Natural selection, which emerged as a result of environmental factors in nature, has now left its place to artificial selection, although not completely. We have brought together examples that answer the question of what is artificial selection.
Natural selection, one of the cornerstones of the theory of evolution, is still a controversial topic. Basically, it is considered an order in which the strongest species survive as a result of environmental factors. If artificial selection means the existence of plants and animals that are entirely due to human or other human-induced factors. As a result of new developments in the field of biology every day, artificial selection Examples are increasing and appearing in daily life.
What is artificial selection? There is an answer to the question that can be understood by everyone. However, the processes for this selection process are a process that can only be understood by experts. There are species produced as a result of artificial selection in every aspect of our daily life. Developed to offer humanity a better nutrition and life. artificial selection examples can be quite surprising.
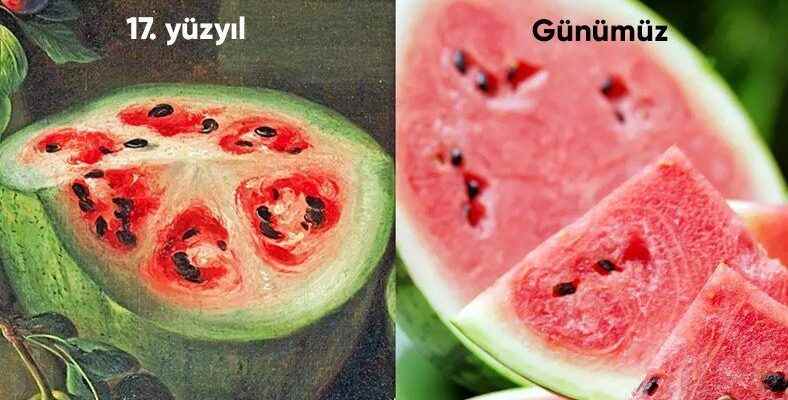
Here’s what a 17th century watermelon looked like:
What did watermelons look like before artificial selection by an artist named Giovanni Stanchi? In a painting he made in the 17th century we can see. These watermelons with plenty of seeds, cavities inside and just resembling a watermelon as we know it, have not been in our lives for a long time. It seems that the seeds of old watermelons during their adulthood were much larger and harder than today’s watermelon seeds.
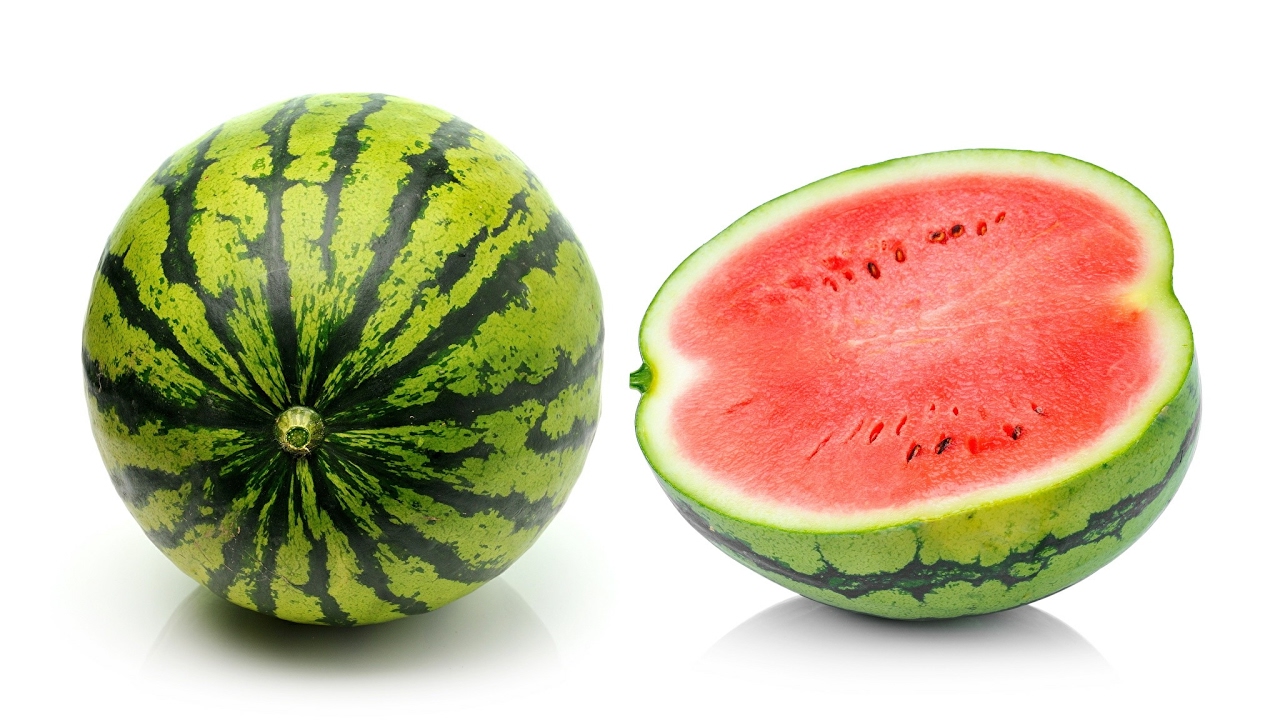

Today’s watermelons produced by artificial selection, which we can call modern watermelons, are almost as we know. seedless, fleshy and juicy are fruits. Especially with the studies carried out in recent years, it is very difficult to see kelek or seed watermelon. Artificial selection is the only cause of change in watermelon in only a few centuries.
Bananas 10,000 years ago had seeds, below we see a representatively produced banana:
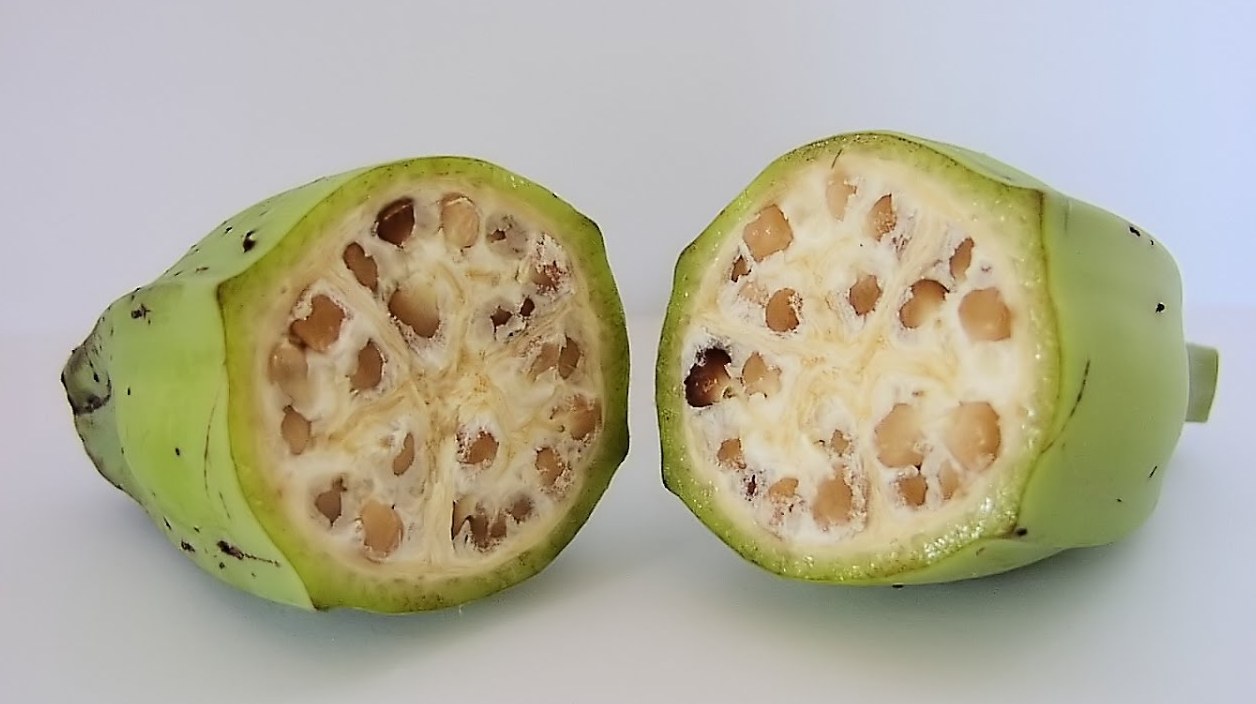

Although banana has become an easily accessible fruit especially in our country in the last 20 years, the first bananas about 10,000 years ago, It is thought to have been bred in what is today Papua New Guinea. There is a big difference between the old bananas and the bananas we know. The most striking point is the large and hard kernels inside.
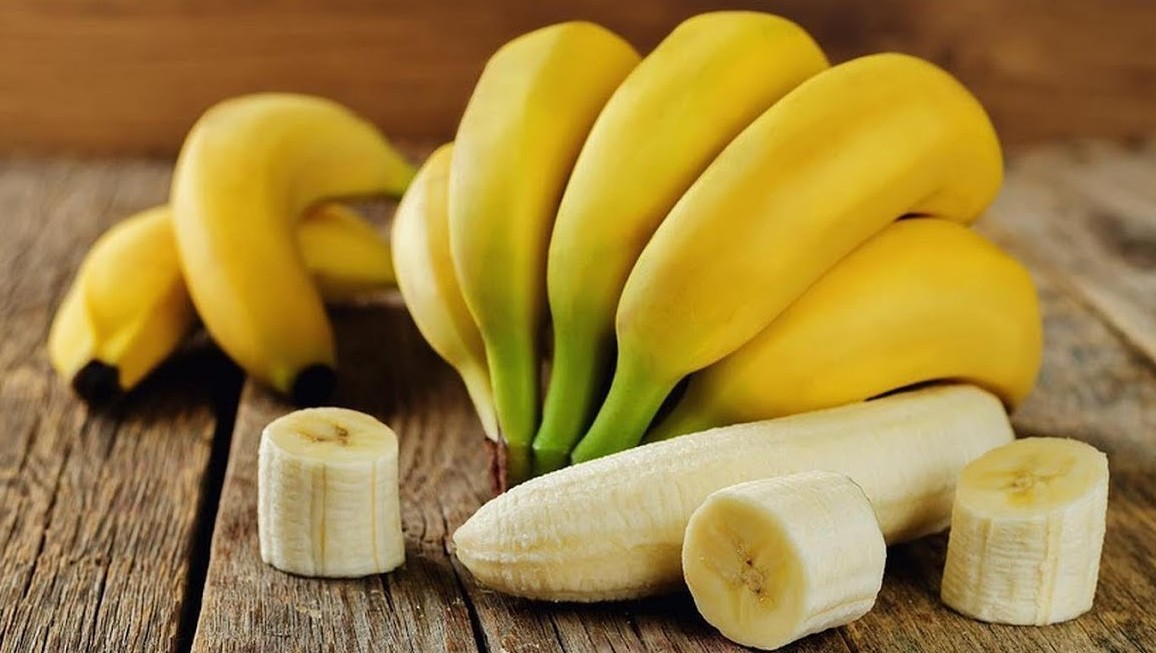

Today’s bananas, which are produced by artificial selection, which we can call modern bananas, are even eaten or chopped. cannot be seen or felt They have very small and soft cores. Moreover, today’s bananas have taken a delicious place in our lives, as they can be peeled easily without any tools.
Eggplants weren’t just purple in color. Below you can see a yellow and spiky type of eggplant:

The history of eggplant has a history as long and old as the history of humanity. However, old eggplants, which we can call wild eggplant, Unlike today’s eggplants They appeared in many different colors such as white, blue, yellow and purple. It is also known that some wild eggplant species have large spines on the stem attached to the plant body.
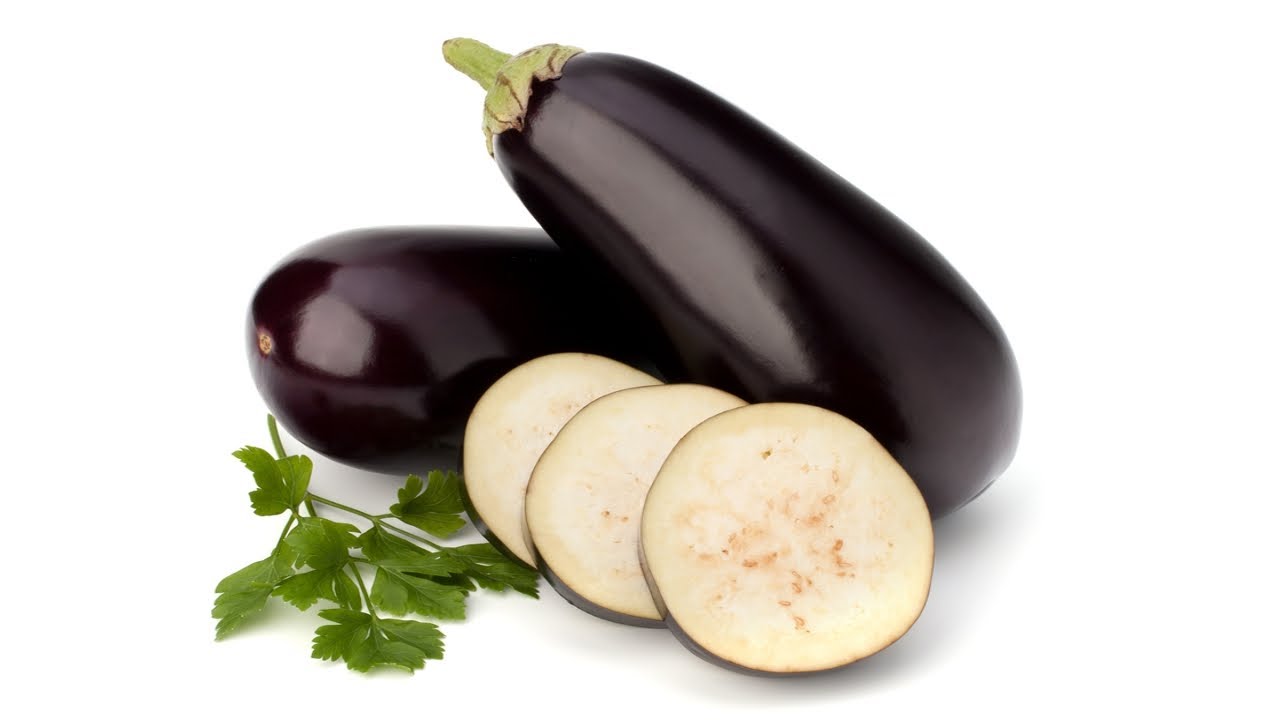

Today’s eggplants produced by artificial selection, which we can call modern eggplant, are generally grown in China. They don’t look like their primitive relatives at all. The thorns have given way to small hairs, the strange colors have been replaced by a blackish purple, and the shapes, each different, have been replaced by curves best suited for eating. The core state, like all products of artificial selection, is small and soft.
In the 10th century, carrots were colorless as follows:
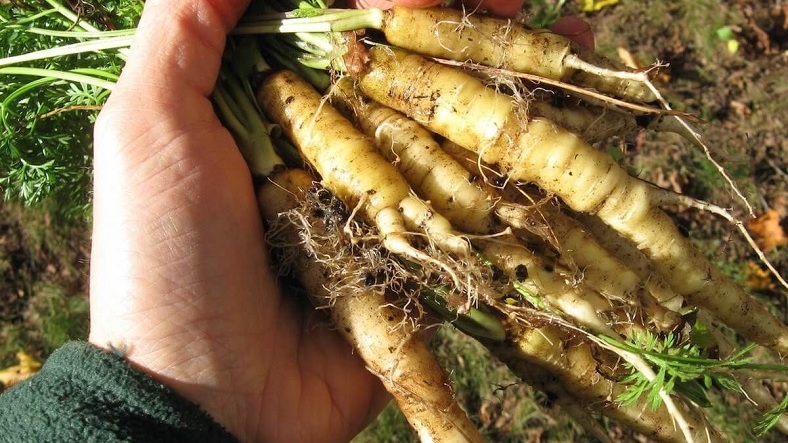

It is known that ancient carrots, which we can call parsnip, were first grown in today’s Iran and Asia Minor in the 10th century. But the first carrots were neither orange nor good-looking. primitive carrot It was generally white and purple in color. Moreover, there were many root extensions with a forked appearance on it.
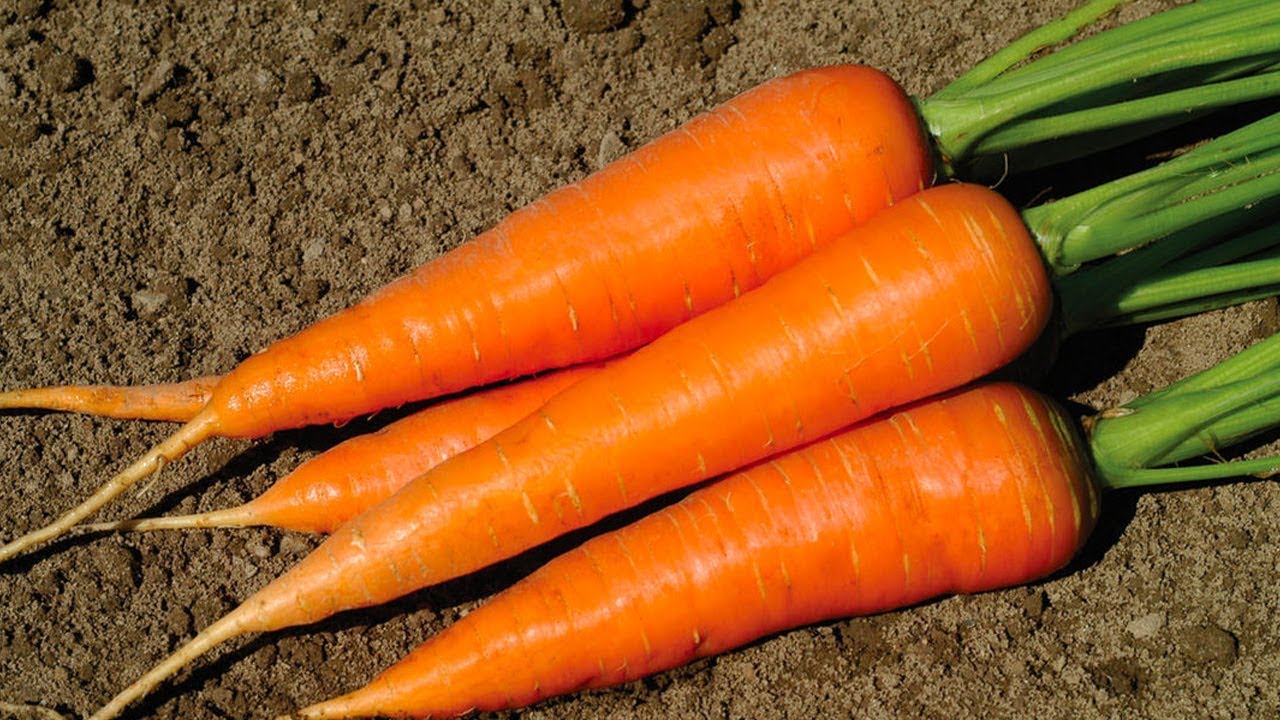

Today’s carrots, produced by artificial selection, which we can call modern carrots, have a cute and orange color. Besides ugly and difficult to eat The forked roots have been replaced by white roots that are thinner than hair. As a result of selective breeding, today’s carrots flower every two years, becoming part of a more efficient production process.
The Egyptians were as follows 9 thousand years ago:

Corn is a vegetable native to the Americas and is a type of corn as we know it today. Native to North America. sweet corn type. Corn, which was domesticated for the first time in 7000 BC and used as an agricultural product by humans, looks more like green beans and the corn kernels in it are said to be extremely hard.
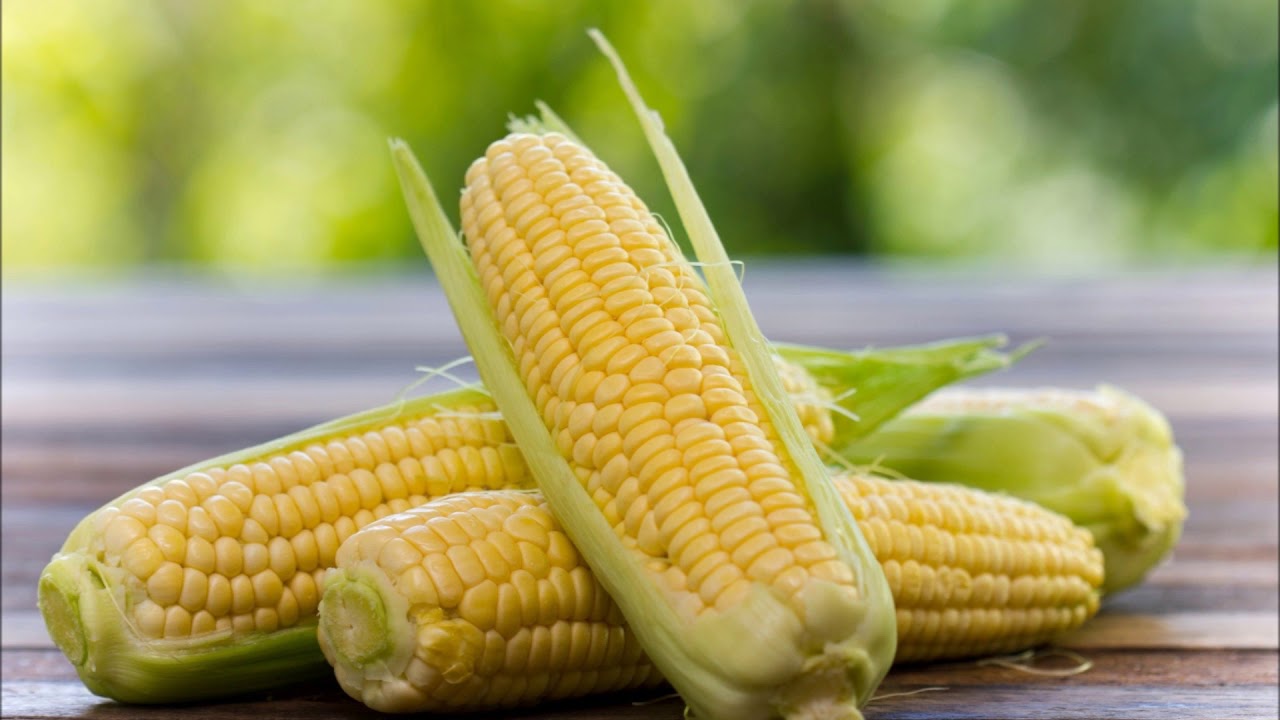

Today’s maize produced by artificial selection, which we can call modern maize, is They are a thousand times larger than their ancestors 9,000 years ago. As they grow and develop easily, their shells are peeled off in one go. The sugar ratio in wild corn was 1.9, while the sugar ratio of today’s corn is 6.6. This great development in maize started with the cultivation of maize by Europeans in the 15th century.
Peaches would have large seeds and taste a little salty:
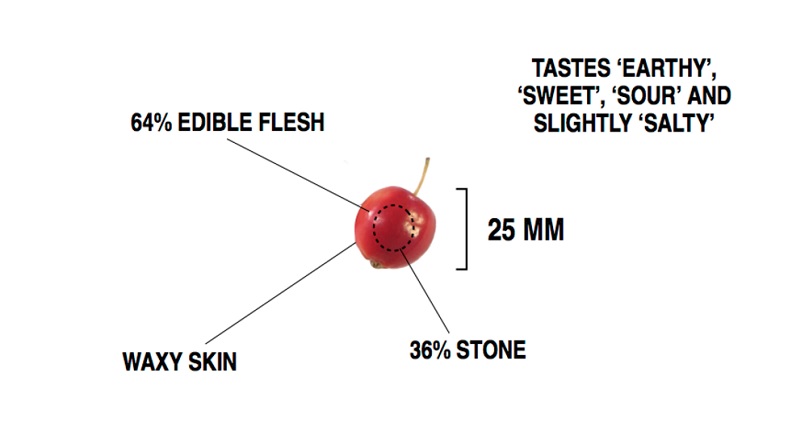
Primitive peaches, the ancestors of today’s hairy, fleshy, juicy peaches, are the size of a cherry, rather fleshless and has a slightly salty taste It’s really surprising to know. The peach, which was used as an agricultural product by humans, was a small fruit with a large seed, which was first published in China in 4 thousand BC.
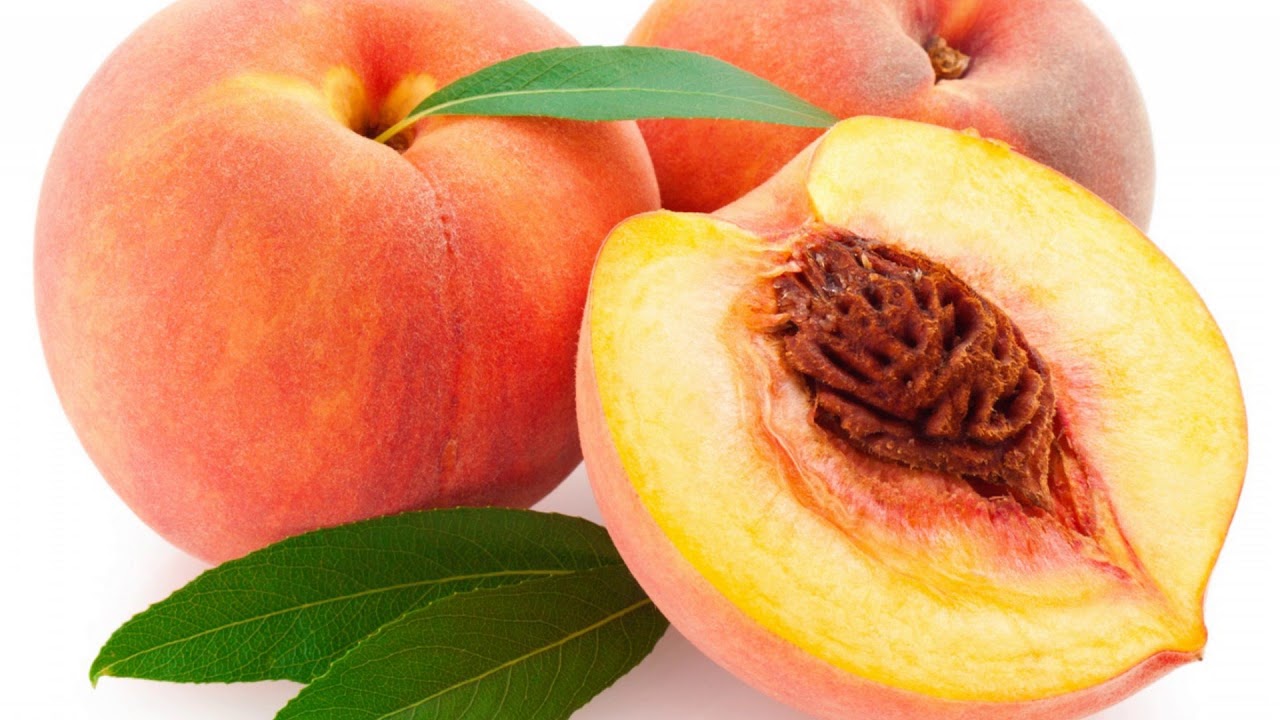

Today’s peaches produced by artificial selection, which we can call modern peaches, are after thousands of years of effort they became almost as big as a fist, fleshy, juicy and sweet. Today’s peaches are 64 times larger, 27 percent juicier and 4 percent sweeter than their ancestors. It is estimated that the seeds of peaches will be reduced even more in the future.
Although definitions such as artificial selection and genetically modified food may sound a bit repulsive, they are actually as long as human history We are already playing with the genetics of plants and animals. Small artificial selections like this don’t sound all that bad without getting mixed up with different chemicals that would upset the balance of nature.
What is artificial selection?
Artificial selection is the process of producing the best genes of microorganisms and creating plant and animal species that pass these good traits from generation to generation. selective breeding in plants As a result of artificial selection, which is called as artificial selection, it is aimed to survive the most productive species and to eliminate unproductive species by transferring these powerful genes from generation to generation.
Natural selection versus artificial selection The main difference between them is the human factor. In natural selection, weak species that cannot withstand environmental factors disappear, while in artificial selection, species that are unproductive for humans disappear or genetic changes are made to be more efficient.