Situations that differ in their objective reality with their visual perception are called visual illusions, a kind of illusion of the eye. In other words, our eyes are playing tricks with our brain.
There are many scientific explanations for optical illusions, and there are basically two types of visual illusions in themselves: physical and cognitive. While physical illusions depend on environmental and physical factors such as light, location, distance, cognitive illusions may vary a little more depending on the individual’s intellectual inferences or character traits.
It’s still being researched how it looks like this, and unsolvable There are also illusions. It is a subject that is always on the radar of the scientific world. We’ve compiled optical illusions for you that are fun to review and ponder over how they look!
Impossible Trident (Impossible Trident)
Also called impossible fork, blivet, poiuyt, or devil tuning fork, originally impossible trident that is, an undecipherable optical illusion called the trident. It appears to have three cylindrical prongs at one end, but mysteriously transforms into two rectangular prongs at the other end.
in 1964 DH Schuster An aerospace magazine advert said he had noticed a new kind of vague figure, calling it the ‘three-bar fork’. He described the illusion as “a real shift in image fixation, unlike other obscure drawings.”
Bezold Effect
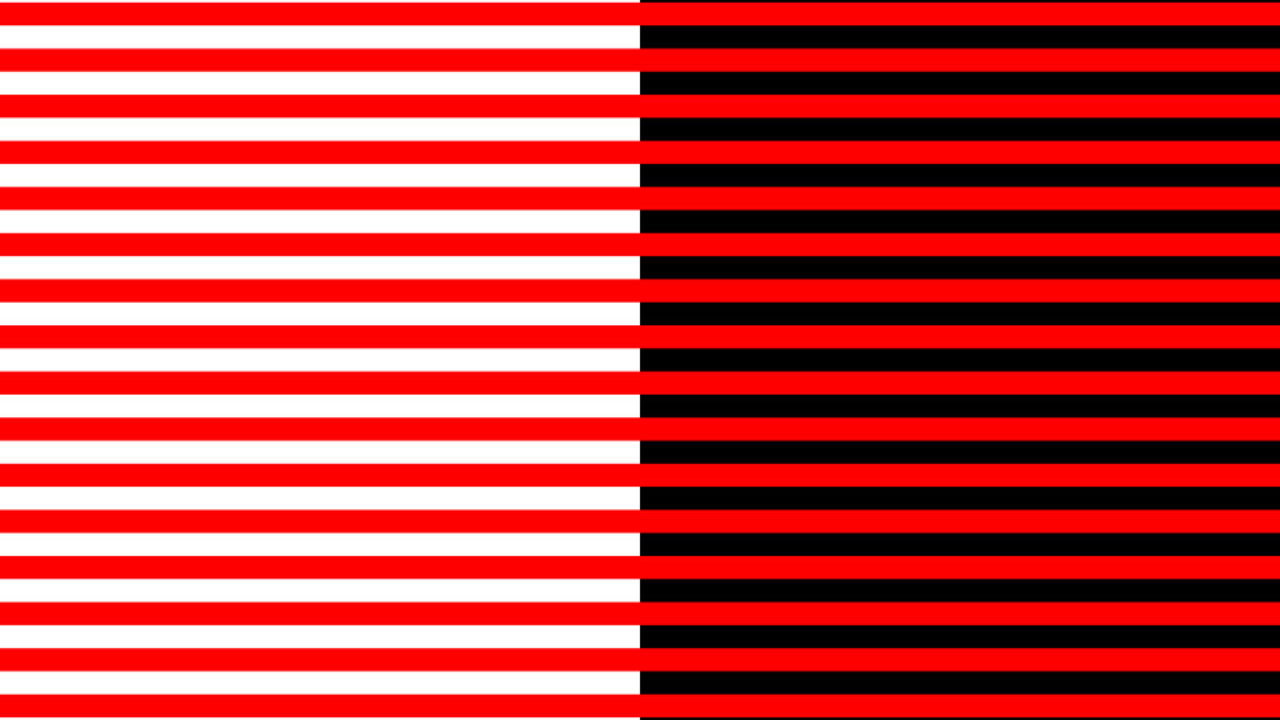
Bezold Effectis an optical illusion named after German meteorology professor Wilhelm von Bezold, who discovered that a color can look different depending on its relationship to adjacent colors. As can be seen in the Bezol effect image above, the red with white more open but with black it looks darker.
Cafe Wall Illusion
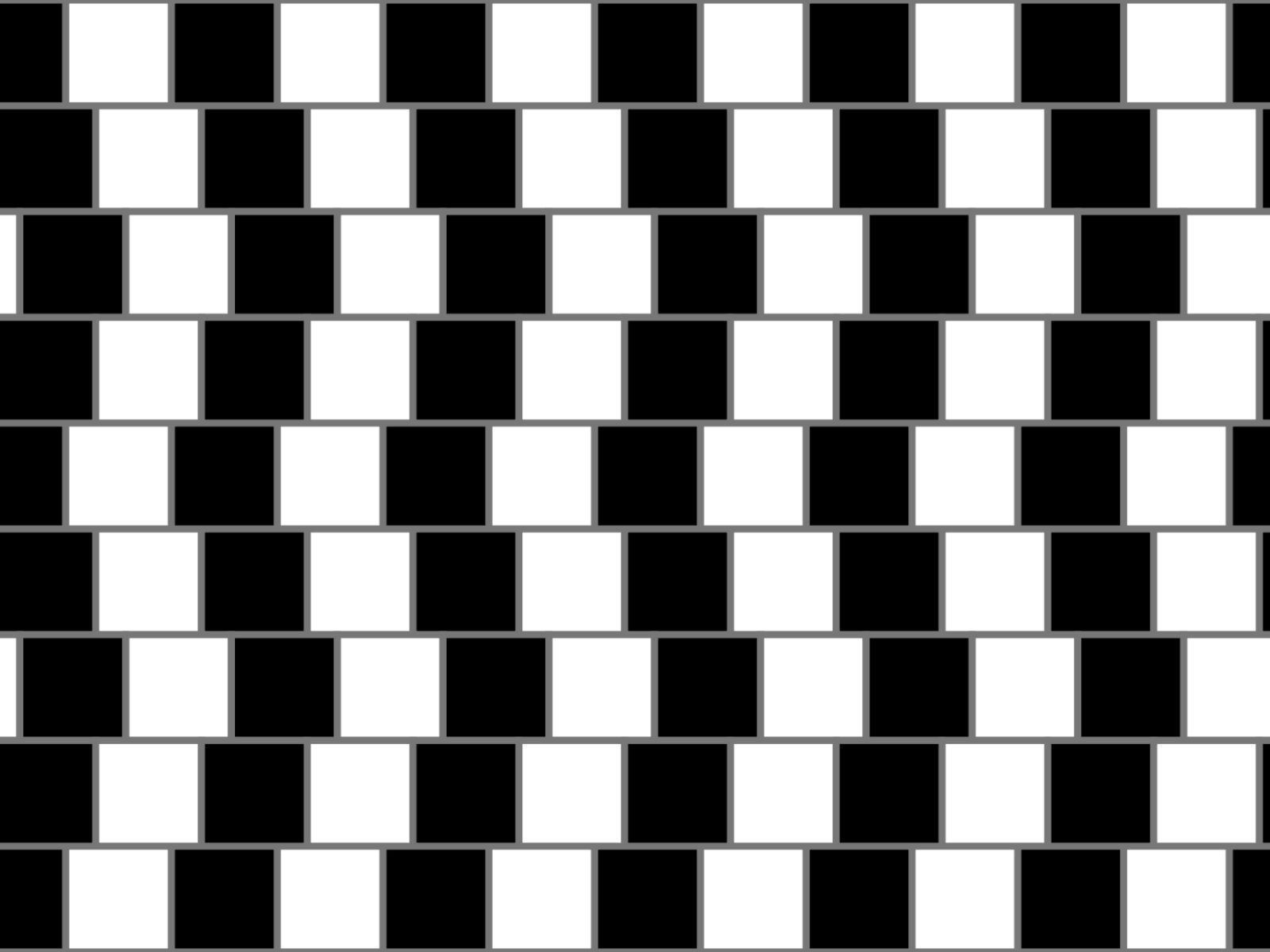
cafe wall illusionis an optical illusion first described by Doctor Richard Gregory. This interestingly effective optical illusion observed on the wall of a cafe in Bristol is despite the fact that parallel straight horizontal lines are not. like bent makes it appear. To create the illusion, light and dark tiles are laid in staggered rows, thus creating a distorted image.
Chubb Illusion
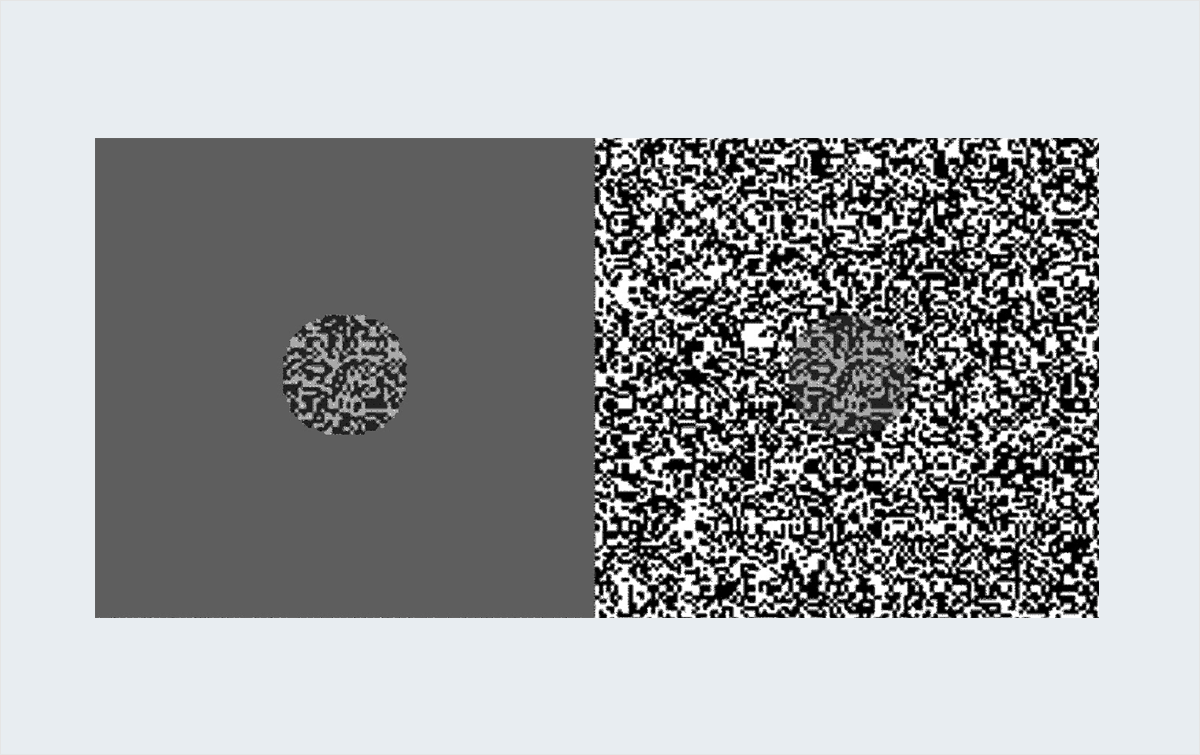
Chubb illusion, with the area where the size of an object is displayed depending on contrast It is obtained by changing according to the viewer. This optical illusion is of particular interest to researchers as it is thought to provide valuable information regarding human visual systems.
In the example in the image above, the centers of the two rectangular areas are actually the same, but because the backgrounds are different, the centers appear to be different for the two sides.
Ebbinghaus Illusion
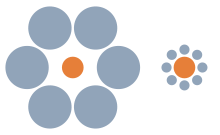
Named after the German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus, who discovered it, and relativity of size perception It is an optical illusion based on In the most familiar version of the illusion, circles are placed around two circles of the same size, one large and one small. However, the center with large circles around it appears larger than the other.
Fraser Spiral Illusion
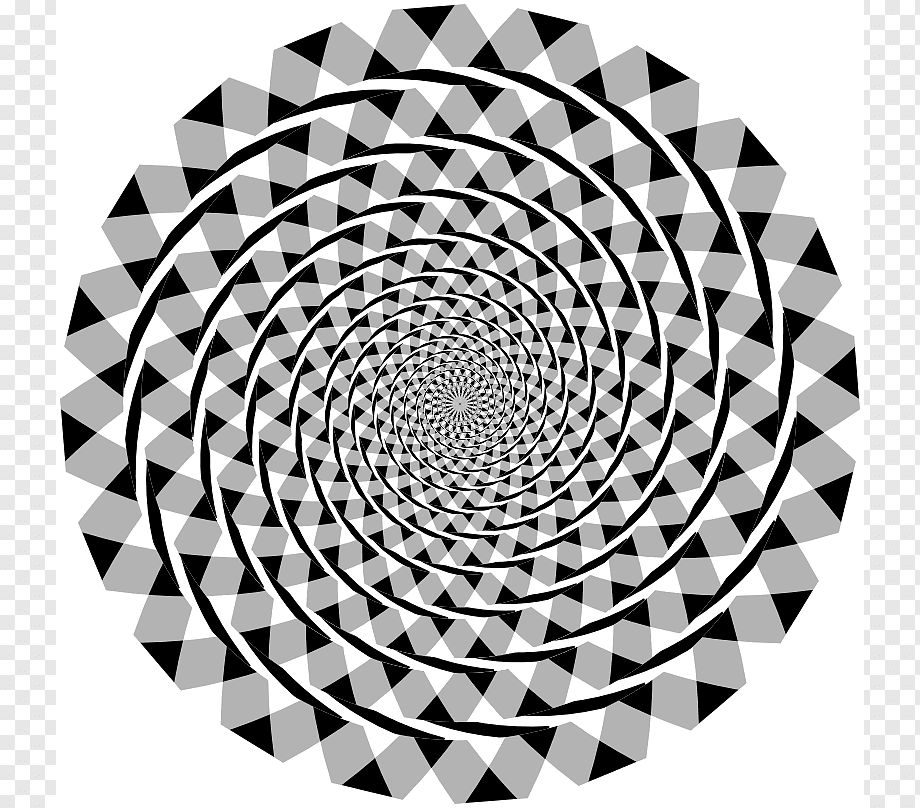
For the first time by a British psychologist Sir James Fraser The Fraser spiral illusion described by fake spiral or twisted cord Also called illusion. In the illusion that looks like a spiral as a result of the overlapping of the black arc parts, all the arcs are actually concentric circles. The reason for the visual illusion is that there are misaligned pieces in the background of the circles.
RELATED NEWS
The Brain-Burning Sound Illusion You Can’t Get Out of When You Listen (Video)
Hermann Grid Illusion
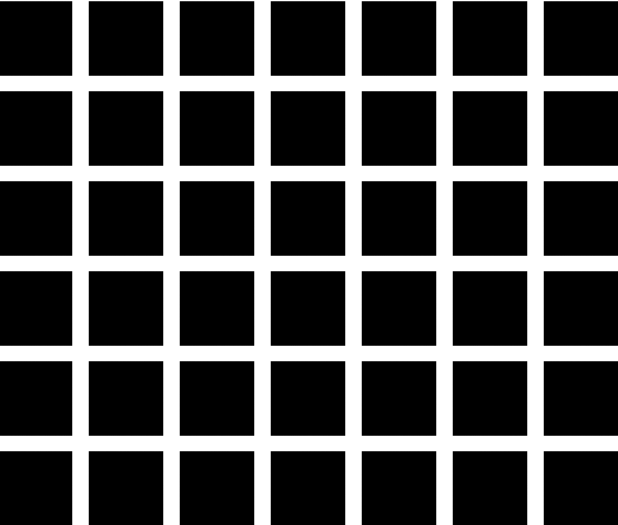
It was first discovered incidentally by Ludimar Hermann. grid illusionappeared by detecting gray spots at the intersections of a white-colored grid on a black background.
Jastrow Illusion
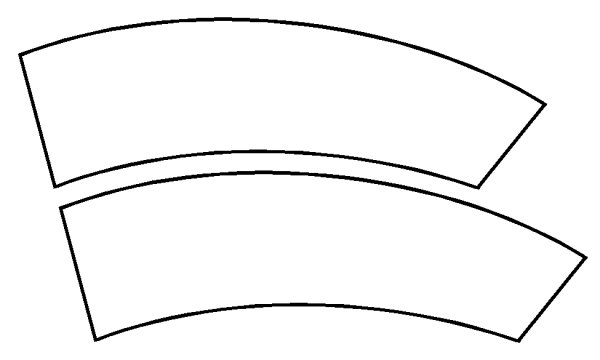
First discovered by the American psychologist Joseph Jastrow and named differently such as Jastrow, Ring-Segment, Wundt, this optical illusion has equal length and identical train spring When two objects that are like the above are placed on top of each other, the upper one appears to be shorter than the lower one. Although there are various theories as to why our brains play such a game, there is no certainty. cause not explained.
Checkers Shadow Illusion
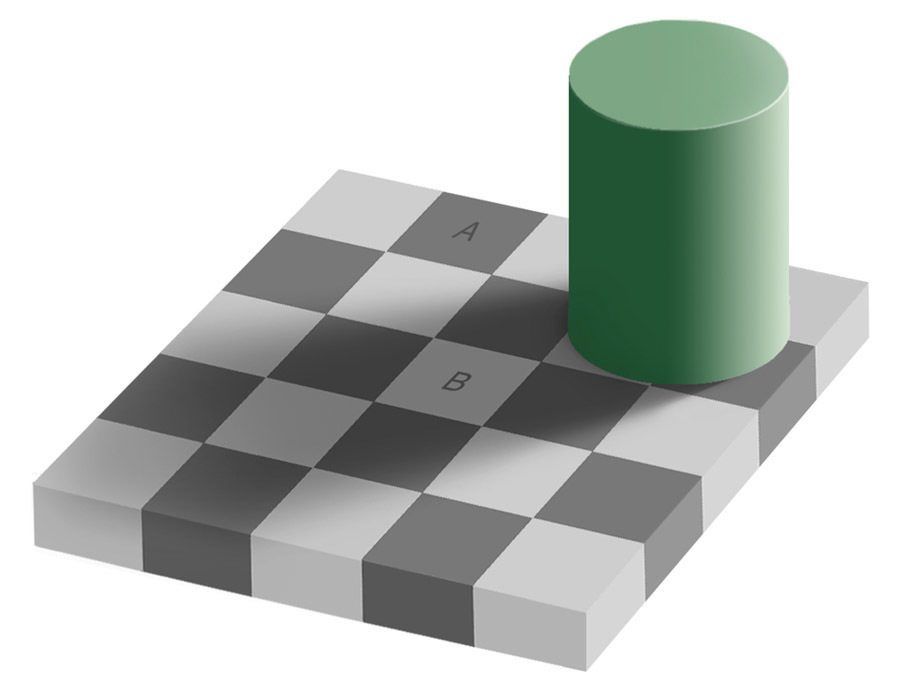
In the checker shadow illusion, it is indicated as A and B through the shadow created by a cylindrical structure on a checkerboard. the color of the two squares is different it is thought to be. However, the two squares are exactly the same color.
In order to verify the illusion, we can observe two squares that we think are of different colors by combining them with the help of a strip of the same color.
RELATED NEWS
Mysterious Hallucination Epidemic of 5 Irrelevant People
Poggendorff Illusion
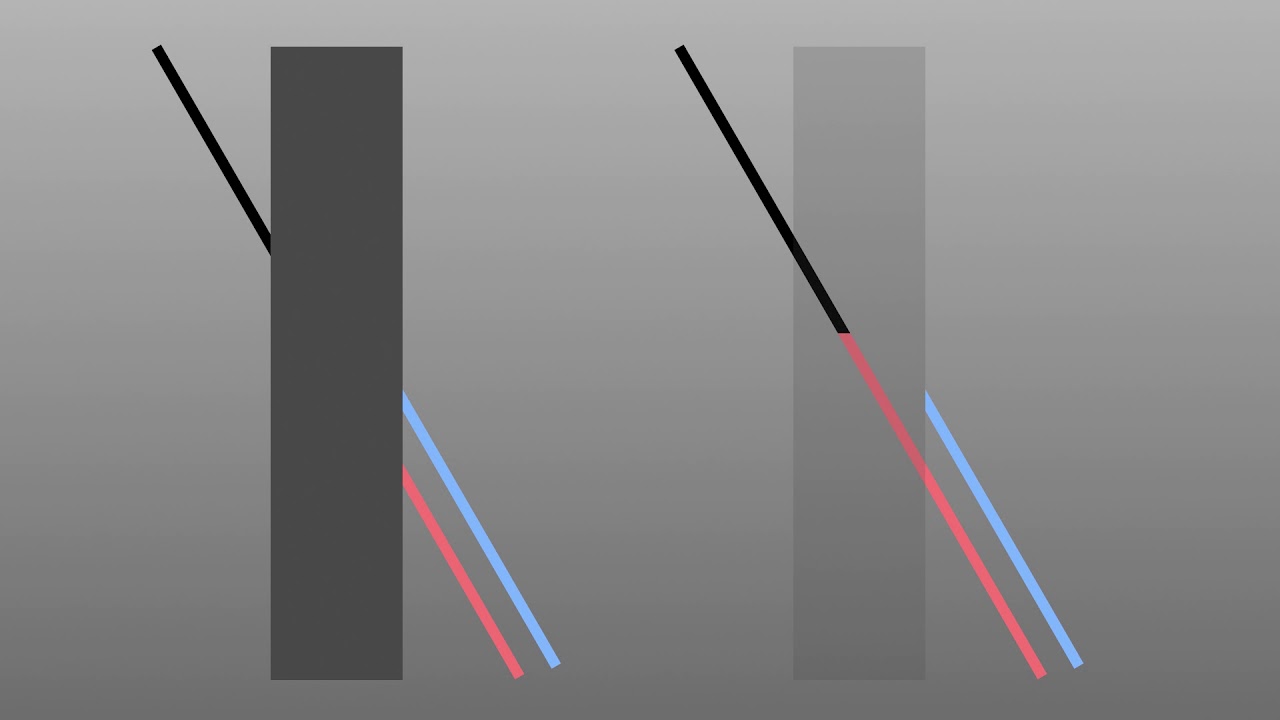
Poggendorff illusion, It is an optical illusion that involves the brain’s perception of the interplay between diagonal lines and the horizontal and vertical edges. German physicist named after him for the first time by Johann Poggendorff has received.
As seen in the image above, a solid black and red line is hidden by a gray rectangle. But in the illusion, instead of the red line, it seems as if the blue line is connecting to the black.
