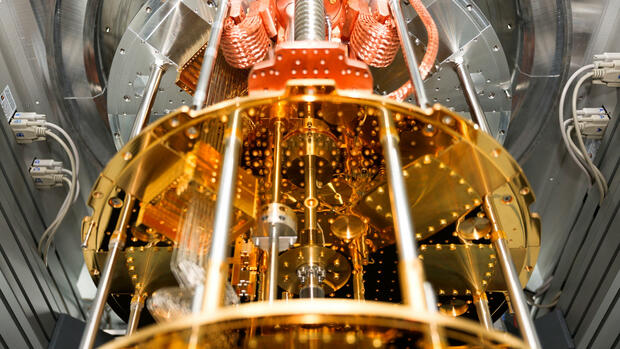
Berlin The federal government wants to ensure that Germany also has a powerful universal quantum computer by 2026. The country should come “on par with international developments” in the USA and China. This is the aim of the federal government’s new “action concept for quantum technologies”, which is available to the Handelsblatt.
In total, funds of 2.2 billion euros are earmarked for the ministries as part of the concept up to 2026, of which 1.37 are allocated to the lead research ministry. In addition, there are around 800 million euros in the budgets of the state-financed large research institutes. The cabinet should launch the concept at the end of April. Quantum technology is “crucial for Germany’s technological sovereignty,” said Federal Research Minister Bettina Stark-Watzinger (FDP) to the Handelsblatt.
Quantum computers are considered to be the key technology of the future because they can perform calculations in seconds that even very powerful computers need years to do. Information is passed on in bits in conventional computers and in qbits in quantum computers. While bits translate information into zeros and ones, qbits can take any value in between and are correspondingly more powerful.
Three billion euros in funding
The now planned German quantum computer should have a capacity of at least 100 qubits by 2026 and be expanded to 500 qubits “in the medium term”. For comparison: The US company IBM presented a quantum computer with 433 qubits at the Quantum Summit 2022 last year – this would be four times as powerful as the planned German computer in three years.
With a total of around three billion euros, Germany is expanding the previous funding and is thus positioning itself “at the top end in a European comparison,” says Frank Wilhelm-Mauch. He is the coordinator of the European EU project OpenSuperQPlus, which is based at Forschungszentrum Jülich and is the leading project in Europe. What is decisive, however, is that this will “trigger further large investment sums in the industry”.
Quantum technology is a key technology of the future and crucial for Germany’s technological sovereignty, said the Federal Research Minister.
(Photo: dpa)
Because Germany and Europe lack big players like Google or IBM, who can invest many billions in the construction of quantum computers. Public funding in the United States is also not transparent, “because a lot happens here through the military.” There are no reliable figures from China, said Wilhelm-Mauch.
Quantum computers are not yet ready for practical use, but hopes for their possible uses are high. These range “from the simulation of new active ingredients in drug research to tap-proof communication to innovative sensors that detect contaminated ordnance or enable navigation without satellite support,” said Stark-Watzinger.
>>Read here: How the supercomputers of the future threaten cyber security
In addition to funding quantum computers, the quantum strategy bundles various efforts by the ministries involved to use the technology in the future. There is already a lot of interest in business. The management consultancy Boston Consulting Group estimates the market for quantum computer software at 850 billion US dollars.
The opportunities for the German economy lie primarily in the development of software, the construction of components and the use of quantum technology, says Wilhelm-Mauch. In some cases, it is not just about opportunities, but rather about averting major damage: Experts have been warning for a long time that the USA is also hindering the export of components in order to secure its leading position in technology.
>> Read here: Chip makers develop protection against quantum computers
Bosch is one of the pioneers: the automotive supplier recently started a cooperation with IBM. With the help of material simulations made possible by quantum computers, rare earths in electric motors should one day be replaced. The Swabian laser specialist Trumpf also develops quantum computer chips and has already launched the first industrial-ready quantum sensor that can measure very fine particles.
Infineon has developed the first chips that are encrypted in a quantum secure manner. This is a major challenge for conventional digitization: the extreme computing capacity of quantum computers could soon make all conventional encryption systems obsolete.
>> Read here: Bosch secures access to quantum computers from IBM
In addition to the construction of the computer itself, the traffic light’s quantum strategy has set itself numerous other specific goals for the promotion of the technology as a whole: By 2026, “at least 60 end users of quantum computing should be active in Germany”. Here Germany should “be among the top three within the EU and at least reach the level of the USA or Japan”.
At least five new accurate gauges by 2026
In quantum sensors, i.e. very precise measurements using quantum technology, such as at Infineon, “five new products are expected to be on the market” by 2026. In addition, there should be optical clocks “that meet the requirements of the next generation of Galileo clocks”.
It is about hyper-precise clocks that are being developed at the German Aerospace Center DLR. These are central to satellite navigation, on which traffic, but also financial transactions, energy supply and agriculture depend.
In the project in Jülich, 28 partners from 10 countries want to implement a user-oriented 100-qubit system for the first quantum applications by the end of 2026.
(Photo: Research Center Juelich)
There are already atomic clocks that are accurate to the nanosecond – one billion nanoseconds is one second. And the next generation will be “many times more accurate,” according to DLR. And the better the time is determined, the safer, for example, navigation on earth.
The traffic light is also setting big goals for communication and encryption: In three years there should be “the first tap-proof, i.e. quantum-encrypted, communication test routes between selected authority locations”. In addition, the first test satellites for quantum key distribution are to be launched and cryptography is also to be developed for the high-security area.
More: Quantum computing from the cloud – federal government finances new offer for industry