Earthquake, which is one of the natural disasters that can have devastating results in our country and all over the world, worries us at regular intervals, sometimes with its successive occurrence in the same or different regions.
These earthquakes can sometimes manifest themselves more than once, not just once. These great earthquakes, which scientists bring to the agenda and warn us at every opportunity, and which we have witnessed many examples in our country over the years, in very short time intervals can occur.
The succession of two major earthquakes centered in Kahramanmaraş in the past days raises this question even more. Big earthquakes, how come one after another and the underlying cause of these severe earthquakes possible cause why?
An earthquake with a magnitude of 7.8 in Erzincan in 1939 was the beginning of the largest series of dominoes the world had ever seen.
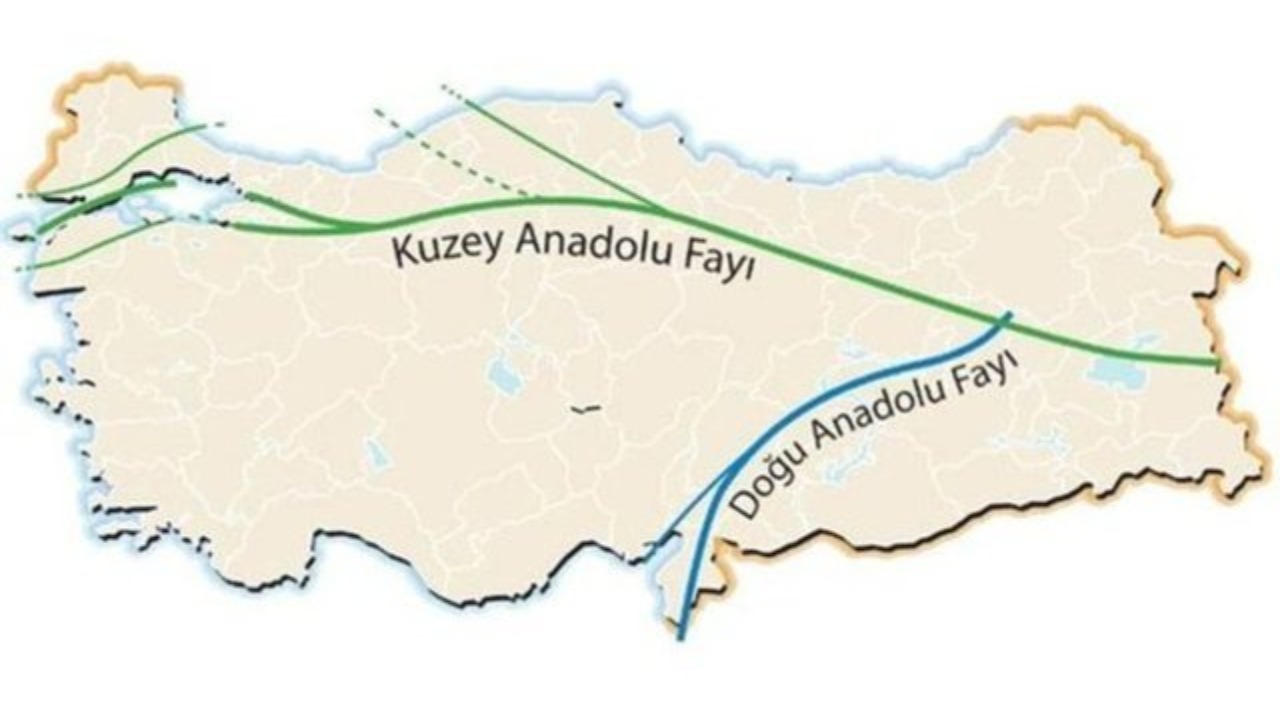
This domino effect shattered the series of 12 major earthquakes that took place on the North Anatolian Fault over 60 years for 1,000 km from one end to the other. In its simplest form, this one earthquake that constantly triggers the next earthquake.
More precisely, the domino effect can be defined as the earthquake’s ability to affect nearby faults when a problem occurs on a certain surface.
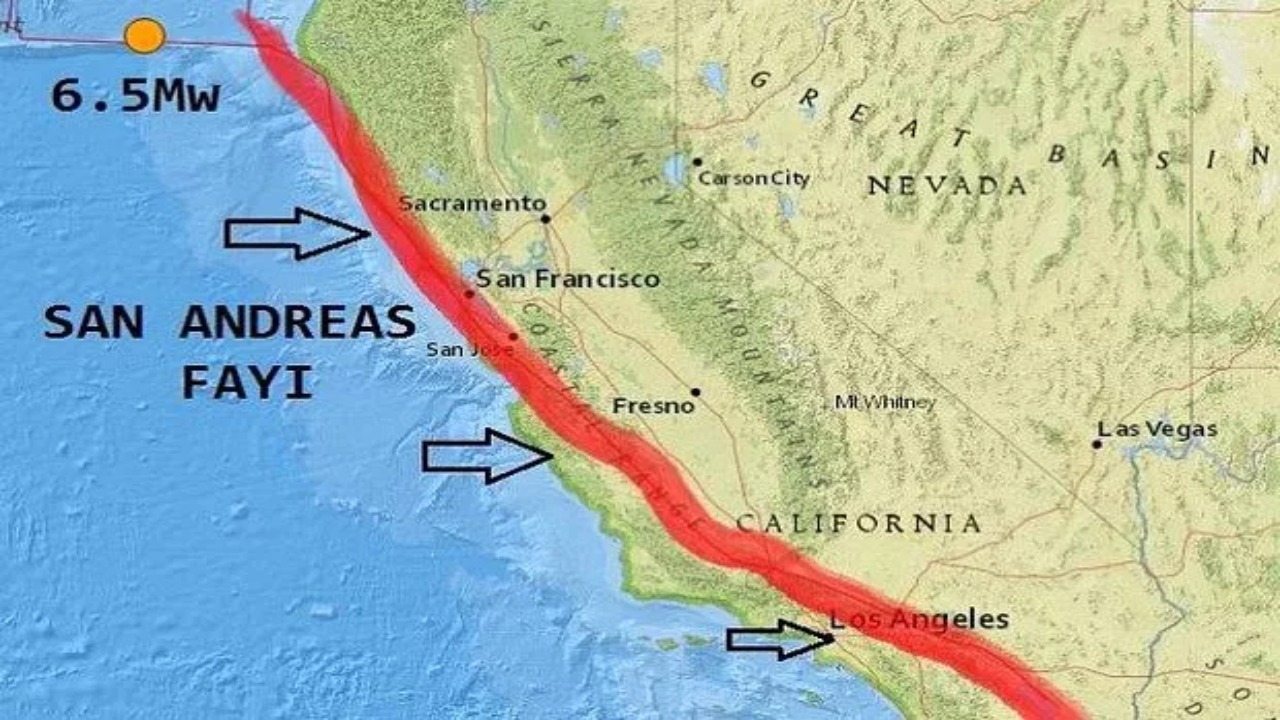
Starting from the question of how long a surface area earthquakes would spread, scientists at the University of Nevada looked at 22 earthquakes that occurred around the world, including in Japan, New Zealand and California. Researchers have identified each of these earthquakes as a fault slipped against another confirmed the cause.
Complex areas with overlapping fault segments, such as those from California’s San Andreas fault system. how long a breakout can last making measurements difficult.
The Kahramanmaraş disaster, which caused the destruction of thousands of buildings and the death of approximately 40 thousand people in Turkey, is one of the earthquakes triggered by the domino effect that started with the Erzincan earthquake.
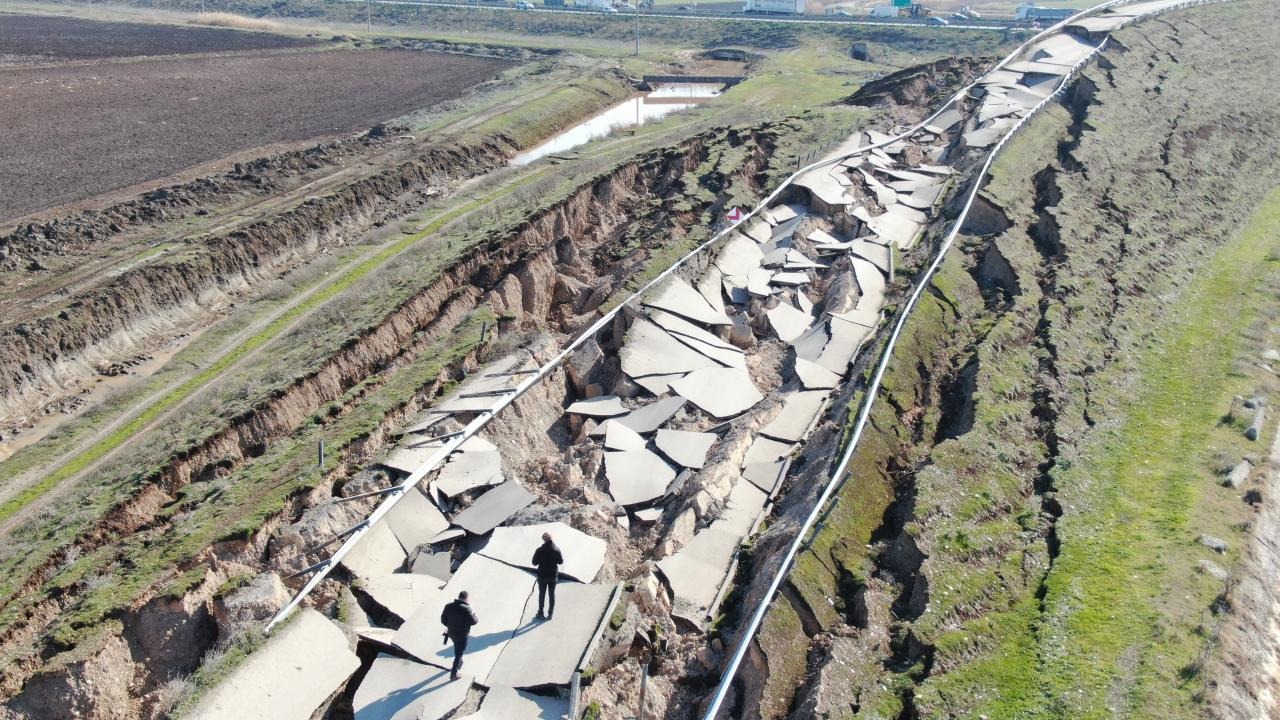

In addition to this domino effect, there is a shallow earthquake that can be called as shallow at 8.6 km in the first earthquake and 7 km in the second earthquake, which makes the surface movements more intense. fault rupture stated why.
While experts state that 32 times more energy was released in the first earthquake with a magnitude of 7.7, 32 times more energy was released than the second, while an earthquake with a magnitude of 7.0 would be stronger than an earthquake with a magnitude of 6.0 due to the logarithmic scale of the earthquake. 10 times bigger manifests itself in intensity.
While seismologist Ross Stein states that Turkey is almost squeezed in a tectonic vice, he adds that Turkey is moving towards the north of the Arabian Peninsula and in this direction has been pushed to the fixed border of Northern Europe. In short, Turkey squeezing west.
Due to the domino sequence formed along the North Anatolian Fault, the Kahramanmaraş-centered earthquakes may not have ended yet.
Earthquakes interact through stress currents, and this is a kind of chain reaction It means. An earthquake can reduce the stress in the broken parts, but this tension is transferred to the other parts.
The aftershocks that come to mind in this direction, on the other hand, proceed entirely on this logic. Aftershocks do not only occur in areas with ruptures. At fairly large distances, around that area may also occur.
Scientists did not think that strong earthquakes would cause tremors in remote areas. Until 1992, when we found that California’s 7.3-magnitude Landers earthquake caused tremors in an area as remote as Yellowstone National Park.
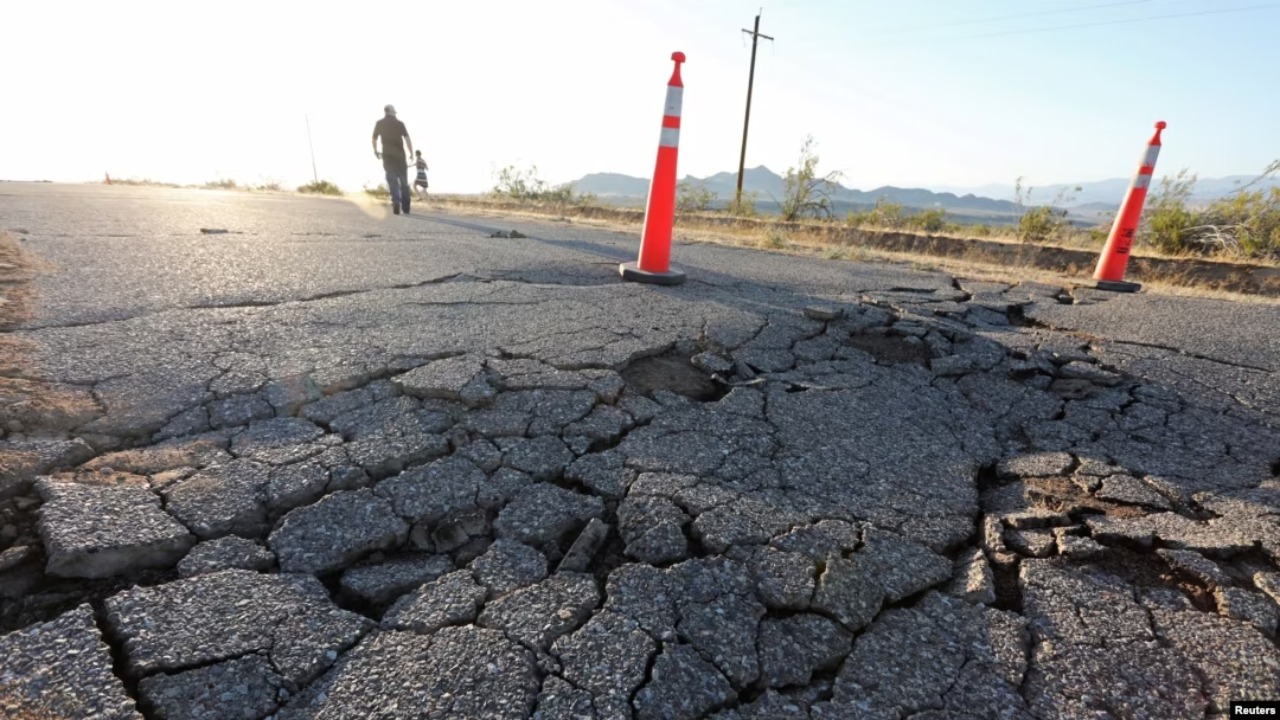

Scientists who have started to do more research on the subject have started to investigate the earthquakes of magnitude 7 and greater that have occurred since 1990, including the Indian Ocean in 2004 and the 1999 Izmit earthquake in Turkey. 15 major earthquakes analyzed.
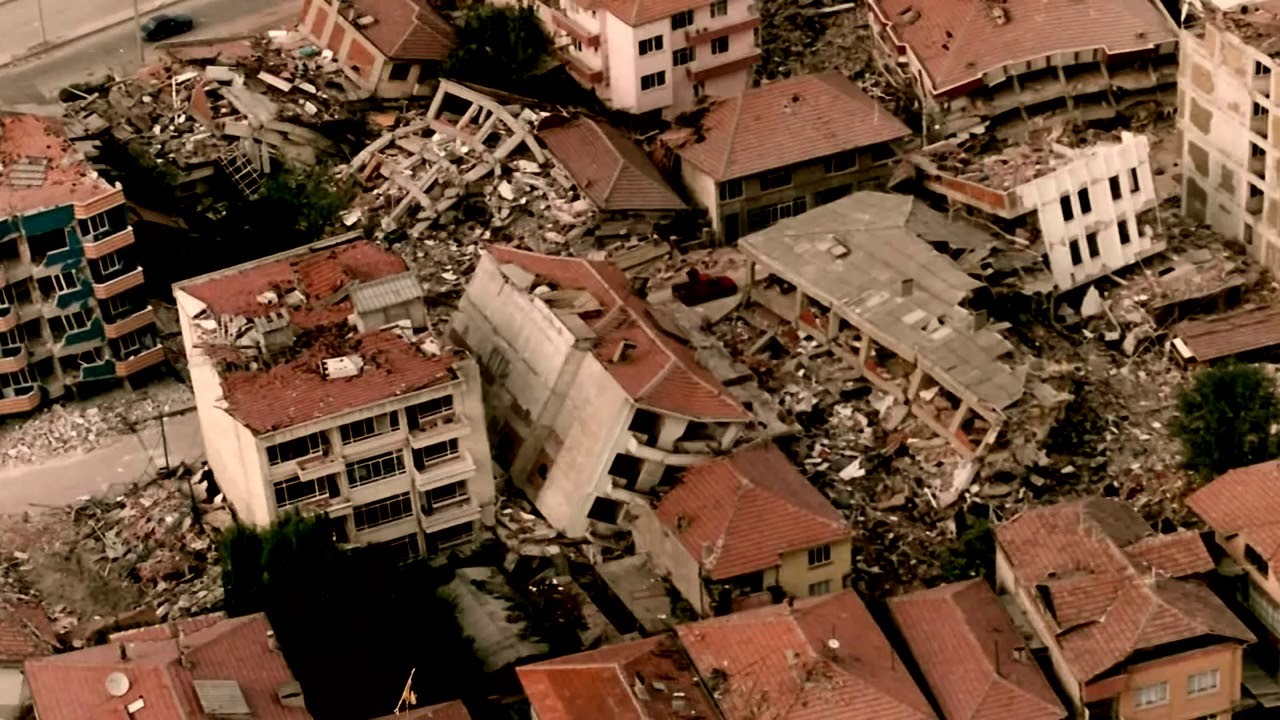

Researchers examined the sounds in the regions 5 hours before and after these earthquakes, and 12 of these large earthquakes caused earthquakes in various parts of the world. produces surface waves Has detected.
For example, the Indian Ocean earthquake of 2004 triggered small earthquakes in remote places such as Ecuador, Alaska, California. In summary, researchers have found that surface waves from large earthquakes are mostly May cause earthquakes of 4 or less reached its conclusion.
Opinions are that the 9.3 magnitude earthquake that hit China in 2008 could trigger other earthquakes around the world.
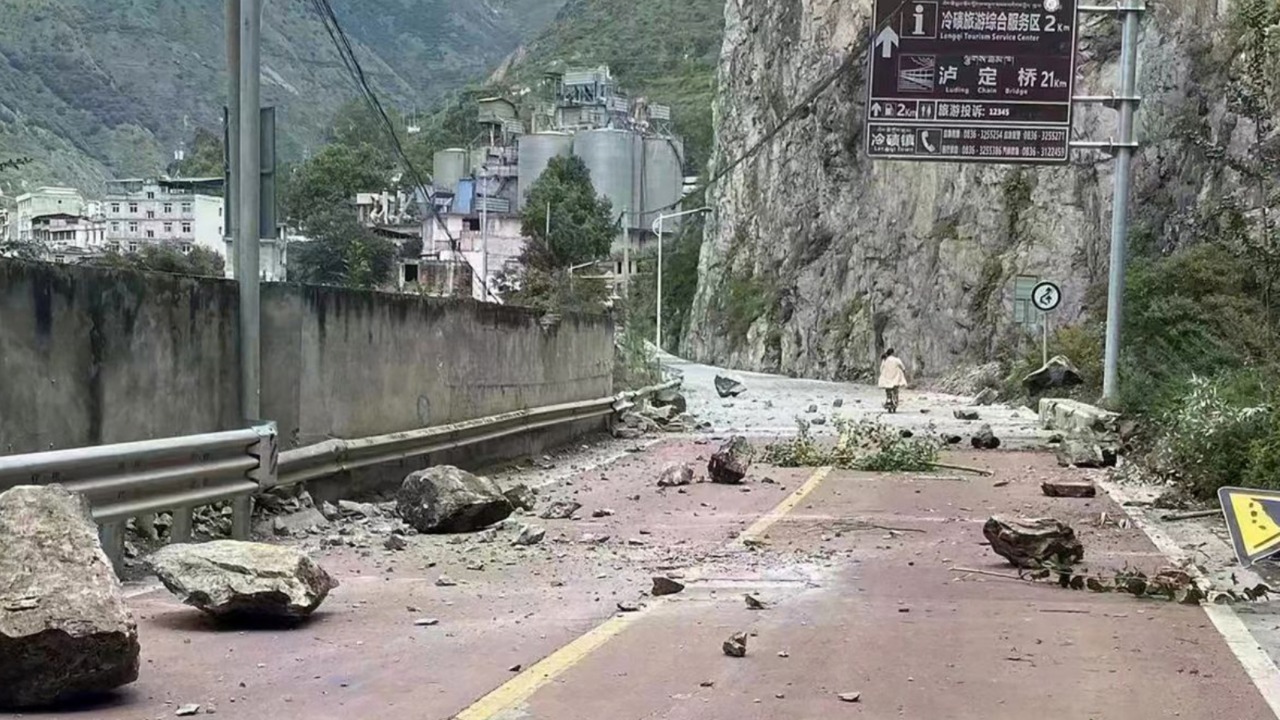

While studies confirm that large earthquakes can affect many different parts of the world, regions that are not prone to earthquakes. shows that even routinely it can encounter minor jolts.
RELATED NEWS
Floors, Rents, Cries: Why Haven’t We Made a Barley of Earthquakes in 24 Years?
RELATED NEWS
The Most Possible Scientific Explanations for the Mysterious Lights Revealed in Major Earthquakes
RELATED NEWS
