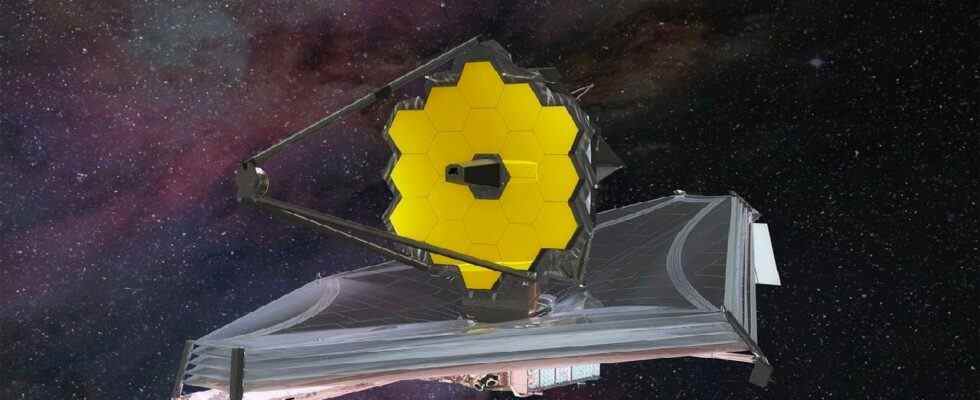
The American Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched the James Webb space telescope, which it has been working on for many years with many countries for the exploration of the universe, with the Ariane 5 rocket on December 25, 2021. On January 24, he left the Earth, where he would work for 10 years. 1.5 million kilometers farther away Langrange-2 (L2) had reached the point.
The telescope, which is expected to shed light on many unknowns about the universe, is currently completing its installation. NASA has released the first full-color images from the telescope. on July 12 He said it will be published. On the other hand, the observation targets of the James Webb Space Telescope have been determined.
Infrared early universe, Super-Earths and more
Hubble, the architect of all the information the Earth knows about the universe, only 500 kilometers is at a distance. Webb is from Earth 1.5 million kilometers next second Lagrange positioned at the point. James Webb Hubble Telescope100 times stronger than . In another sense, by traveling in time 13.5 billion light years ago will be able to see. Here are the 10 observation targets of the Webb telescope…
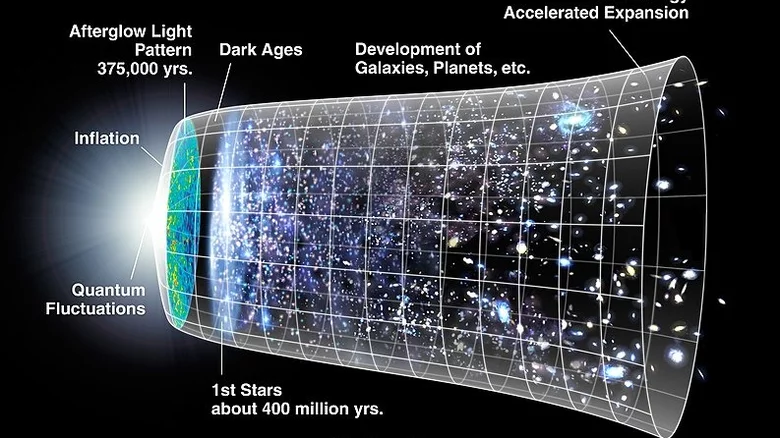
Infrared early universe
The James Webb space telescope will actually observe thousands of years ahead while making its observations. The telescope will shed light on the early universe and visualize the early universe by observing it in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The most distant and oldest galaxies
One way to pinpoint early galaxies is by observing the six most distant and brightest quasars. Quasars, which hold the important secrets of the universe, work by feeding supermassive black holes. James Webb researchers, on the other hand, will use quasars, which have a marked impact on the galaxies around them, to understand their evolution.

Jupiter-sized exoplanets
In the last 30 years, the definition of exoplanet has begun to evolve. These planets, which are usually connected to their star in the form of tide, are always day on one side and always night on the other. So much so that there are currently more than 4,000 registered exoplanets. With James Webb, this number is expected to increase considerably.

100 Galaxies at Once
The James Webb Space Telescope has a wide range of observation capabilities. So much so that researchers will observe galaxies from wide angles and study their movements and transformations.

Super Worlds
Super-Earths, in other words, are in the category of exoplanets. So much so that these planets, which are at least 10 times larger than Earth, are considerably lighter than planets of their own size, such as Neptune. Super-Earths, which can even consist of completely dense gas layers, are not included in any system.

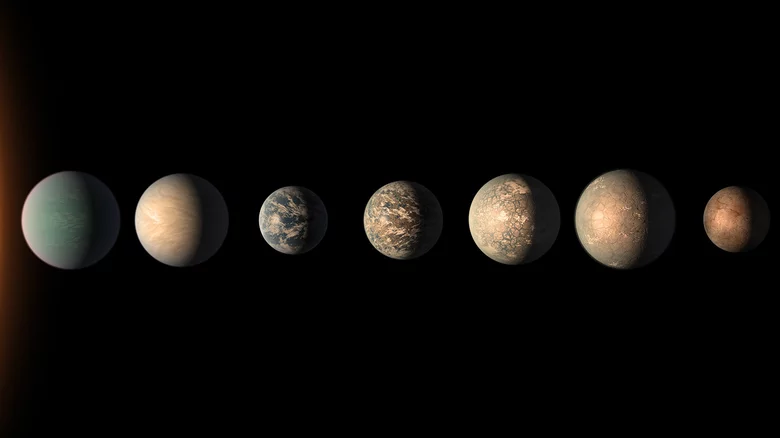
TRAPPIST-1 system
Located 41 light-years from Earth, the TRAPPIST-1 system was discovered in 2017. The most important feature that distinguishes this system from other systems is that it resembles the world in its system and is livable for human beings. So much so that its seven worlds are in the habitable zone of its stars.

Organic molecules and planetary birth
One of the most important features of the James Webb Space Telescope is its infrared imaging. With this feature, the telescope will be able to peer into the dense, massive clouds of interstellar gas and dust where stars and planets are born.

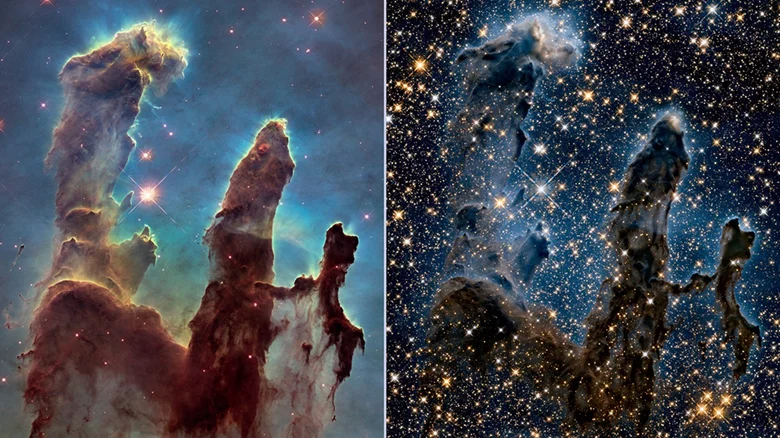
Pillars of Creation
The Pillars of Creation undoubtedly stands out as one of the most aesthetic landscapes in the universe. Hubble, on the other hand, had collected details of star birth processes in the columns. Now, James Webb will reveal details about the space region with his infrared ability.

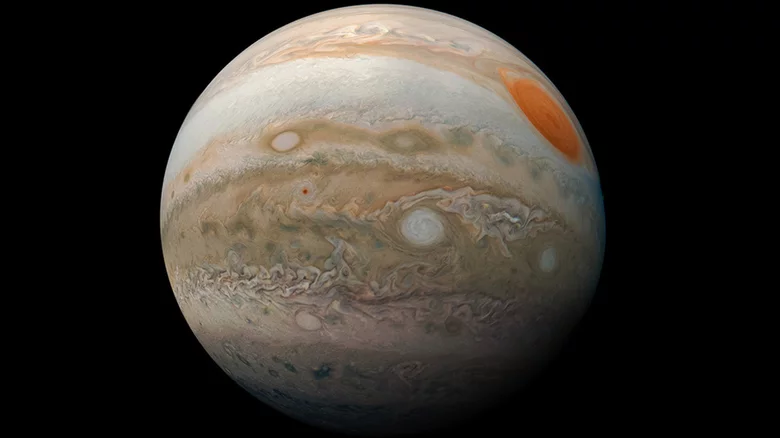
Jupiter, Its Rings and Moons
The James Webb Space Telescope will generally study objects thousands of light-years away. However, it will also work to have more detailed information about the solar system. A team of more than 40 researchers will study Jupiter, its ring system and two moons with the Ganymede and Io programs.

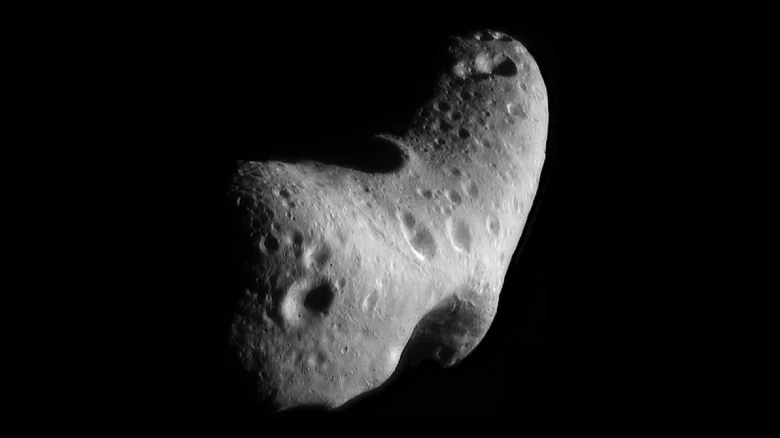
Asteroids and Near-Earth Objects
NASA classifies comets and asteroids as Near-Earth Objects (NEOs). The movements of these objects, which may be affected by the Earth’s gravity, will be followed. In addition, the structure of some asteroids will be examined to be a step for space mining.

Could the 10 observing targets of the James Webb space telescope capture significant breakthroughs? Please share your views with us in the comments section.
