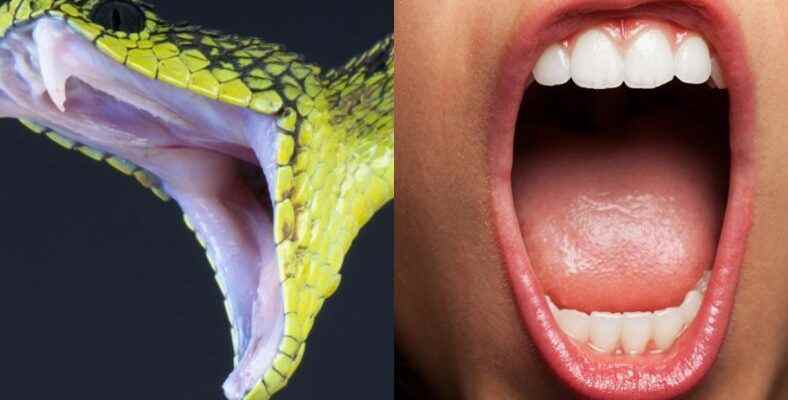
A study done in Japan revealed that the saliva of all mammals, including humans, and the venom of snakes are descended from the same ancestor. The results showed that it is evolutionarily possible for humans to be poisonous, too.
Snakes, some lizards, and even a few mammals have the ability to inflict a venomous bite. The descendants of these poisonous creatures 300 million years ago Although it is known that they diverged from each other, according to a recent discovery, their poison actually came from the same ancestor. The research was published in the journal BMC Biology.
According to the published research, they focused on a class of venom found in most snake venom and all other reptilian and mammalian venoms called ‘kallikrein serine proteases’. As a result of the studies carried out ancestor of the poison class revealed. Thus, the poison in these creatures descended from a common ancestor revealed.
The idea was first put forward as a hypothesis:
This study by the Graduate University of Science and Technology of Okinawa and the University of Australia in Japan actually drew on the results from the previous study as well. In their previously published study, scientists found that mammalian salivary gland and snake venom gland are in a group of regulatory genes. engaged in the same activities had discovered. This is for the development of the poison. that the necessary foundation exists in both snakes and mammals. was showing.
With this study, the existence of a group of genes with venom potential in the ancestors of snakes and mammals was presented as a hypothesis. According to this hypothesis, both creatures followed different evolutionary paths. Mammalian venom has evolved, but not so much. After this research, scientists started a new study to discover the ancestors of the two living things.
RELATED NEWS
World’s Oldest Genealogy Revealed: Dating Back Exactly 6,000 Years
After advances in gene research methods, scientists compared the kallikrein gene found in reptiles, amphibians, fish, and mammals to finally construct an evolutionary tree. The resulting results, snake venom proved that the venom in the saliva of mammals came from the same ancestor.
The resulting evidence, including people showed that it is possible, through evolution, for salivary kallikrein proteins in mammals to also become toxic. However, the fact that the building block that develops the poison is in our genes does not mean that it will definitely happen.
Source :
https://phys.org/news/2021-12-venoms-snakes-salivary-protein-mammals.html