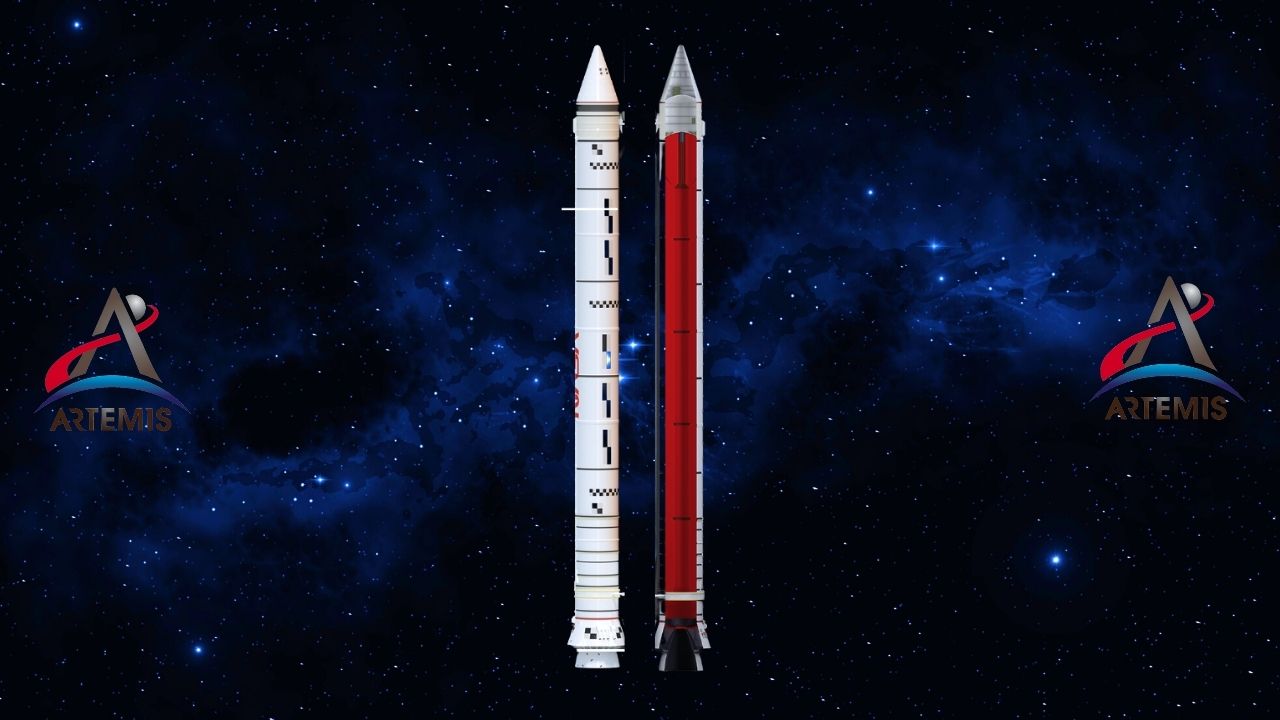
With the Artemis project, we will step on the Moon again. The goal this time is to stay on the Moon. For the realization of this project, there are parts in the rocket system, each of which is different from the other, reaching gigantic sizes. We examined the parts of this rocket one by one.
NASA aims to bring humanity together with the Moon again with Artemis missions and this time as humanity. A permanent order on the moon wants to provide. used for this big project ‘Space Launch System (SLS)’ rocket and ‘Orion’ The spacecraft is of course very powerful and the cost is quite high. Each of the rocket parts, some of which were developed by other space agencies, has a different feature.
Recently, NASA published the pieces of the Artemis I system, the first step of its mission to bring humanity to the Moon, in a way that resembles a jigsaw puzzle. Let’s do this together of your parts what works Let’s examine.
RS-25 engines: Designed to reach powerful speeds.
Known as the main engine of the space shuttle RS-25 engine an engine running on liquid fuel. These powerful engines, which have four in NASA’s launch system, make the rocket in the first 8 minutes of flight. 27,359 km/h overclocking. These S-25 engines can withstand temperatures ranging from -253℃ to 3316℃, thanks to the super-cold propellants and hot combustion gases inside.
The main engine of the space shuttle, RS-25s, is produced by the US firm Aerojet Rocketdyne. These engines are NASA’s on the space station was also used.
Core stage: The backbone of the launch system.

Core stage two propellant tank, flight computers and four RS-25 rocket engine contains it. The core stage of the launch system, which can rise 65 meters, feeds the rocket’s engines with 5,678 liters of propellant per second for eight minutes.
core stage of the world highest rocket stage. This stage is designed to run for 500 seconds before reaching Earth orbit, leaving the upper stage and the Orion spacecraft.
Solid rocket boosters: Burn incredible amounts of fuel at 6 tons per second.
Solid rocket boosters are used in spacecraft launch from launch to exit. the propulsion It is basically a propulsive engine used to provide These two solid rocket boosters; It burns 6 tons of solid fuel per second to lift the massive rocket off the launch pad and help it glide into space. The boosters’ missions are completed in two minutes. In addition to any rocket ever built to more mass Specially designed for launching loads with
Liquid hydrogen tank: It carries fuel for rockets.
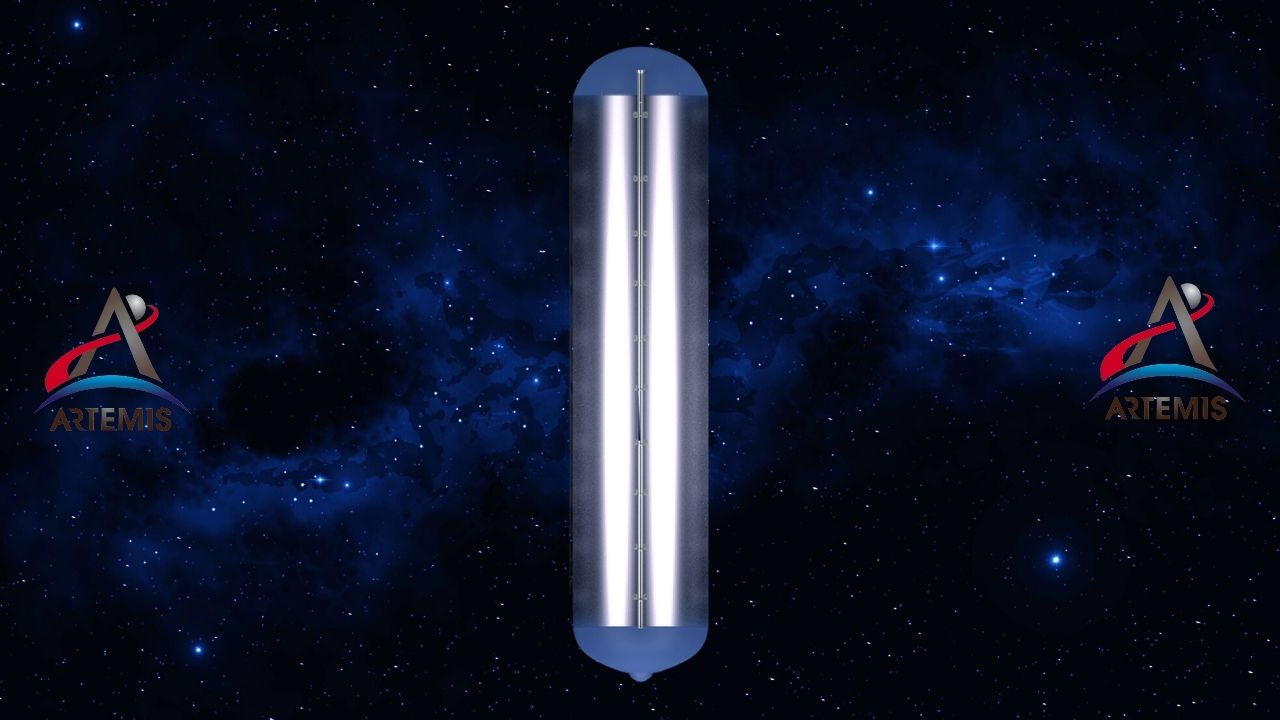
Liquid hydrogen tank ‘SLS RS-25’, fuel for rocket engines It is a tank that stores liquid hydrogen. This liquid hydrogen tank; It stores 2.032,766 liters of liquid hydrogen cooled down to -253°C. The length of the tank exceeds 40 meters, the tank of this length is almost the core stage of the rocket. two thirds it covers. The liquid hydrogen tank will power the massive rocket in its first integrated flight with the Orion spacecraft, and the hydrogen fuels inside will flow towards the RS-25 engine.
Liquid oxygen tank: It stores the booster power inside.
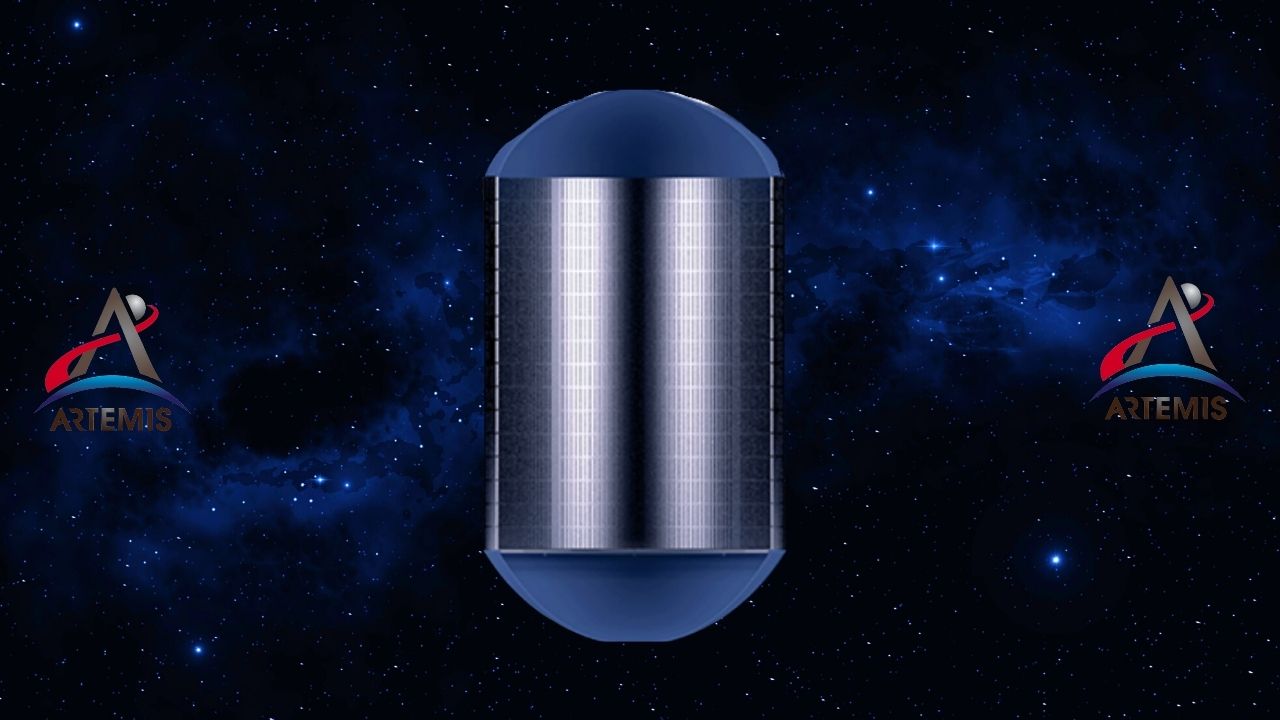
The launch system located inside the core stage liquid oxygen tank It holds 741,940 liters of liquid oxygen cooled to -183°C. The protection of these tanks at high temperatures is done with thermal protection foam sprayed on them. The task of the liquid oxygen in the tank is to feed the RS-25 engines. in the combustion reaction to oxidize.
The RL10 Engine: undertakes one of the main missions to send the Orion spacecraft into space.

The RL10 engine is a type of liquid fuel cryogenic that runs on liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. It’s a rocket engine. During the Artemis I uncrewed test flight, the RL10B-2 engine, which increased to 11,227 kg of thrust, was used during the launch of the Orion spacecraft. cryogenic propulsion stage acts as the main drive.
This rocket engine was developed by Pratt & Whitney in the late 1950s and made its maiden flight in 1963. From those years until today from 500 pieces More RL10 engines launched into space.
Launch vehicle stage adapter: As the name suggests, it connects stages.
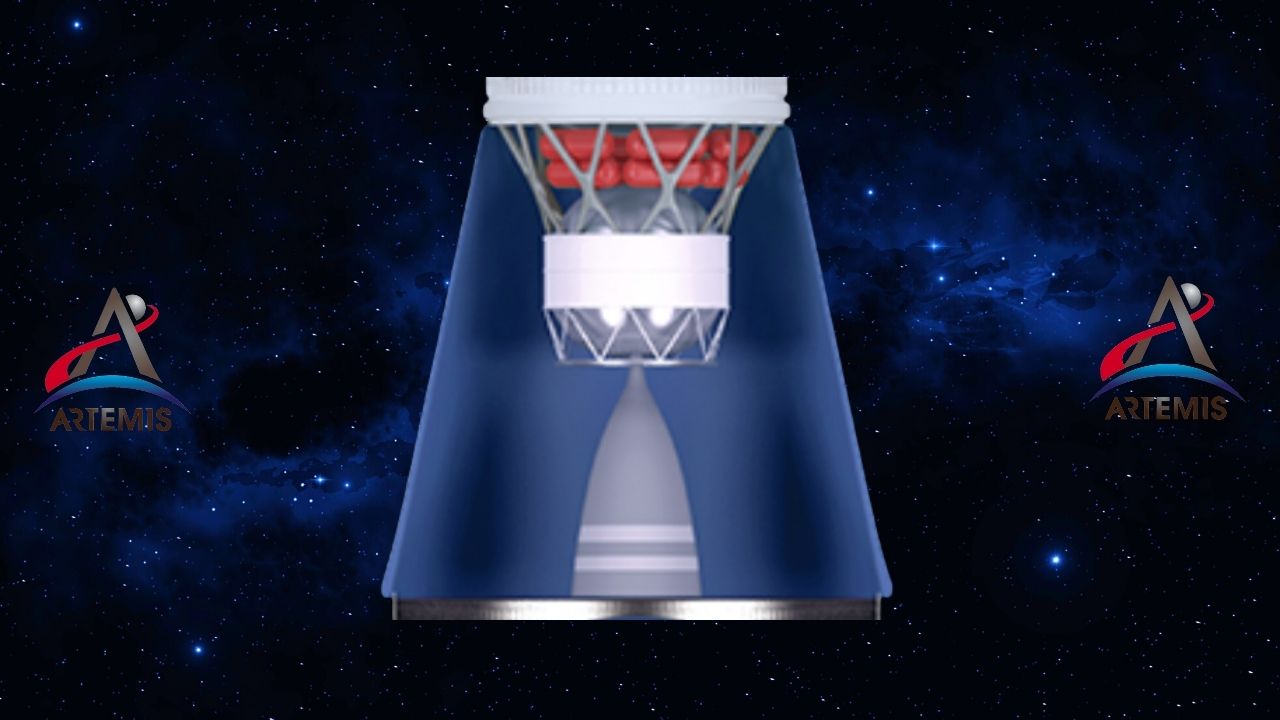
The launch vehicle stage adapter, which is designed as a cone, is used during the launch of the rocket. Covering the RL10 engine It acts as the main stage, connects the cryogenic propulsion stage to the main stage and provides connection to the Orion stage adapter. This adapter provides structural support for the ejection and separation system as well as electrical devices. excessive vibration and noise protects against potential problems.
Temporary cryogenic propulsion stage: Provides motion after launch.
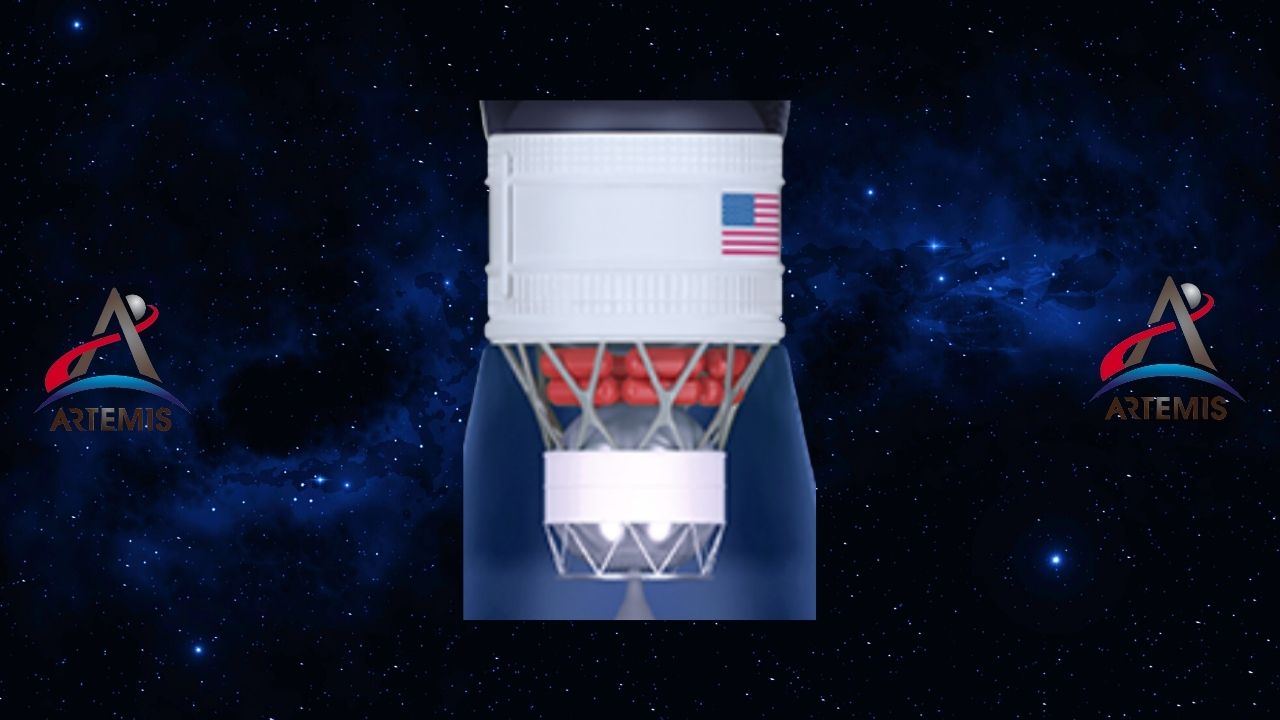

This system, called the temporary cryogenic propulsion stage, is installed after the solid rocket boosters and core stage are separated from the system. movement in space provides. This system consists of a height of 13.7 meters and a diameter of 5.1 meters. Basically, it works with liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. This stage system to earth orbit is placing it correctly.
During the uncrewed test mission of Artemis I, Orion and SLS; The temporary cryogenic propulsion stage required to fly beyond the Moon before returning to Earth great power of movement will provide. In addition, this stage is supported by the RL10 engine.
Orion stage adapter: connects the Orion spacecraft to the rocket.
Built by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the Orion stage adapter basically powered the Orion spacecraft. connect to other parts for the connection. Gases such as hydrogen, which emerged on the basis of the adapter launch, are sent to the spacecraft Orion. infiltrating acting as a barrier to prevent diaphragm contains. In principle, it can contain 17 CubeSat satellites.
The adapter is in the Artemis I mission; which will enable scientific research in deep space CubeSat satellite will carry. These satellites will play a major role in the Artemis missions.
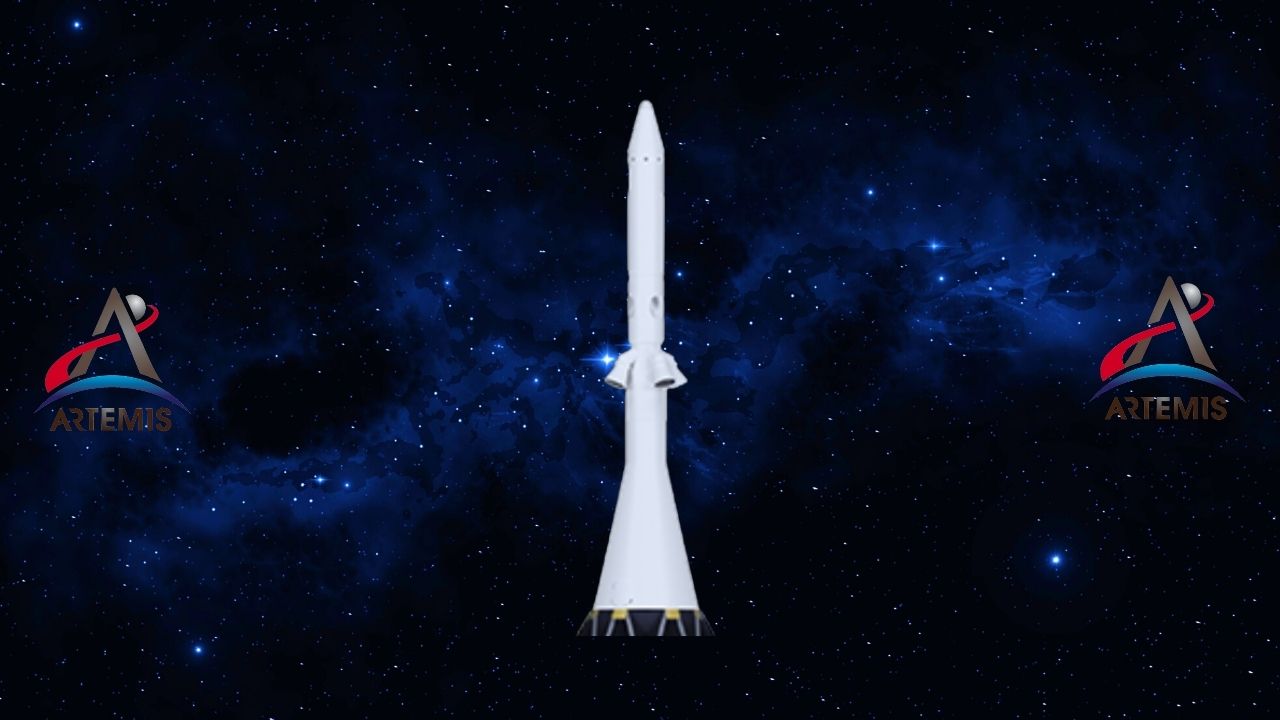
European Service Module: Provides vital support to the crew.

The European Service Module of the Orion spacecraft, supplied by the European Space Agency, enables the spacecraft to fly in space. making it livable and in space pushing forms the powerhouse. Service module spacecraft crew; from takeoff to separation from other parts of the rocket safe makes them.
The systems inside allow the crew to use electrical power and basic control functions. The module basically supplies astronauts with water, oxygen and nitrogen. living environment it creates.
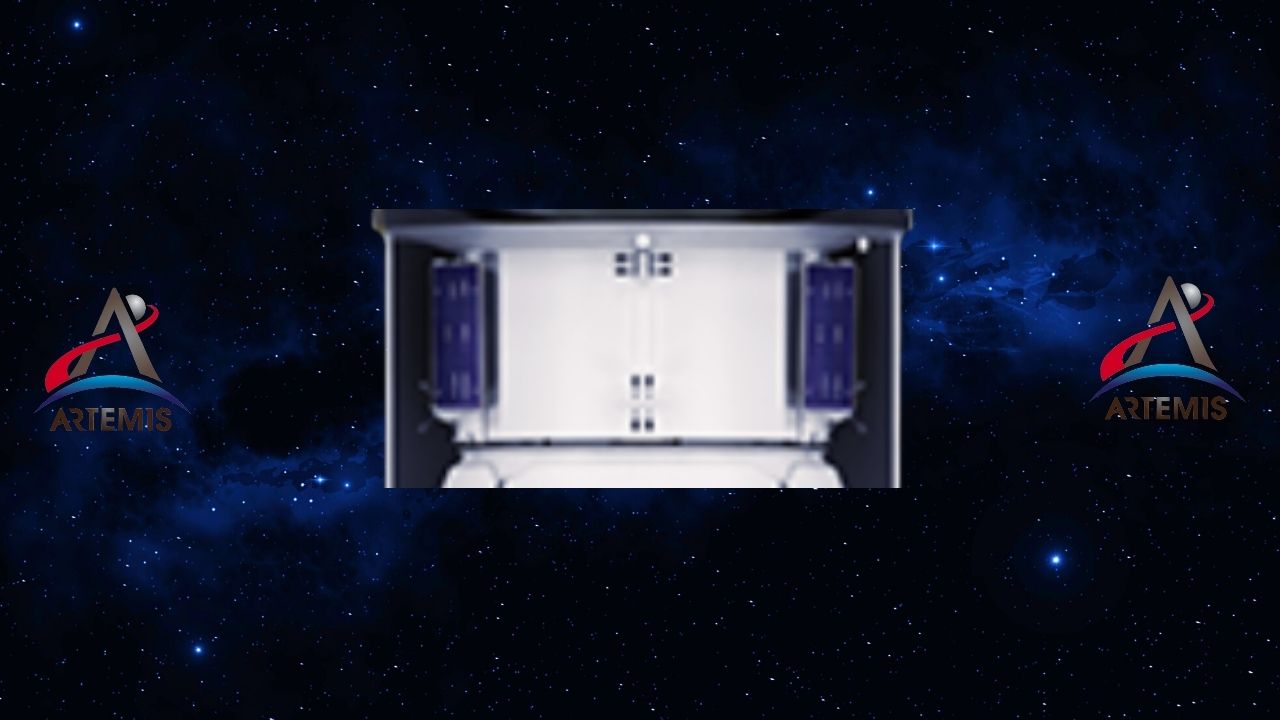
Crew module: Where the crew lives and works.

Orion spacecraft capsule The crew module, also called they will live and in missions their work is the part that contains the pressure they will sustain. The module can accommodate four crew members for up to 21 days. advanced in life support, avionics (spacecraft electronic systems). In addition, the module also has a thermal protection system.
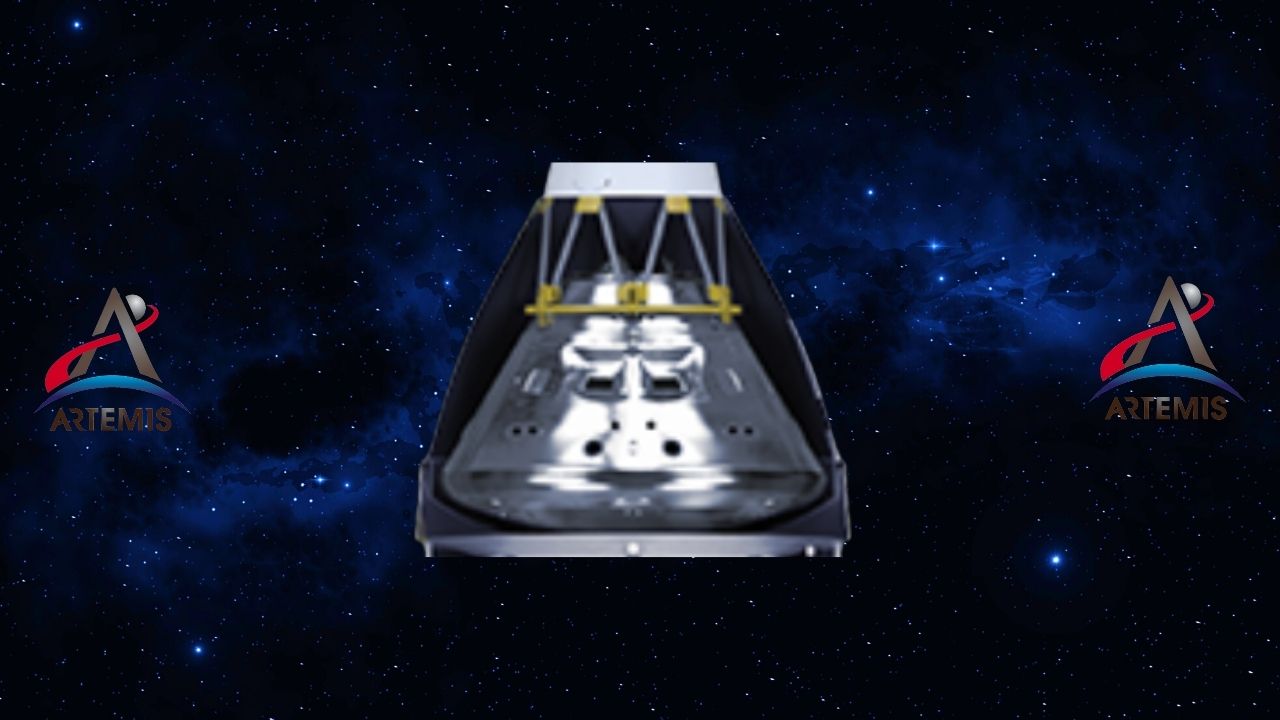
Launch abort system: Its purpose is to evacuate the crew if anything goes wrong with the launch.

The launch cancellation system is located on top of the Orion crew module. In Artemis missions with crew, the rocket is used during launch or ascent. any problem if his crew to protect working for The system is used to move the spacecraft away from the rocket. will activate in milliseconds was designed in such a way.
The powerful engine in the system is designed to protect the crew if needed in an emergency. 0 to 804.672 km/h in two seconds can accelerate up to speed.
Here’s what Artemis’ rocket looks like when all the pieces are put together:
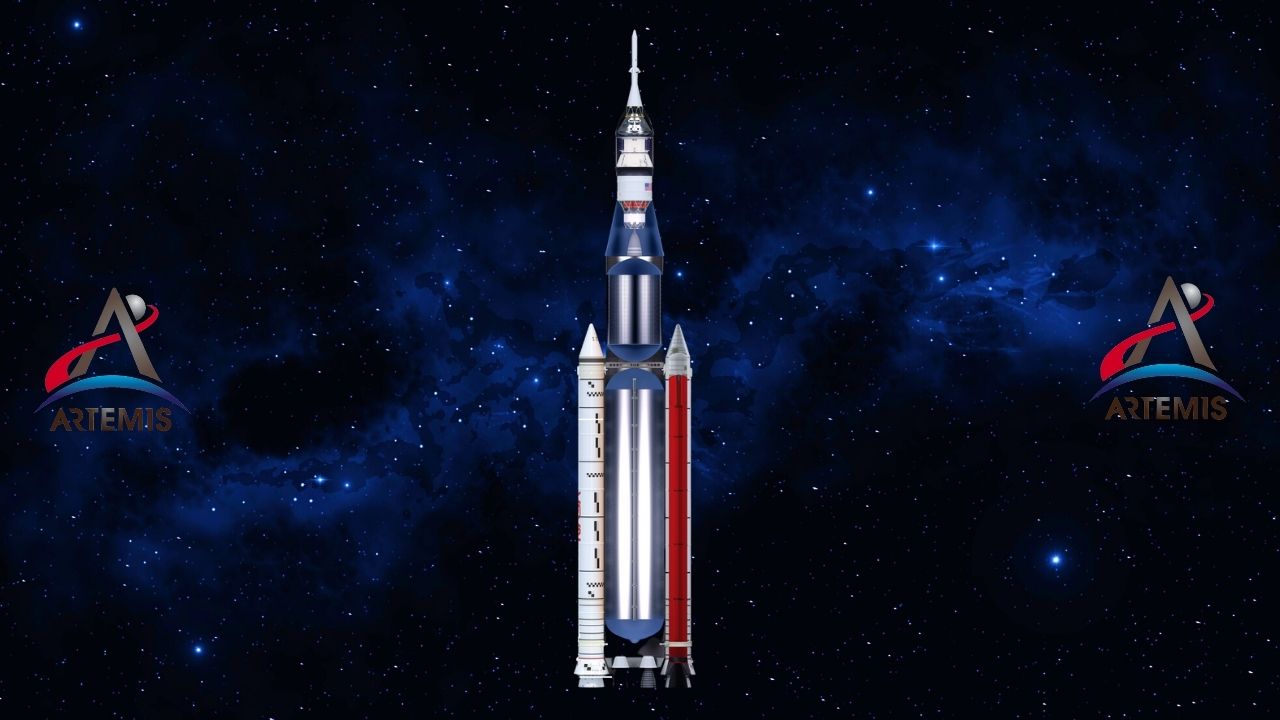

So what do you guys think about the Artemis project? Will humanity be able to establish order on the Moon?
