After the earthquake disaster that burned us and directly affected 10 provinces, the tension and stress on the fault lines are frequently brought up by experts. So what do these terms actually mean?
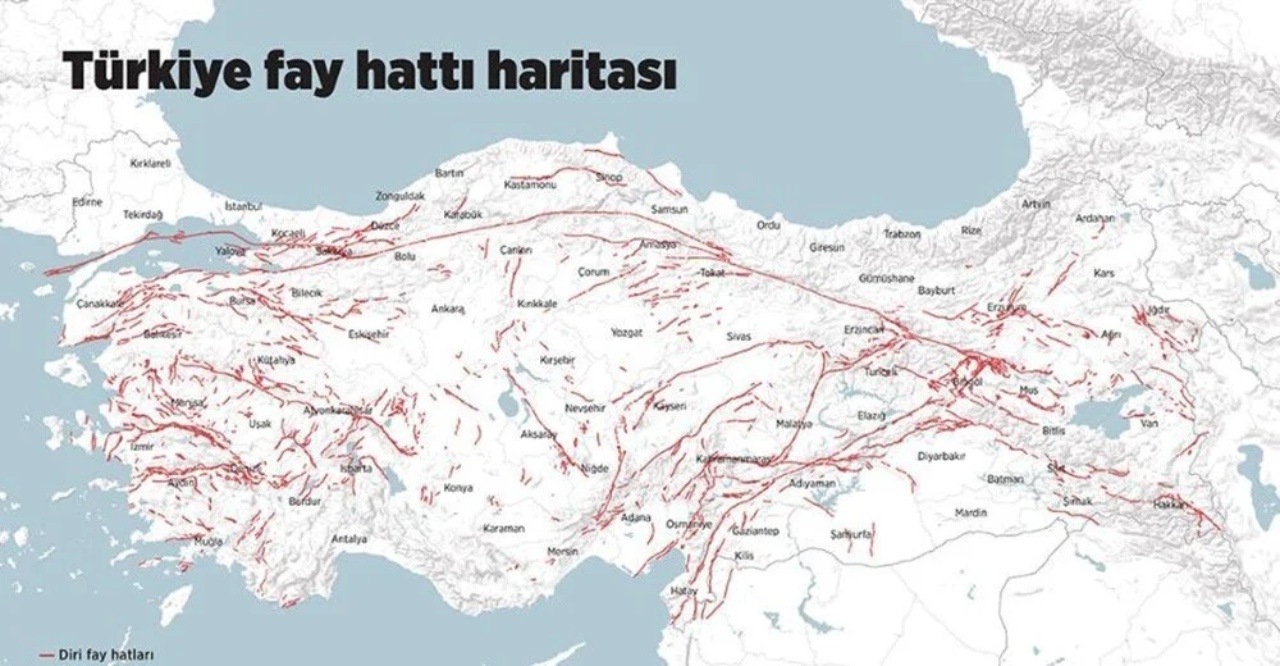
Turkey, in the earthquake zone It is a country located in the middle of nowhere and therefore it frequently witnesses major earthquakes. It is of great importance to understand both the soils and the fault lines under them, as earthquakes have different structures and different effects occur according to the terrain type.
To understand earthquakes stress and tension Understanding the concepts is very important. Stress is the force applied to cause a material to deform or break. Stress is the deformation experienced by a material due to applied stress. In the case of earthquakes, these two terms are used to describe changes in the earth’s crust.
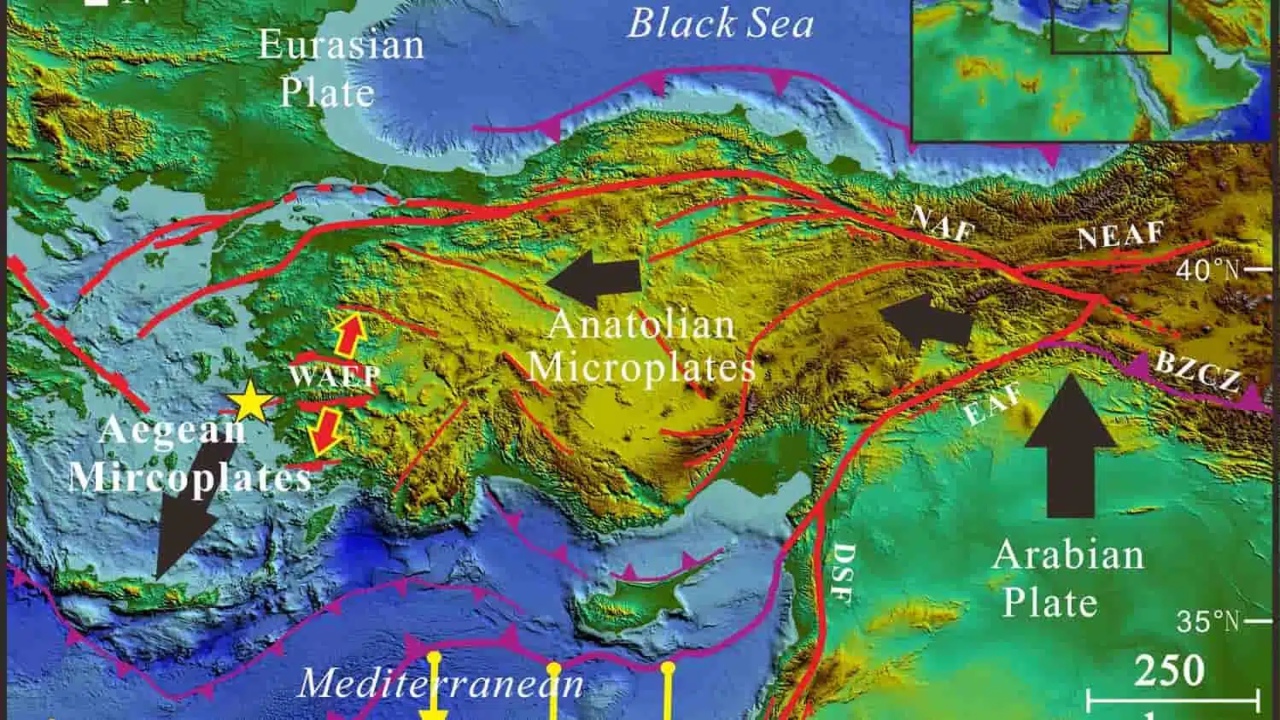
The earth’s crust is actually made up of interlocking plates called plates.
In recent earthquakes, the Arabian Plate has moved northward. He pressed the Anatolian Plate.
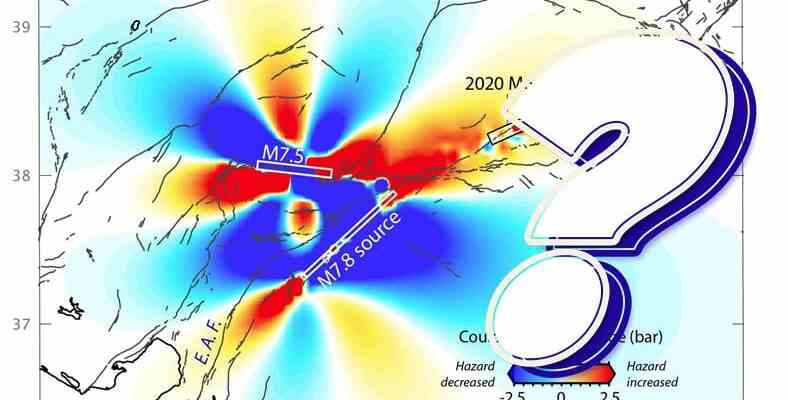
The East Anatolian Fault is a “strike-slip” fault line. In other words, blocks of hard rock exert vertical pressure on each other. When a block of rock fails to hold and collapses, it moves horizontally. This causes an earthquake.
The Earth’s crust is massive, causing it to deform and break, leading to an earthquake. to tectonic forces is exposed. When an earthquake occurs, tectonic tension in the crust produces a series of shock waves that can damage structures at the surface. The strength of these shock waves is applied to the crust before the earthquake. to the amount of stress and the amount of stress experienced during the earthquake. Understanding the interaction between stress and strain is crucial for predicting and preparing for future earthquakes.
How earthquakes occur is also effective on the resulting waves. Earthquakes move in waves.
The first of these waves is the first wave that reaches the surface and is the first measured by the seismograph. primary is a wave.
Then comes the wave called the secondary wave. When this wave comes in solid materials movement begins. Much faster than the first wave.
Next comes the surface wave called the Longitidunal. It is a small wave, but much more devastating has an effect. Especially if alluvium and groundwater are dense, its effect is more.
Finally, the R wave comes, in which the earth’s crust is almost waves in the sea It starts to act like
As the plates repel each other, the effect of the plates grows. to this effect stress/tension is named. stress at one point to earthquakes why is this happening. The amount of stress affects the size of the earthquake.
RELATED NEWS
A Major Error When Comparing the Severity of the Kahramanmaraş Earthquake with “500 Atomic Bombs”
RELATED NEWS