The aim of the “flying tank” project, which stands out among the unique and interesting designs in terms of military history, was to launch surprise attacks behind enemy lines.
World War II, which witnessed the greatest mass deaths in history. in World War II, need to produce weapons It has led to many technological developments. In an environment of intense conflict, the revolutionary idea that had the potential to change the dynamics of war came from the Soviet Union: flying tank.
Not just the Soviet Union USA, Japan and England Let’s take a closer look at the details of this ‘flying tank’ project, in which he is also involved in research. Do you think there will actually be a flying tank?
Why did the need for flying tanks arise?
When you look at the idea of a flying tank, it actually seems quite simple. Put wings on tanks and transform it into a glider. Then pull the tank into the air and fly it deep into the enemy’s vulnerable rear area. Release the tank, float towards land with the crew ready.
In fact, when looked at this way, the idea of a flying tank is useful for providing weapons and armored support to airborne troops. in air battles It was solving the big problem. Heavy combat units were to be deployed to little-known locations unexpectedly by the enemy.
This idea enabled the four major countries we have mentioned to engage in flying tank research in the 1930s and 1940s. Of the countries, only the Soviet Union produced flying tank prototypes and Antonov A-40, the most ambitious in history took him on his first and only flight.
Before we get into how this test turned out, let’s take a look at the flying tank’s chronic design problems.
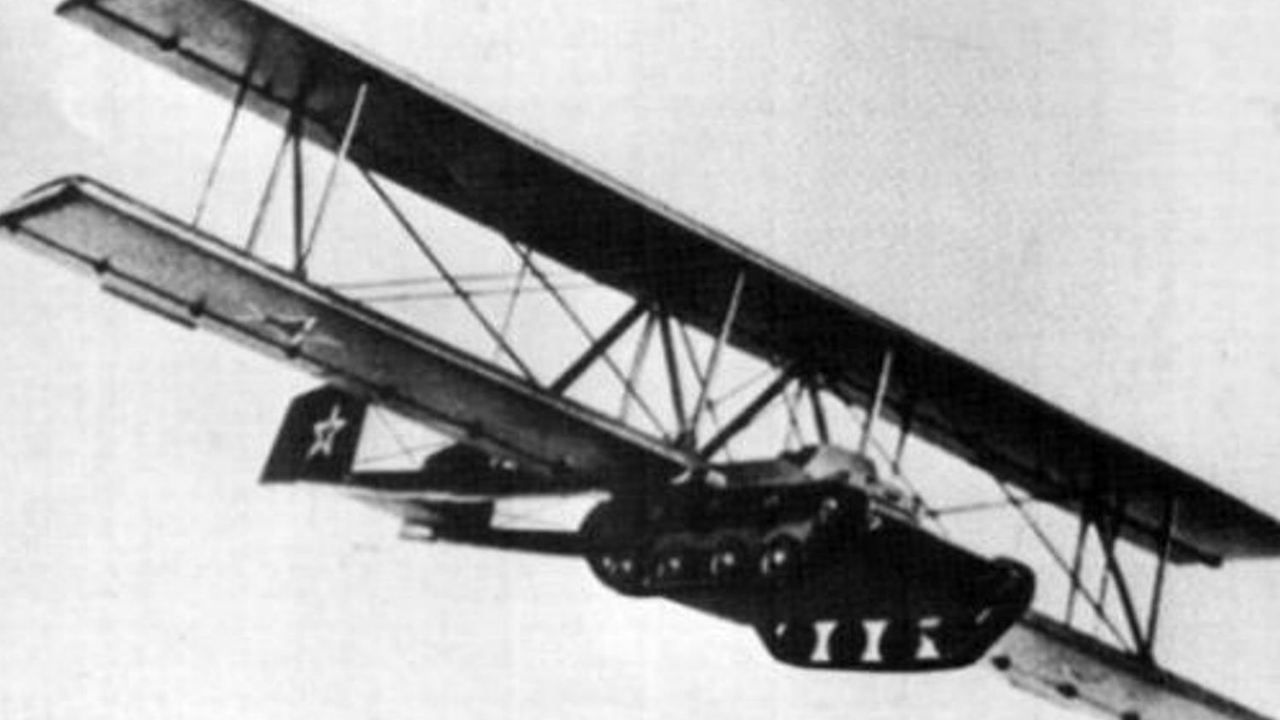

The idea of a flying tank was first American Engineer John Walter Christie It was put forward by in the early 1930s. There was a fundamental problem facing Christie and other designers working on the flying tank idea. That was because planes and tanks were opposites in many ways. For example, if an airplane had to be light, a tank had to be heavy.
Although there is an engineering solution for every engineering problem, this thesis was not valid for tank engineers. Because tank engineers and aviation engineers were quite different from each other in terms of education, knowledge and skills.
In Christie’s project, four ton tank Paired with a pair of wings. Using its own power and tracks, the tank will reach a speed of approximately 55 mph on the track, after which the tank engine will be replaced by powering the propeller and the tank will It would reach speeds of 85 mph (about 136 km).
US military, Christie’s innovative didn’t like your idea. A few years later, another designer in the Soviet Union implemented the design.
The Soviets also experimented with flying tanks during the same years.
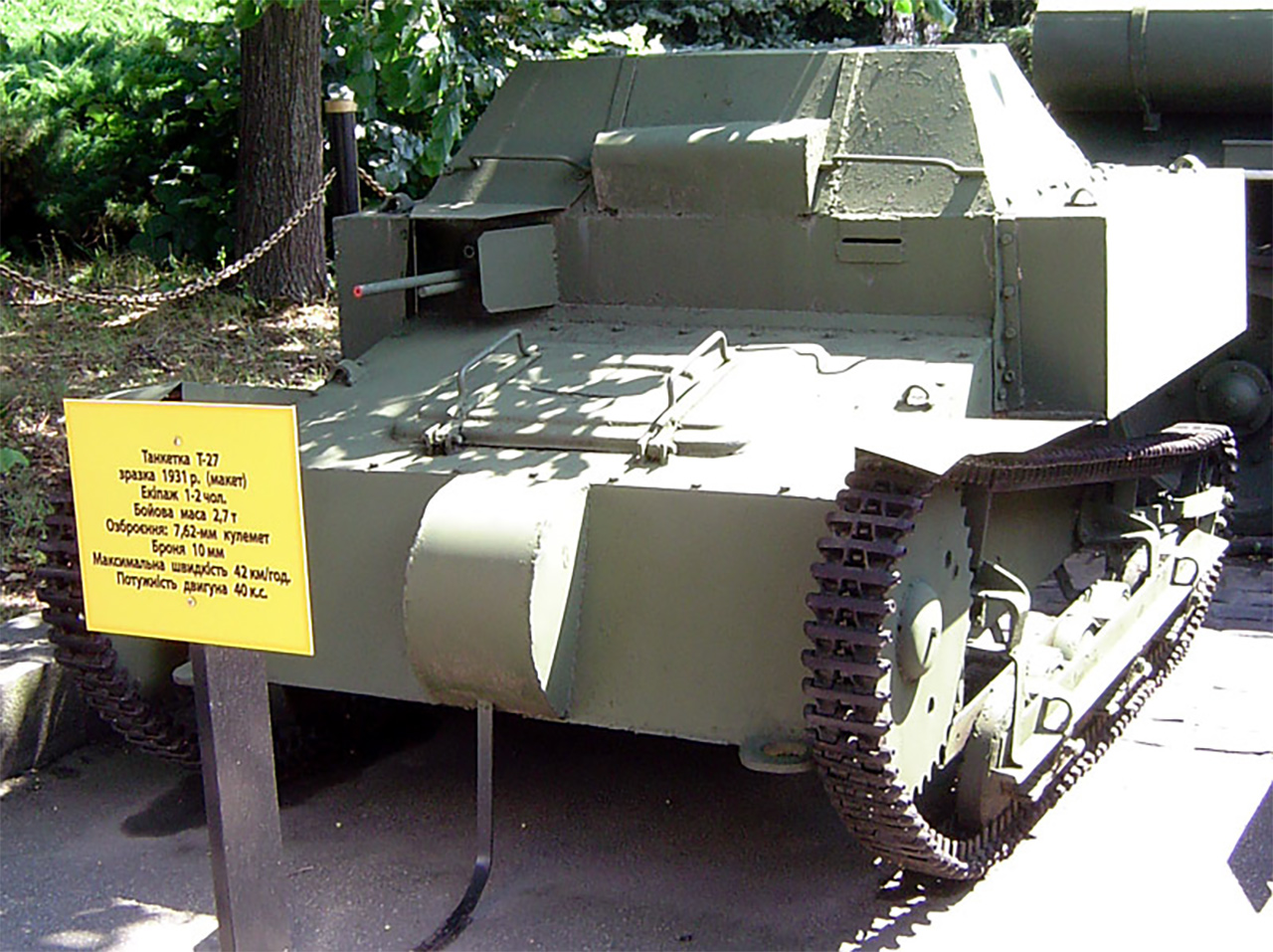

T-27 Tankette
The early 1930s were also a time of efforts by the Soviet Union. T-27 Tankette This work, named, had a light and diminutive tankette, narrow tracks and a 7.62 mm DT machine gun mounted on the chassis. T-27 was the world’s first cantilevered four-engine aircraft named Tupolev TB-3. heavy bomber aircraft It was designed to hang at the midpoint of its body.
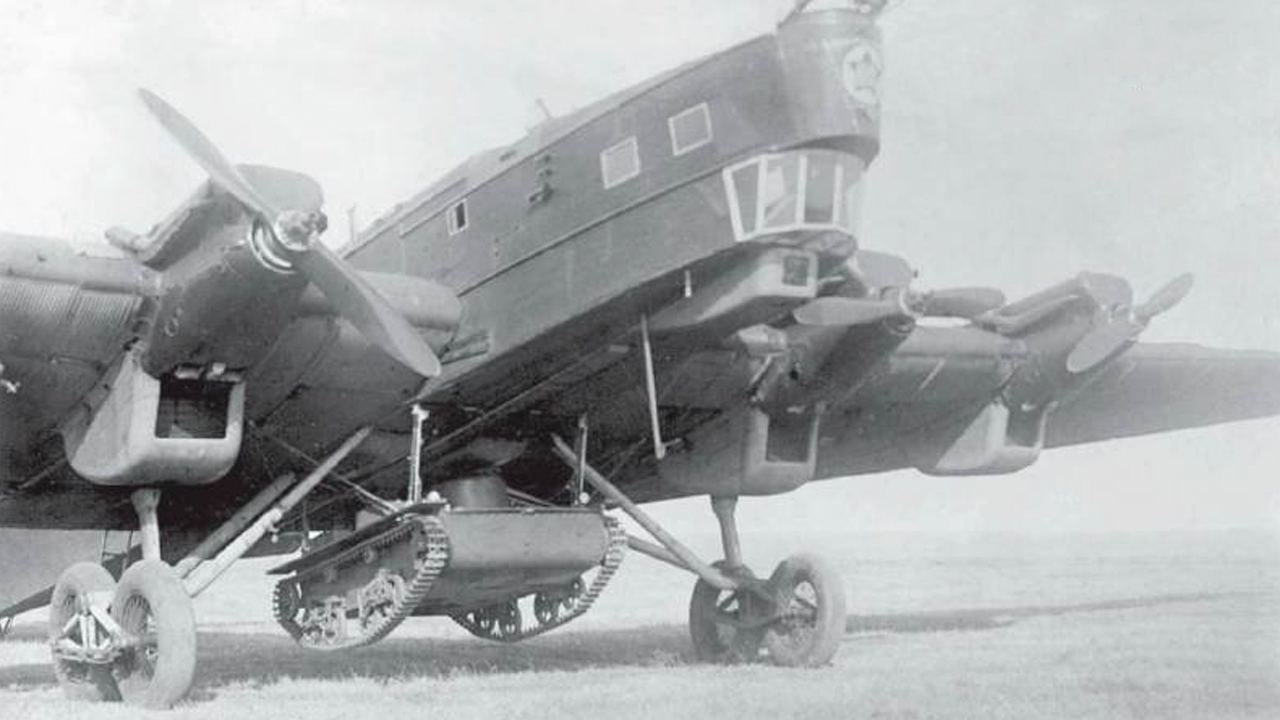
TB-3 heavy bomber
However, the Soviets’ flying tankettes did not fully meet the flying tank. They were very light and since they were not launched from the air, they could be taken down after landing. This essentially turned them into cargo loads on a normal transport plane. Another problem with flying tankettes is Separate delivery of crew to the battlefield was to be And that meant extra time for the tank and crew to rendezvous.
Despite this, the Soviets took several steps to quickly occupy the countryside when the Romanians evacuated what is now the Republic of Moldova. They shot the flying tankette out of the air.
The Soviets wanted more than flying tankettes, and the Antonov A-40 appeared.
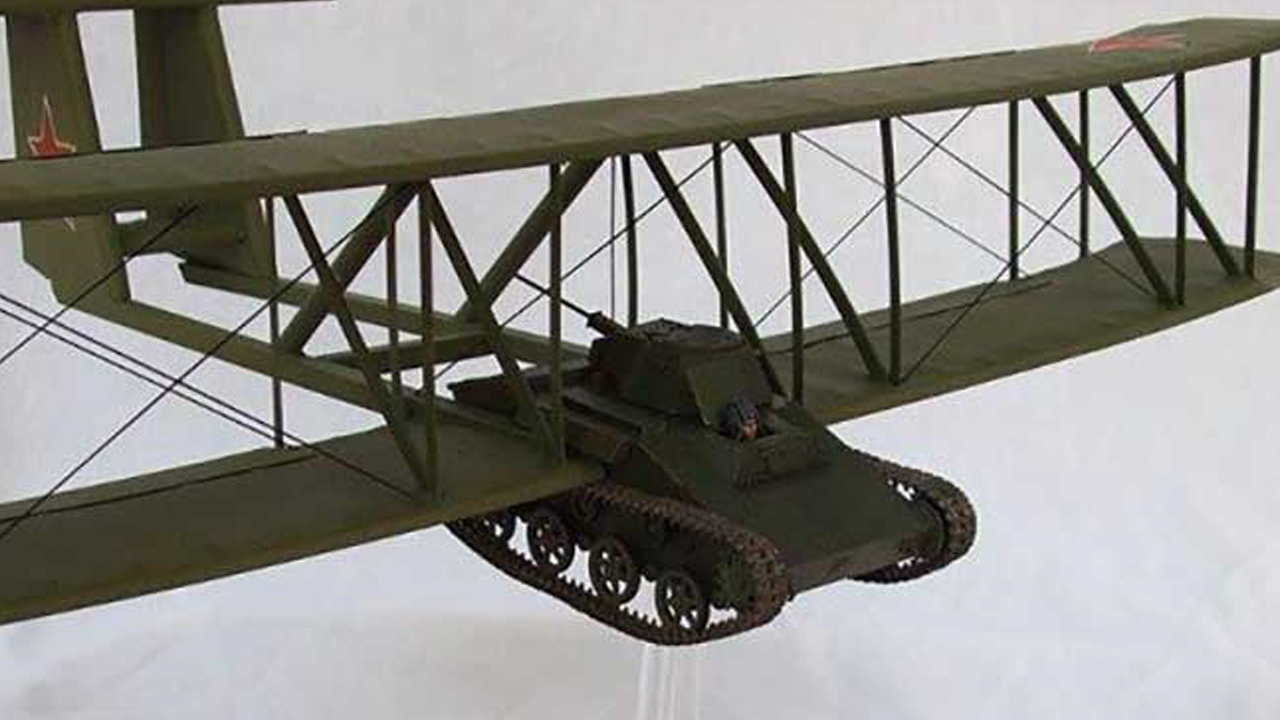

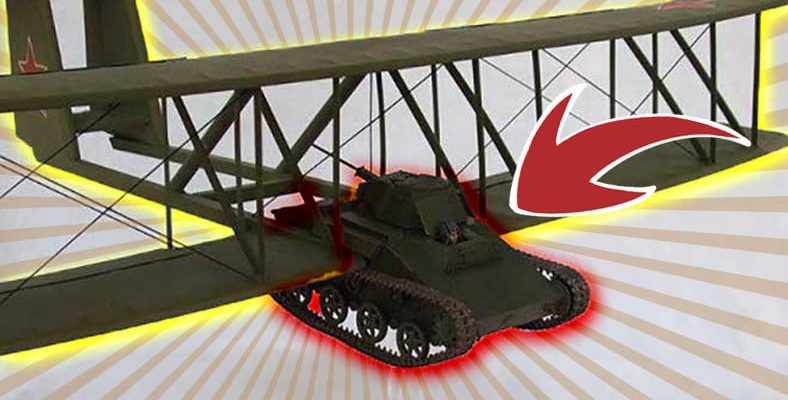
Oleg Antonov, who has admired the aviation industry since childhood, was the chief designer at the Moscow Glider Factory with his talents in design. By Oleg Antonov on the Soviets’ desire to go further than the flying tankette Antonov A-40 Krylya Tanka was designed. The aim of this design is; was for the crew to fly the tank, drop the wings, and immediately attack.
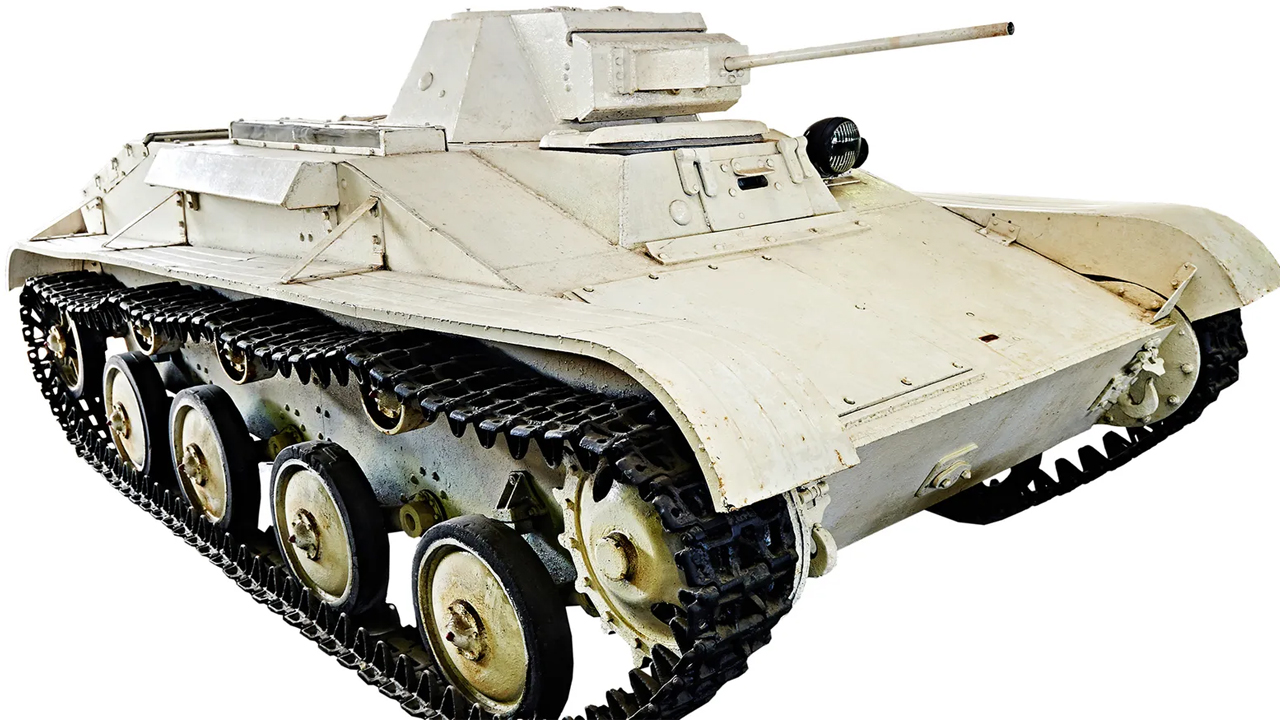

T-60 tank
In 1942, Antonov combined the T-60 tank with the biplane glider wing. For the T-60 tank to fly 18 meter wingspan of the A-40 glider used. Antonov also introduced the double-tail wing design to add lift. The total weight of the A-40’s wings was 2,004 kilograms without the tank. If with the tank total weight up to 7,804 kilograms was reaching.
Thinking that it would be difficult for the tank to fly into the air, Antonov decided to use the four-engine tank used in flying tankettes. heavy bomber TB-3 He trusted.
The first flight took place on September 2, 1942.
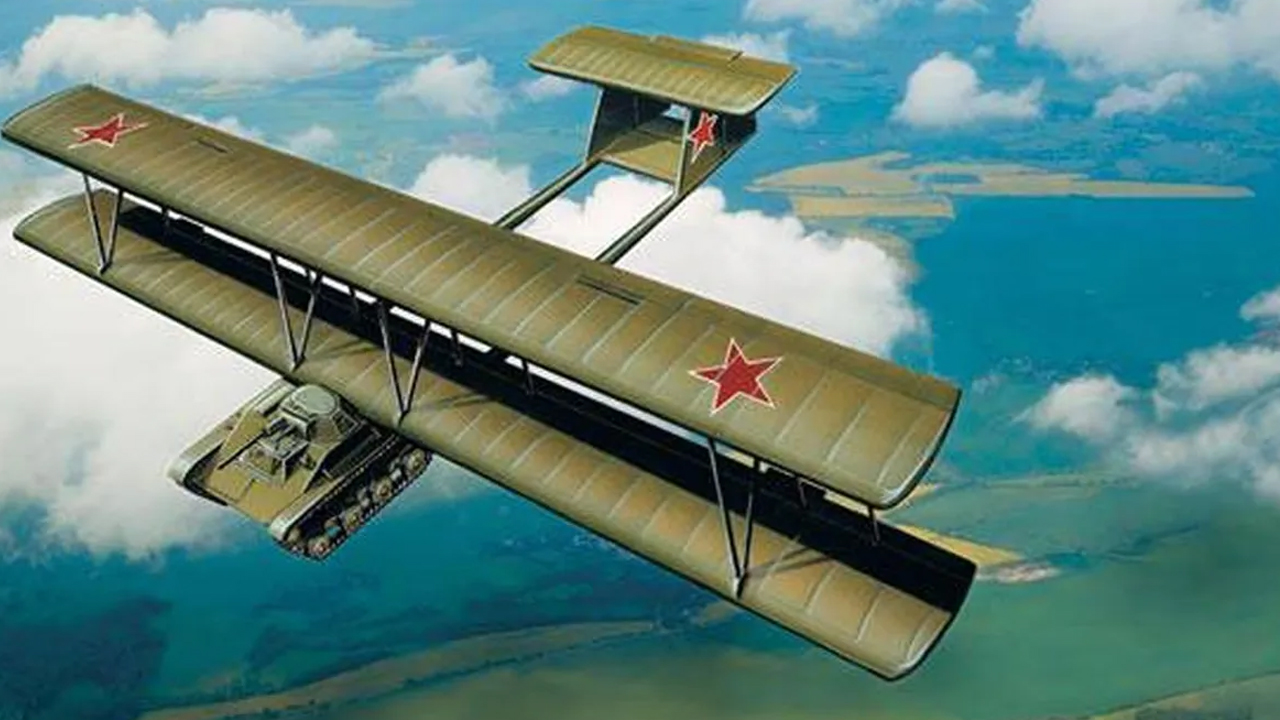

A-40 Krylya Tanka met with T-60 for testing at Zhukovsky Airfield near Moscow. To further reduce the weight, no ammunition was added to the tank and only limited fuel There was. The T-60 was connected to the TB-3 by a tow rope. They were now ready for flight with Sergei Anokhin, one of the expert glider pilots of the Soviet Union, who entered the tank.
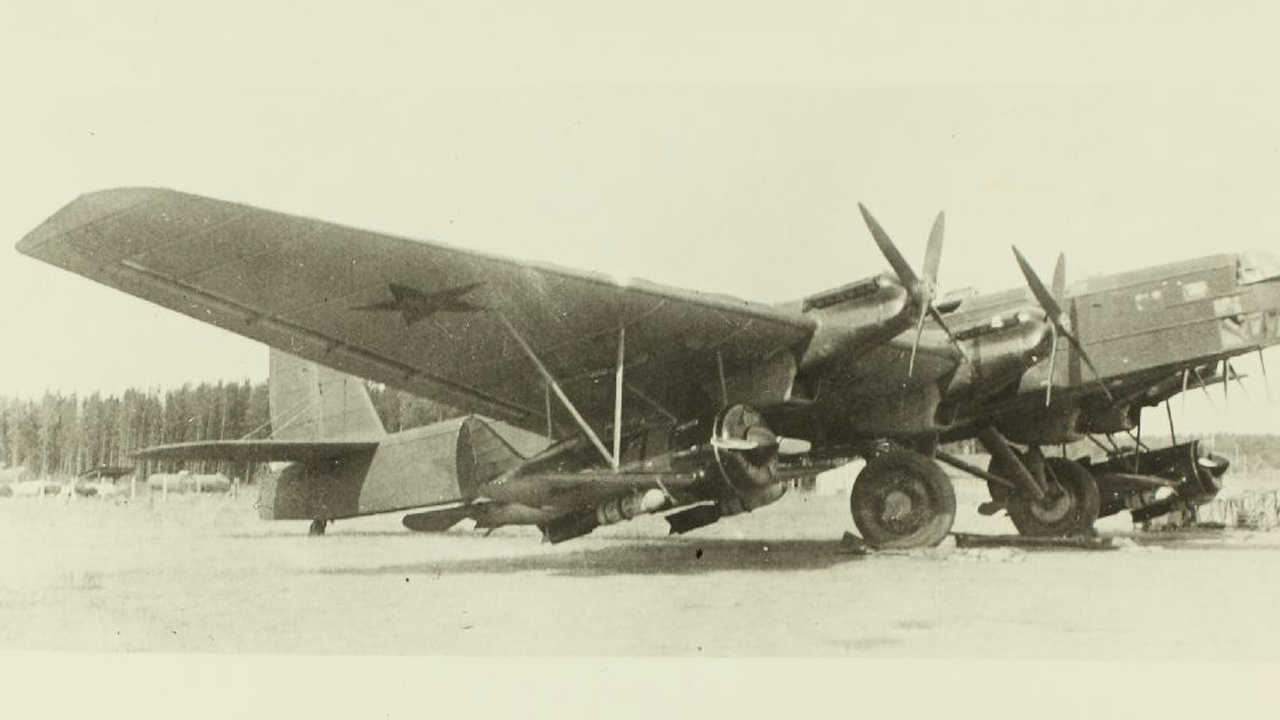

TB-3
Everything looked smooth as the bomber took off, but as the plane climbed into the sky, the tank began to drift. its weight was too much for TB-3 was seen. To prevent the accident, the crew released the tow rope and the tank floated towards the field.
Although the aerodynamics of the A-40 are solid, it was seen in this flight that It was quite difficult to lift a heavy vehicle into the air. When Sergei Anokhin arrived on the ground, he lowered the wings, started the tank engine and returned to base to report.
The reason why the tank cannot be lifted into the air as desired is that the tank cannot be lifted into the air as desired. strong enough to carry it to the battlefield It was because it wasn’t a plane. That’s why the Antonov A-40 turned into a shelved project.
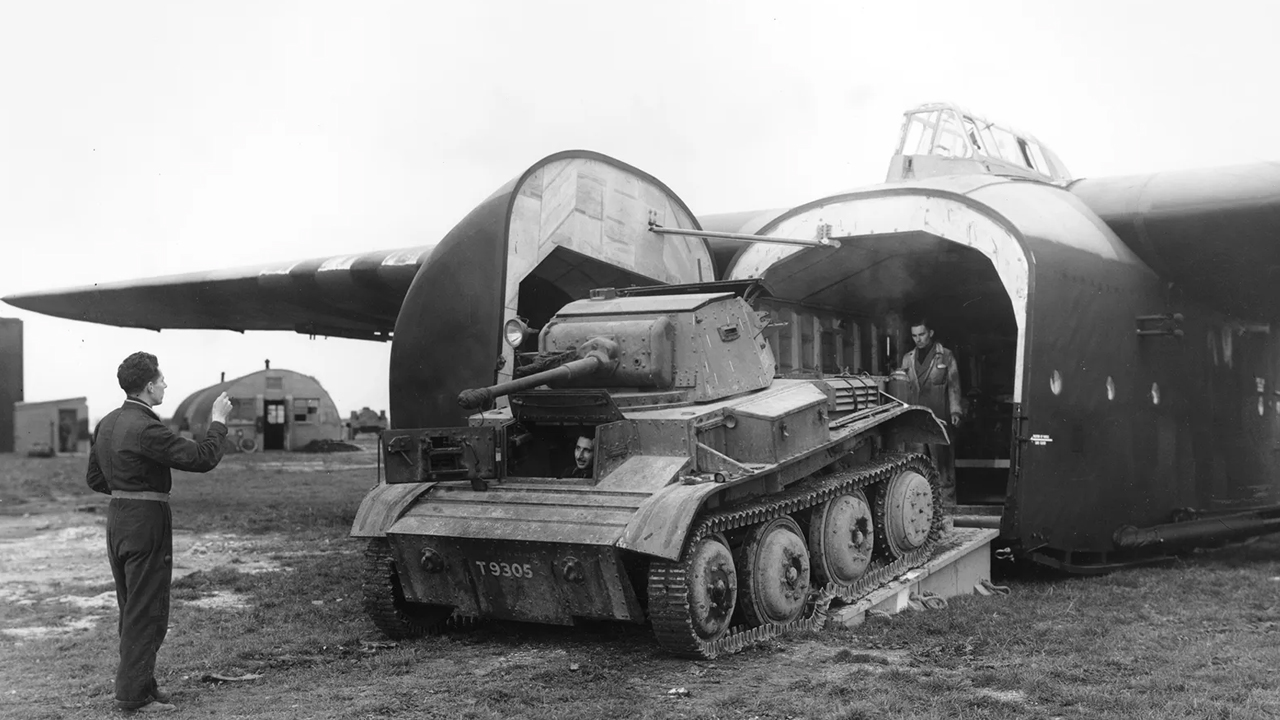

hamilcar
The British found an alternative to the flying tank in 1944 Hamilcar GAL.49 glider It aimed to carry various heavy vehicles and weapons, including light tanks. However, the Hamilcar met the same fate as the Antonov A-40.
II. After the end of World War II special military transport vehicles And with the advent of large helicopters, the idea of a flying tank became unnecessary and remained a fantasy in the history of war.
Our other content that may interest you:
RELATED NEWS
II. Technologies Discovered in World War II that Changed the Fate of the World
RELATED NEWS
10 Information About A-10 Thunderbolt, the Completely Bulletproof Warplane Known as the ‘Tank Killer’
RELATED NEWS
Unique Features of the Doomsday Plane Designed by America to Escape from Major Disasters: It’s Worth 3.5 Billion Dollars!
RELATED NEWS
The Death Machine in the Sky That the USA Has Never Given to Any Country: F-22 Raptor
RELATED NEWS
Rulers of the Skies: The Fastest Fighters in Service Today
RELATED NEWS
