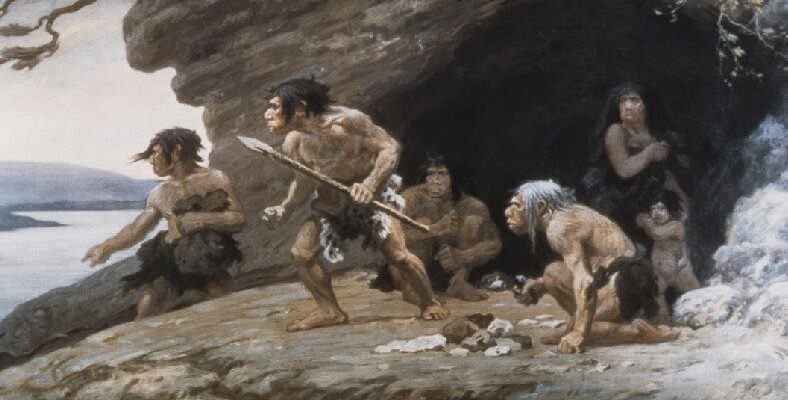
It is the first time that it has been clearly demonstrated that climate change has an impact on human evolution. A new study has determined the environmental conditions in which early humans lived.
climate change on human evolution Whether it has any effect has been a question that has long puzzled scientists. Now, in a study by an international team of scientists, there is a relationship between astronomical climate change and human evolution. a link clear evidence was found.
The team of climate modelers, anthropologists and ecologists has combined the most comprehensive database of relatively accurate fossil remains and archaeological artifacts with an unprecedented new supercomputer model that simulates the world’s last 2 million years of climate history. In this way, scientists are convinced that archaic humans are probably how under environmental conditions was able to determine that he was alive.
Environmental conditions inhabited by prehistoric humans identified
As we mentioned above; in fact, there was already a widespread belief that climate change may have affected human evolution; but climatic records near the sites of prehistoric human fossils insufficient It was difficult to ascertain whether this was true or not. The research team, who wanted to overcome this problem, also developed a computer program according to the archeological records. in the simulations decided to investigate what the climate was like in the times and places where people lived.
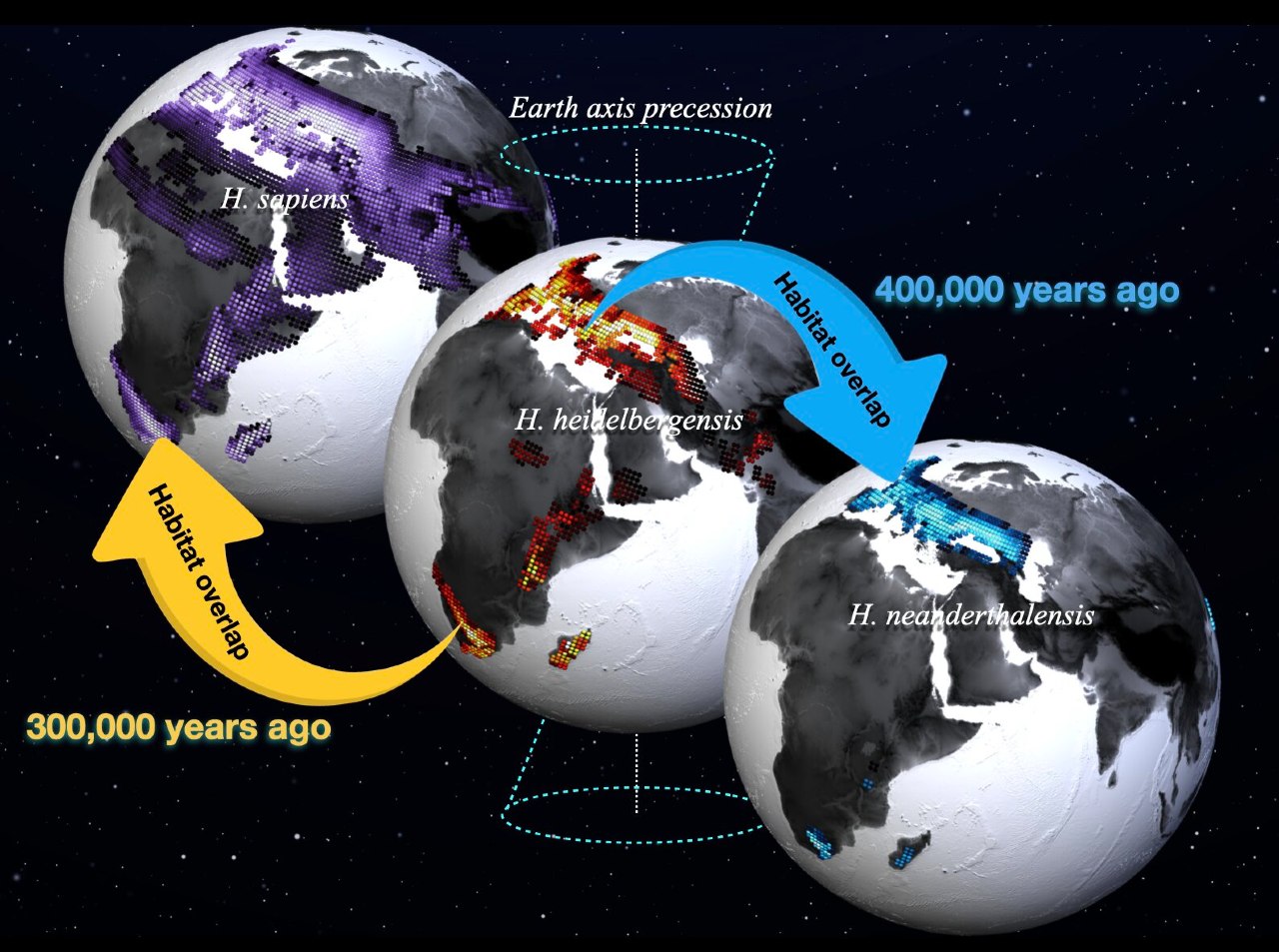
As a result, it was favored by different hominin groups, including Homo sapiens, Homo neanderhalensis, Homo heidelbergensis, Homo erectus and early African Homo. environmental conditions appeared. Starting from this, the team then looked for all the places and times in the model where these conditions occurred and created maps of potential hominin habitats that have evolved over time.
Author of the study on the topic, Director of the IBS Center for Climate Physics (ICCP) at Pusan National University in South Korea Axel Timmermann, “Although different groups of archaic humans preferred different climatic environments, their habitats were all caused by astronomical changes in earth’s axis wobble, tilt, and orbital eccentricity. to climate changes It responded on timescales ranging from 21 to 400,000 years. used the phrases.
It was found that hominin groups differed significantly in their preferred habitats.
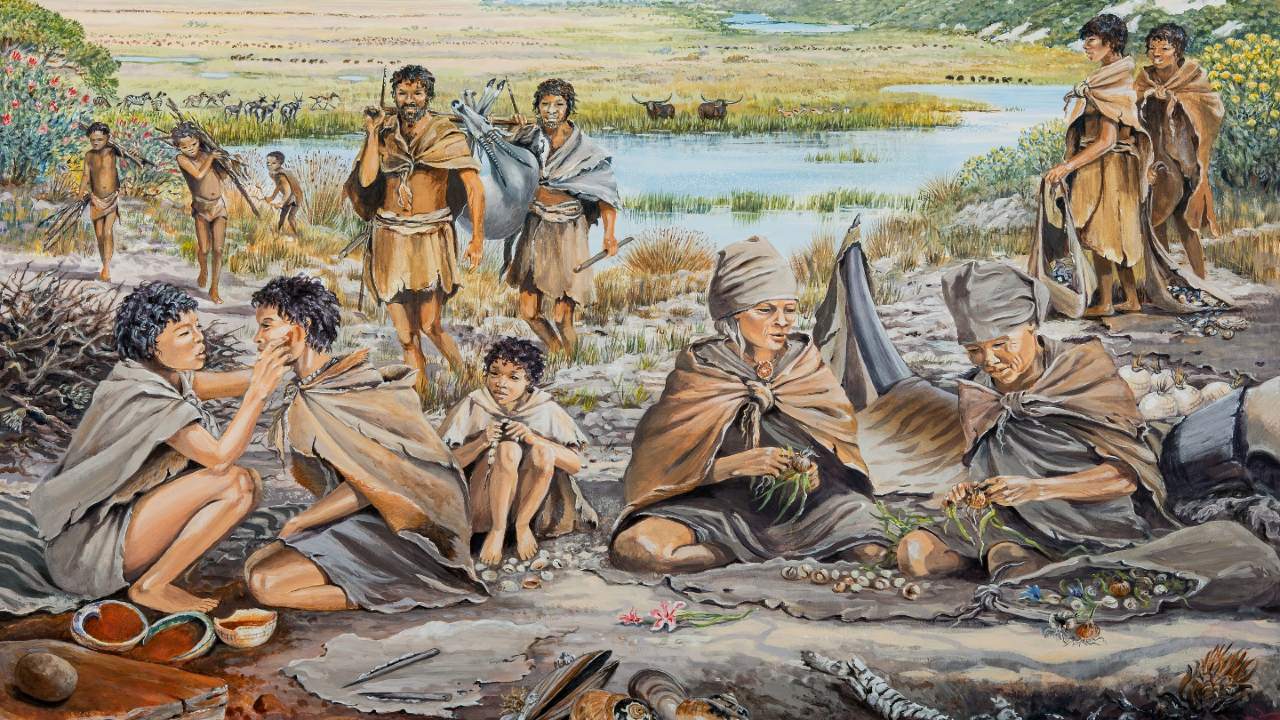

To test the robustness of the link between climate and human habitats, the research team repeated their analysis by shuffling the fossils’ ages like a stack of papers. Past evolution of climate variables, where and when people lived unaffected if so, then this would mean that both methods should result in the same habitats.
However, the researchers used mixed and realistic fossil ages in habitat models for the three most recent hominin groups (Homo sapiens, Homo neanderthalensis and Homo heidelbergensis). important differences they found out. Regarding this, Timmermann “This result suggests that the actual sequence of past climate change, including glacial cycles, over at least the last 500,000 years, is that of different groups of hominins. where do you live and its remains in determining where shows that it plays a central role” recorded as.
The researchers’ next question is about the habitats of different human species. in terms of space and time it was not overlapping. At this point, the contact zones, provided very important information about potential species sequences and mixtures. After analyzing the contact zones, the researchers concluded that Neanderthals and possibly Denisovans descended from the Eurasian Homo heidelbergensis lineage about 500-400 thousand years ago, while Homo sapiens’ roots can be traced back to South African populations of Homo heidelbergensis about 300 thousand years ago. hominin pedigree achieved.
Co-author of the study and postdoctoral research fellow at the IBS Center for Climate Physics, Dr. Regarding this, Jiaoyang Ruan said, “Our climate-based reconstructions of hominid lineages rely on recent estimates from genetic data or analysis of morphological differences in human fossils. looks pretty similarwhich increases our confidence in the results” used the phrases.
“We are the way we are now because we have managed to adapt to slow changes in the past climate”
On the other hand, the simulation in question; The last of the world’s climate responses to the growth and reduction of ice sheets, to changes in past greenhouse gas concentrations. 2 million years environmental history and 1 million years It is said to be the first continuous simulation with a state-of-the-art climate model that first covers the marked shift in the frequency of glacial cycles.
Co-author of the study from the University of Zurich, Prof. Christoph Zollikofer is“Until now, the paleoanthropology community has not tapped into the full potential of such continuous simulations of paleoclimate models. Our work clearly demonstrates the value of well-validated climate models for addressing fundamental questions about our human origins.” stated as.
RELATED NEWS
Darwin’s Lost Notes Containing the Roots of the Theory of Evolution Returned Like the Movies: “Happy Easter, Librarian”
With that, the research team decided to raise the bar a notch higher and went beyond the question of early human habitats and the times and places of origin of human species to look at how humans lived within the last 2 million years. changing food sources He also addressed the question of how he could adapt. To this question, study co-author Elke Zeller, a PhD student at Pusan Ulusak University, said: “When we looked at the data on the five major hominin groups, we discovered an interesting pattern. About 2 million years ago, early African hominins preferred stable climatic conditions. This limited them to relatively narrow habitable corridors. After a major climate transition approximately 800,000 years ago, Homo heidelbergensis a group known under its umbrella, much more a wide range of food sources It has adapted, enabling them to become global travelers, reaching remote areas in Europe and East Asia.” replied in the form.
If Timmermann “Our work shows that climate has changed in the evolution of our Homo genus. basis documents that it plays a role. We are the way we are now because of slow changes in climate over the past millennium. to adapt we succeeded” He underlined that their work is a proof of the role of climate change on human evolution.
