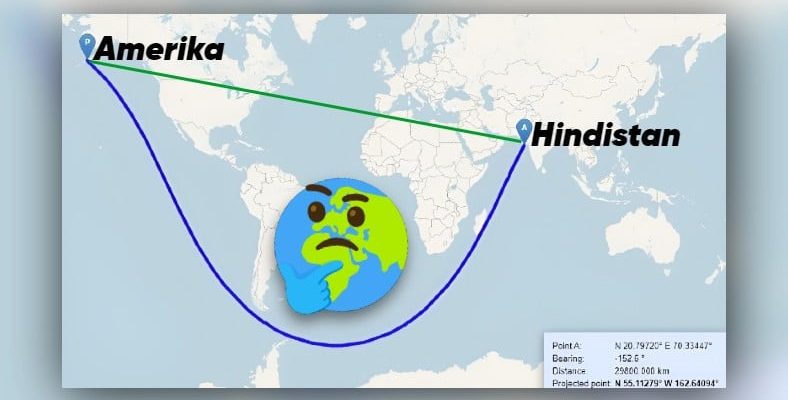
Did you know that you can reach the USA from India by going straight ahead? And without touching any land!
Sailors; theoretically, starting from India and ca. 29800,000 km without even touching the steering wheel, You can reach it by going straight ahead.
Well, ocean currents and Antarctic ice sheets How much it allows this is another matter, but as we said, it is theoretically possible. Let’s see how it goes.
The line on this map connecting India and the United States is actually straight.
The top line is straight on this map, but in reality the bottom line is straight.
of the world is a three-dimensional sphere, Let us remind you that maps are flat and two-dimensional.
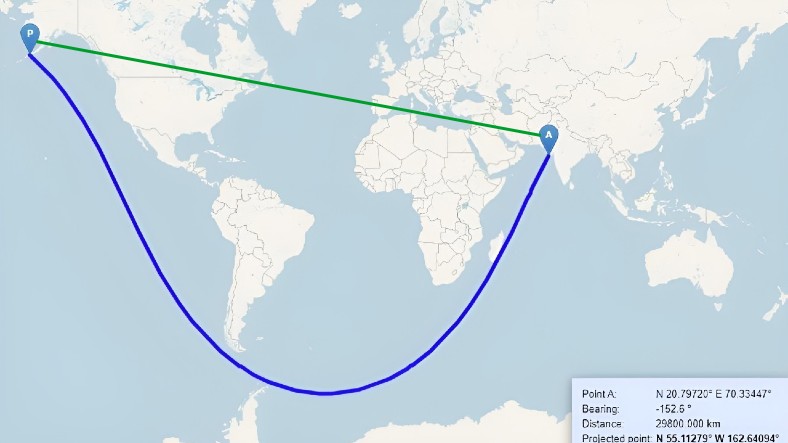
In other words, the trapezoidal line drawn in blue on the map is actually on Earth. a straight route It creates. At the end of our content you will have a better understanding of how.
So what will this route be like?
The journey, which is assumed to start via the Indian Ocean, passes near Madagascar, enters the Atlantic Ocean, passes through the eastern coast of the Southern USA and reaches the Pacific Ocean from the Equator. Finally, North Alaska, located in the western United States welcomes us.
Thus, starting from India and continuing to the United States, A straight route is completed. It is interesting, is not it?
If you don’t understand exactly what this straight line is like, you can check out the animation below:
It’s weird, it’s like we live on a globe (!). You that such a route is possible Could you guess?
Our other content that may interest you:
RELATED NEWS
What is the Secret to Less Gravity in This Interesting Region in Canada? (Should we move to weigh less on the scale?)
RELATED NEWS
Why Didn’t Sailors Going to the Ocean Catch Fish Even If They Ran Out of Food?
RELATED NEWS
We Asked the Marine Engineer: Why Aren’t Ships Having Headlights, Which Are Vital in Other Vehicles?
RELATED NEWS