Even being tens of light years away is sometimes insufficient to escape from supernovae, one of the universe’s greatest destructive forces. So at what distance would a supernova explode, damaging the Earth?
one of the most glorious events in our universe, supernova explosions have attracted the attention of almost everyone interested in space. These huge explosions are powerful enough to destroy everything around them. Considering that there are countless stars around us, I have always thought about how they would make such a finale for us people.
First of all, there are two ways a star can become a supernova. The first of these is our SunThey are stars that have a much greater mass than our own and have much shorter lifetimes than other stars. Along with these, white dwarfs in the binary star system can also create supernovae.
What is the safe distance for our Earth to be protected from a supernova?
Made in Midjourney.
For Earth to avoid the harmful effects of a supernova, according to NASA required distance 50 light years. Of course, there are some negative effects that will affect the Earth at distances above 50 light-years, but it seems unlikely that we will survive a close supernova explosion at this distance.
For example, around the world If a supernova occurs 25 light-years away, our planet will lose its entire atmosphere. and life as we know it disappears. Let’s put your mind at ease at this point: There are no stars near Earth that would cause such an explosion.
50 years apart, only 1 star explodes in the Milky Way Galaxy, turning into a supernova.
Considering that the Milky Way Galaxy contains between 200 and 400 billion stars, you might think that supernovas are very rare explosions. However, when we consider the entire universe, on average It is thought that 30 supernova explosions occur every second. This shows us how large a place the universe is.
The Earth is located in a region called the “Local Bubble”.
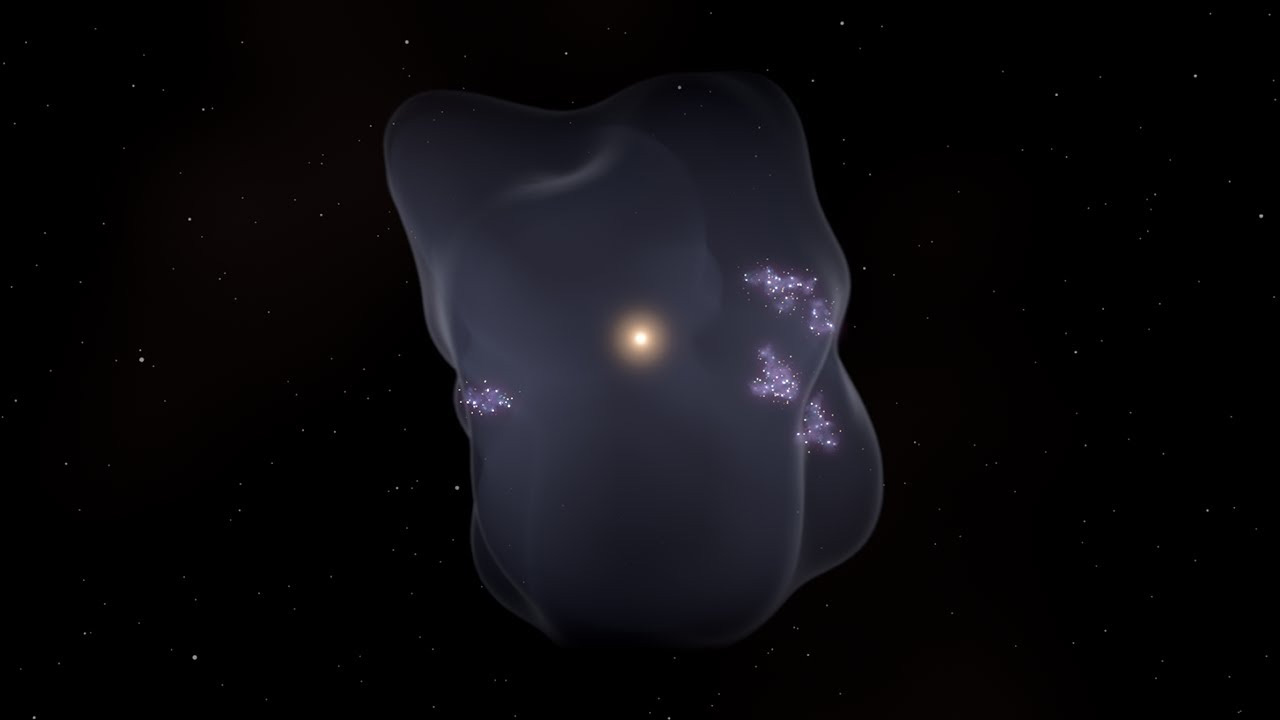
The Local Bubble, an area about 30 light-years across, contains the Solar System, to peanuts a special field. This area is thought to have formed as a result of a supernova explosion as recently as 10 million years ago.
In fact, there are high-energy gases from the supernova around this bubble that protects us by cleaning many things around us. If there is another supernova explosion near us, these gases can come to Earth with the effect of the explosion and increase the amount of high-energy radiation.
Between 1.7 and 3.2 million years ago, a supernova explosion occurred 325 light-years away.
Although this explosion was far from us, its effects were felt. Due to this explosion, which took place 6.5 times further from the danger zone Some iron from the core of the star has reached our planet. We can still observe traces of this eruption on the ocean floor.
No supernova in known human history is known to explode within 50 light years. in 1987 Supernova 1987A A supernova was observed. However, this explosion took place at a distance of about 168,000 light years from our planet.
RELATED NEWS
‘Last Light’ from a Star Spotted: Here’s What Supernovas Look Like [Video]
As Carl Sagan said: Actually, we are all stardust.
Calcium in our teeth, oxygen that we constantly need to live, iron in our blood and more. The elements that make up us and everything around us were actually produced in the stars (Everything except hydrogen). Especially big stars that will go into supernova form heavier elements such as lead, gold and uranium, apart from relatively lighter elements such as oxygen towards the end of their lives.
RELATED NEWS
Why Can’t the Temperature Drop Below -273 °C While It Can Reach Billions of Degrees?
Afterwards, a huge In the explosion, all these ready elements are scattered into the interstellar medium. The elements on our Earth, too, from the gold ring on our finger to carbon, one of the basic building blocks of life, were produced inside a star.

RELATED NEWS
Where Exactly Is The Big Bang? When You Find The Answer, You Will Dive Into The Void!
It is comforting to all humanity that a supernova explosion that will harm the Earth is not expected in the near future. However, it would be very nice to see a supernova explosion with our own eyes. It’s unclear exactly when it will explode, but is expected to go supernova in the near future. betelgeuse Its star is constantly observed. Betelgeuse, which is 642 light-years away, will not harm the Earth when it explodes. Of course, the visual feast it creates will be magnificent.
Sources: ESO Supernova, EarthSky, Business Insider
