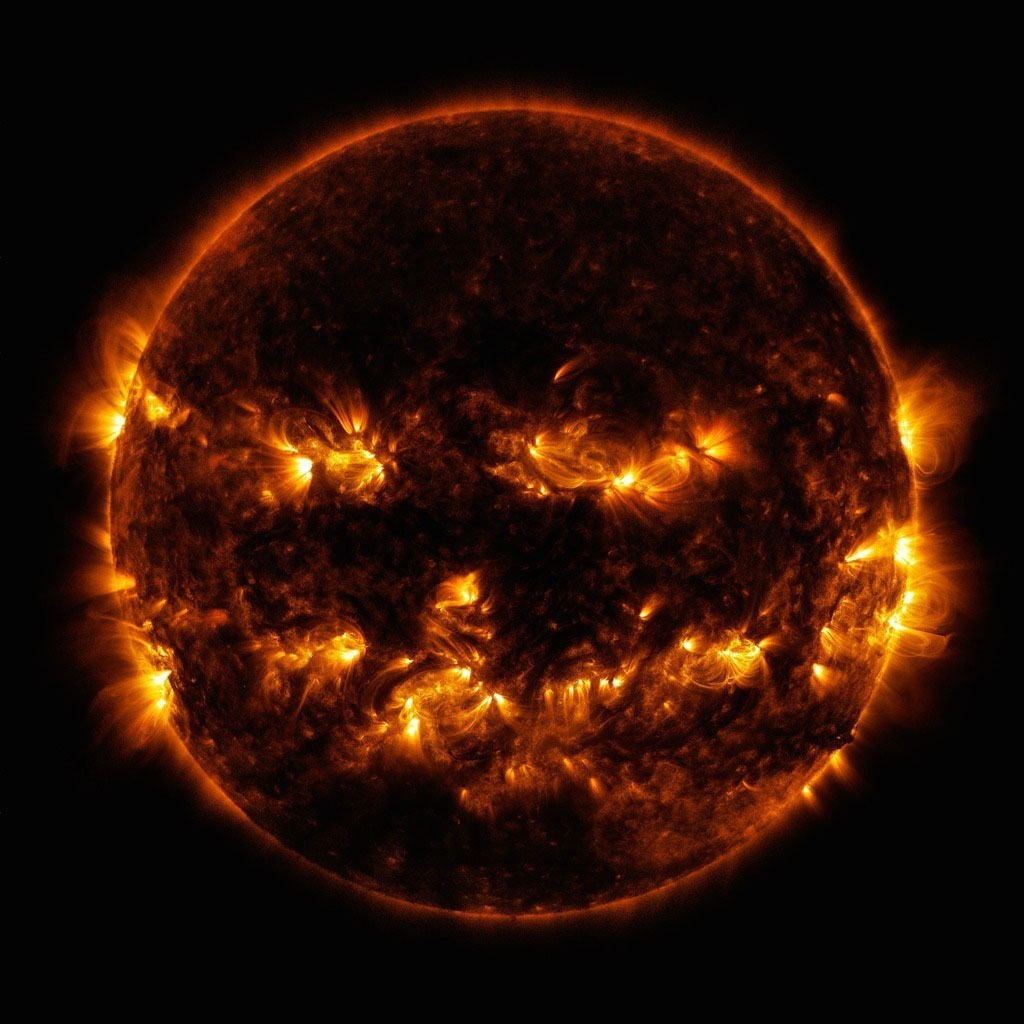

Even though the dark areas you see here make the Sun cute, they show areas where energy and gas levels are low.
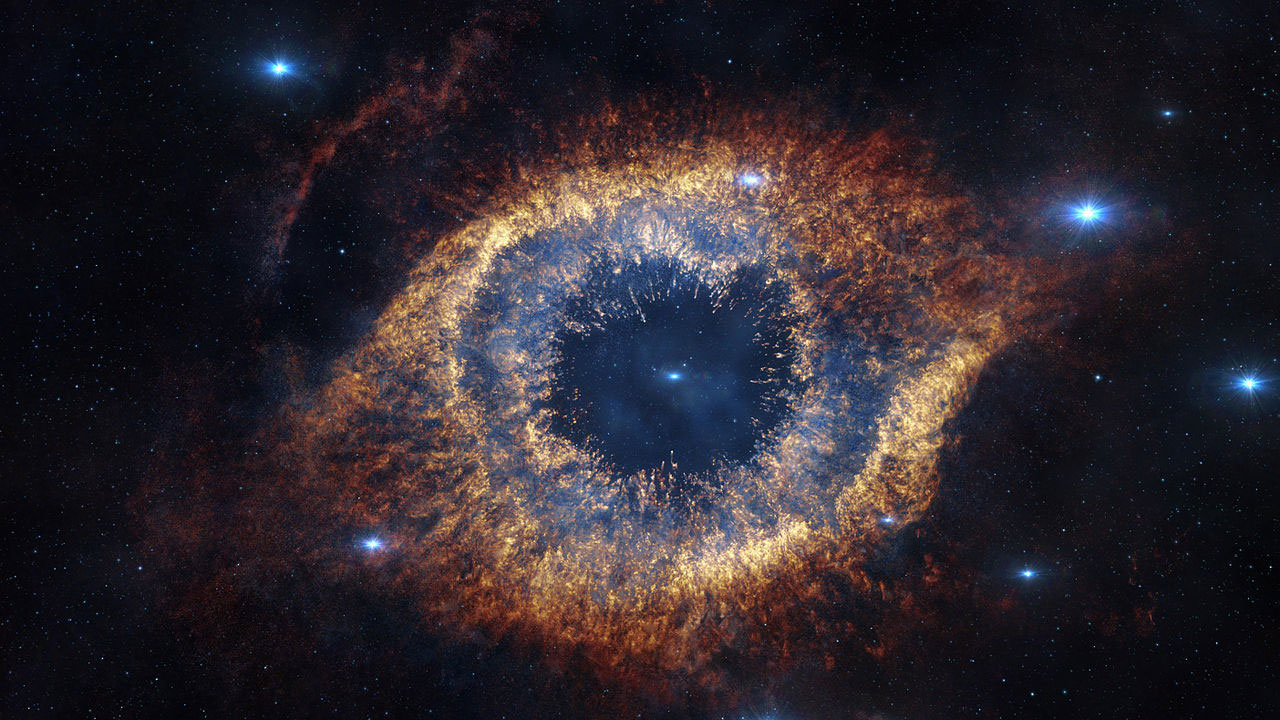
This object, which looks like a giant eye in space, is known as the Helix Nebula.
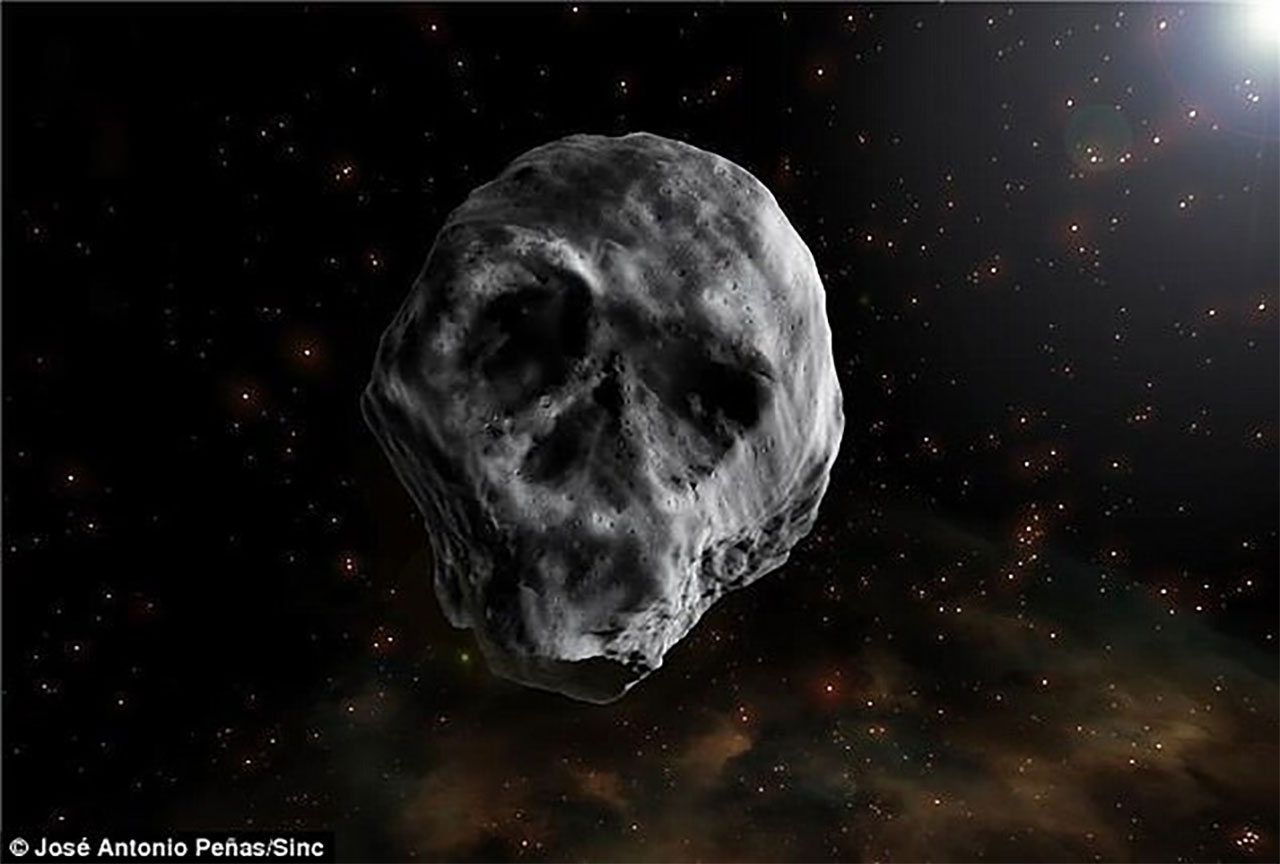
Finally, this skull-shaped object you see is a comet.
Here is a photo of a rock that resembles an animal face.
RELATED NEWS
NASA Shares Eerie Image of a “Dying” Star That Resembles a Human Hand [Video]
RELATED NEWS
Unique in the World: An Absurd Incident in which a Cow Killed by a Satellite Piece Falling from Space Triggered the Tension between the USA and Cuba
RELATED NEWS
50 Completely Unreal Psychological Misconceptions That Often Cause Us to Make Wrong Decisions in Daily Life
RELATED NEWS
