The last major earthquakes we experienced in the southeast of our country taught us the realities of the earthquake in the most painful way. The effects of those days, the traces of which we cannot erase, continue. While we are trying to heal our wounds, on the other hand, all corners of our country continue to shake with earthquakes, big and small.
After Kahramanmaraş, many of our provinces were shaken by new earthquakes. In fact, some of these provinces were Malatya, Hatay and Osmaniye, which had been badly damaged in the previous earthquakes. However, the earthquake spread and Regions such as the Mediterranean and the Aegean began to shake.
When we look at the recent earthquakes even now, these small earthquakes, especially in the Aegean and Mediterranean, as well as our provinces in the earthquake zone, started to frighten us all. Thus a great destruction We’ve just left it behind.
Some of the non-destructive earthquakes we are experiencing at the moment, which can reach 4-5 magnitudes, are the effects of the Kahramanmaraş earthquakes.
As a matter of fact, not only did they increase in number, they also spread almost all over Turkey. Informing all of us with his earthquake research and his posts on Twitter. Earthquake Researcher Baturhan ÖğütWe asked the reasons for these earthquakes we experienced. According to the information we received from him; The reason for these earthquakes seen in various regions of our country is the big earthquakes we experience. pressure exerted on fault branches.
After the Pazarcık and Elbistan-centered earthquakes, The P wave reached the Northern Hemisphere within seconds. Because pressure on other fault lines and this caused earthquakes in various regions.
You can watch the seismic wave movements after the Kahramanmaraş earthquake here:
RELATED NEWS
Stunning Animation Showing How Seismic Waves in Kahramanmaraş Earthquake Reached America [VİDEO]
So what is this “P wave”?
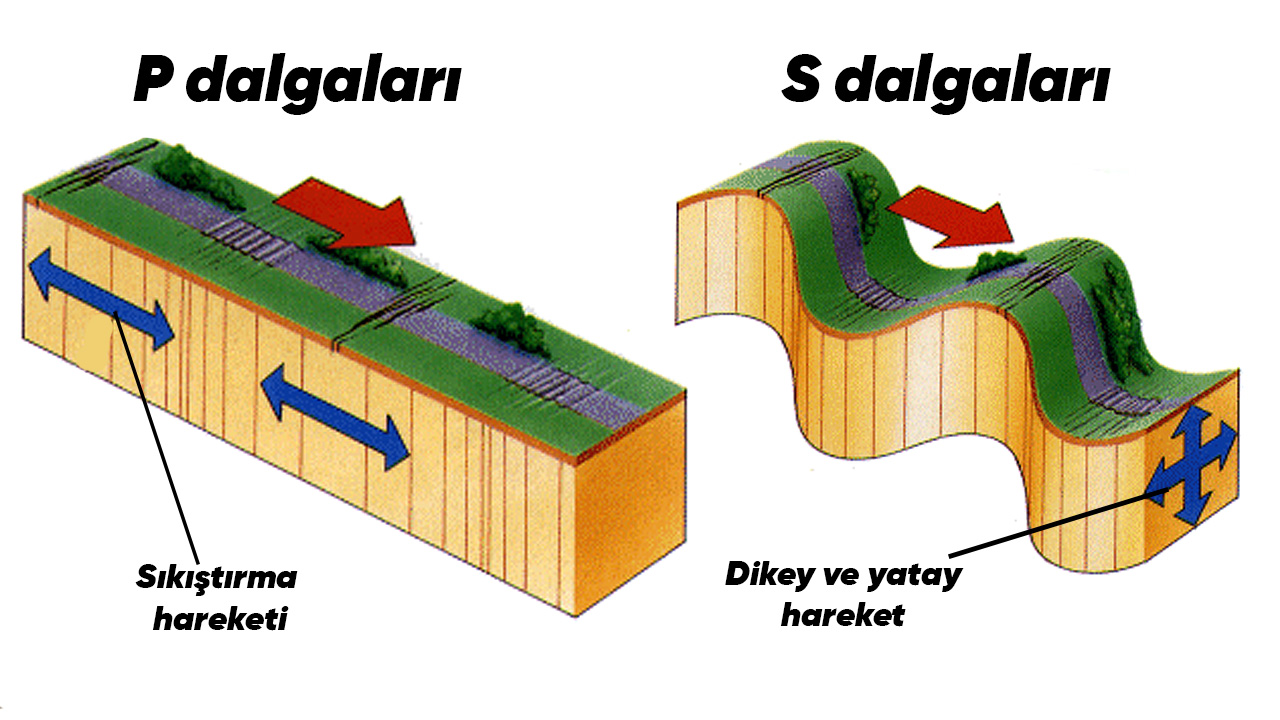
There are several types of waves seen in earthquakes. The first of these, which we have just mentioned; faster-moving, able to pass through anything liquid and solid, and generally non-destructive “P” waves.
At the same time, when an earthquake occurs, these waves reach the earth first. Due to their rapid movement and ability to pass through solid and liquid objects, they can go much farther from the earthquake zone. Therefore, although the destructive effect of P waves is small, they can exert pressure on faults and plates. Therefore small earthquakes caused by P waves in different regions may occur.
Compared to P waves 40% slower moving However, another type of wave with a more destructive effect is “S” waves. Compared to other types of waves more destructive has effects. While P waves move horizontally; P waves moves upright.
RELATED NEWS
What Is “Stress and Tension” on Fault Lines Actually?
We witnessed a similar situation in the 99 earthquake, one of the biggest destructions in our history.
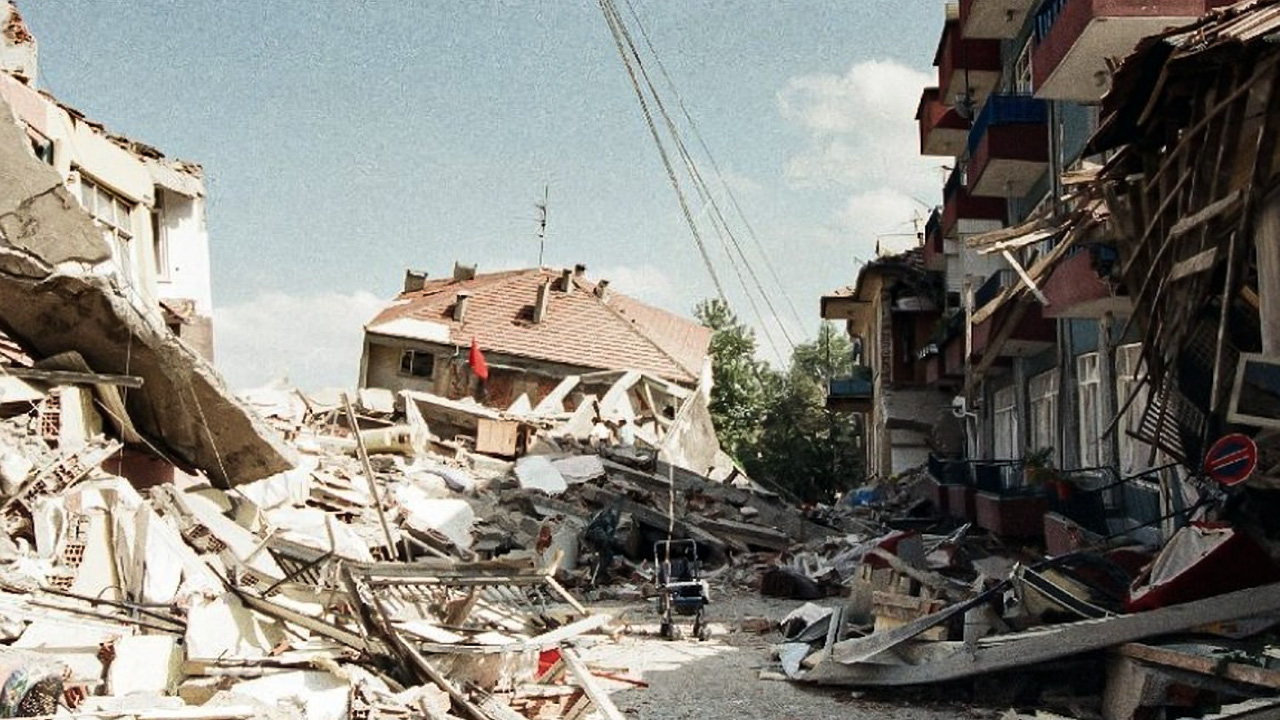

- A visual from the 17 August 1999 earthquake.
After the 99 earthquake, the P wave applied pressure to the subduction zone between the Nazca plate and the South American plate thousands of kilometers away, and then Earthquakes have occurred in different regions.
To summarize simply; P waves propagating after a major earthquake can cause interplate movements or pressures on faults. This is just like even if it is far from the earthquake zone It can create earthquakes in different regions.
Again, according to the earthquake researcher Öğüt, the earthquakes caused by these waves up to 1 year it may take. Because the beam stones between the faults, by exceeding the strength resistance as a result of pressure may cause earthquakes for a while. As a matter of fact, there have always been earthquakes in our country and unfortunately they will continue to happen.
RELATED NEWS
Detailed Earthquake Map “Seismic Map” Prepared by Evolution Tree Is Published
RELATED NEWS
