Although many people are not aware of it, we owe much of what we know about space today to the NASA Voyager mission and the Voyager 1 spacecraft sent on this mission. Where is Voyager 1, which serves humanity as a satellite in outer space, what is it doing, what information does it give us? Let’s take a closer look at all these details.
Today we know a lot about interstellar space, planets and space regions that are relatively far from our Earth, such as Saturn, Jupiter, Neptune, Uranus. All this hard-to-reach information is sent to and within the NASA Voyager mission. We owe it to the Voyager 1 spacecraft. sent into space in 1977 Voyager 1 The rover has been telling us about space for much longer than most of us have been.
It was thanks to NASA engineers of the time that we got information about so many planets and regions with a single spacecraft. Voyager 1 The date was chosen so accurately when they were sent into space that they managed to kill quite a few birds with one stone. It is still working for humanity in space, giving us visuals and information that almost all of us know today but unimaginable for that period. What you need to know about the Voyager 1 spacecraft We explained the details.
What is Voyager 1?
Voyager 1 was sent to space in 1977 as part of the Voyager mission and was sent to space in our Solar System such as Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. tasked with discovering important planets is a spacecraft. The Voyager 1 spacecraft, which has been traveling on a determined, sometimes changed course in space for more than 43 years, still sends data about interstellar space even today.
Voyager 1 is currently the most distant man-made vehicle between us. It will introduce the culture of the period inside the vehicle, namely if he encounters aliens he will tell them about us There are many objects. Such a thing might be possible because after the planetary missions were completed, Voyager 1 went into outer space and is located in a region far away from us, now known as interstellar space. His mandate is scheduled to last until 2025.
Voyager 1 isn’t actually the first vehicle to be sent into space:

NASA decided to send two vehicles for the mission, originally called Mariner Jupiter / Saturn 1977, but later named Voyager. These vehicles were launched at different times and They reached their destination at different times. For this reason, the vehicle that was sent first but would arrive at the destination later was named Voyager 2, and the vehicle that was sent second but that would arrive at the destination first was named Voyager 1.
An employee named Gary Flandro, who was an intern at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory at the time, provided the creation of the Voyager route. The planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune would align in the late 1970s that is, it was foreseen that it could be visited via a single route and it was decided not to miss this opportunity.
Such an opportunity would only come once in 176 years. For this reason, all NASA employees worked with all their strength to take the Voyager 2 spacecraft on August 20, 1977, and the Voyager 1 spacecraft on September 5, 1977 to Jupiter. The data we obtained with this journey into the unknown consists of unique information.
What did we learn with the Voyager mission?

Voyager 1, which reached Jupiter at the end of its 15-month journey, and Io, the satellite of the planet, have an active geological structure. The most active geological region in the Solar System appeared to be. Jupiter’s magnetosphere was much larger than thought, its structure was hydrogen-dense, suspicious rocks were found around it, and moons such as Thebe, Metis and Adrastea were discovered.
The Voyager 1 Saturn discovery showed that the planet’s moon, Titan, was not as large as thought. Over the Titan hemispheres, which have an axial structure different seasons were found. Among those fascinating rings of Saturn, the influences of moons such as Prometheus, Pandora and Pan have been discovered.
Reaching Uranus after a five-year voyage, Voyager 2 measured temperatures of -216 degrees Celsius on the planet, and a day was found to be about 18 hours. on the planet which also records high-energy radiation In addition to 10 new moons, the vehicle also made discoveries such as the rings of Uranus, Ophelia and Cordelia.
It was 1989 when Voyager 2 arrived at Neptune. Unexpectedly, Neptune had active volcanoes. On a planet so far from the sun It was a surprise to everyone to see such an event. Many new moons of Neptune, which is calculated to take about 16 hours a day, were discovered, the structural components of the planet were detected, and the planet was found to have strange rings, along with Thalassa and Naiad.
Where is Voyager 1 now?

Voyager 1 has become an angel, baby, it wouldn’t be wrong to say, because after years of successful planetary exploration mission, our spacecraft is far away from us, leaving our Solar System. went to interstellar space. But that doesn’t mean we’re no longer in contact with him. Voyager 1, the first man-made vehicle this far away, still continues to send unique data about those unknown realms.
Currently, both the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft are in the interstellar region. However Both cameras were turned off. Because it is required to store the energy required to record any image and send it to the world, and to send only basic data. Basic data is considered more important than images, but it would be nice to see some photos.
What you need to know about Voyager 1:
- Voyager 1 and 2 vehicles are the longest in space.
- The main purpose of the Voyager mission is to understand the energy and radiation system in space.
- There are greetings in 55 different languages, plaques, encrypted notes, photographs and many other cultural objects placed in the vehicles to tell the aliens about us.
- Each of the vehicles weighs approximately 720 kilograms.
- Voyager 1 is the first vehicle to pass through the outer space heliosphere known to be more powerful than the Sun.
- It is the first man-made object to reach interstellar space.
- It was the first to discover many things about Jupiter and Saturn.
- Voyager 1 will be shut down in 2025, when signals are no longer expected.
- When closed, it will be the first human garbage we drop into interstellar space.
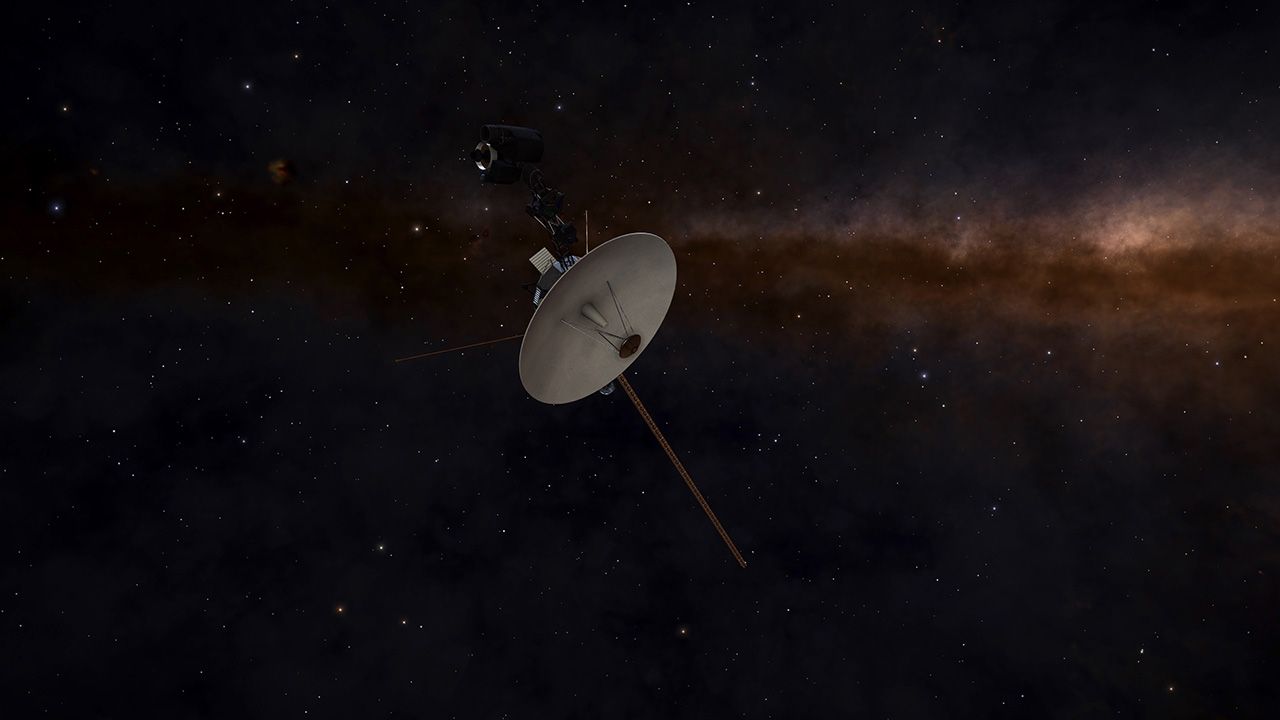
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft are important vehicles that have marked the greatest and first in human space history. In order for today’s astronomy world to continue its work, The vast majority of the necessary data was collected through these tools. The data sent by the vehicles helped us understand not only the target planets, but also the universe and space.
It has been circulating for us in the unknown darkness of space for years and shaping today’s space science thanks to the data it sends. What you need to know about Voyager 1 and its sister Voyager 2 We explained the important details. Who knows, maybe our first contact with aliens was or will be thanks to these vehicles.
