The crescent, which we see on the flags of countries such as Tunisia, Pakistan and Algeria as well as Turkey, is a symbol that can be interpreted from many different perspectives.
Contrary to popular belief, the crescent spread in the Islamic world between the 13th and 15th centuries through the Ottoman Empire and was previously encountered in the mosaics of Byzantium does not have the same meaning.
This symbol, which is known to have a history of thousands of years, whose origin is discussed even today, is an indispensable part of the Turkish flag. on different flags what it means And what direction is it looking at? Have you ever wondered?
First of all, let’s talk about the past uses of the symbol.
The earliest use of the crescent symbol, as far as is known today, is in the mythological and astrological representations of Ancient Greece. Greek Moon goddesses of Artemis And Selene’s It is frequently used in the depictions of other countries such as Serbia. Orthodox Christian also found in countries and in Istanbul before the conquest It is known to be a symbol used in
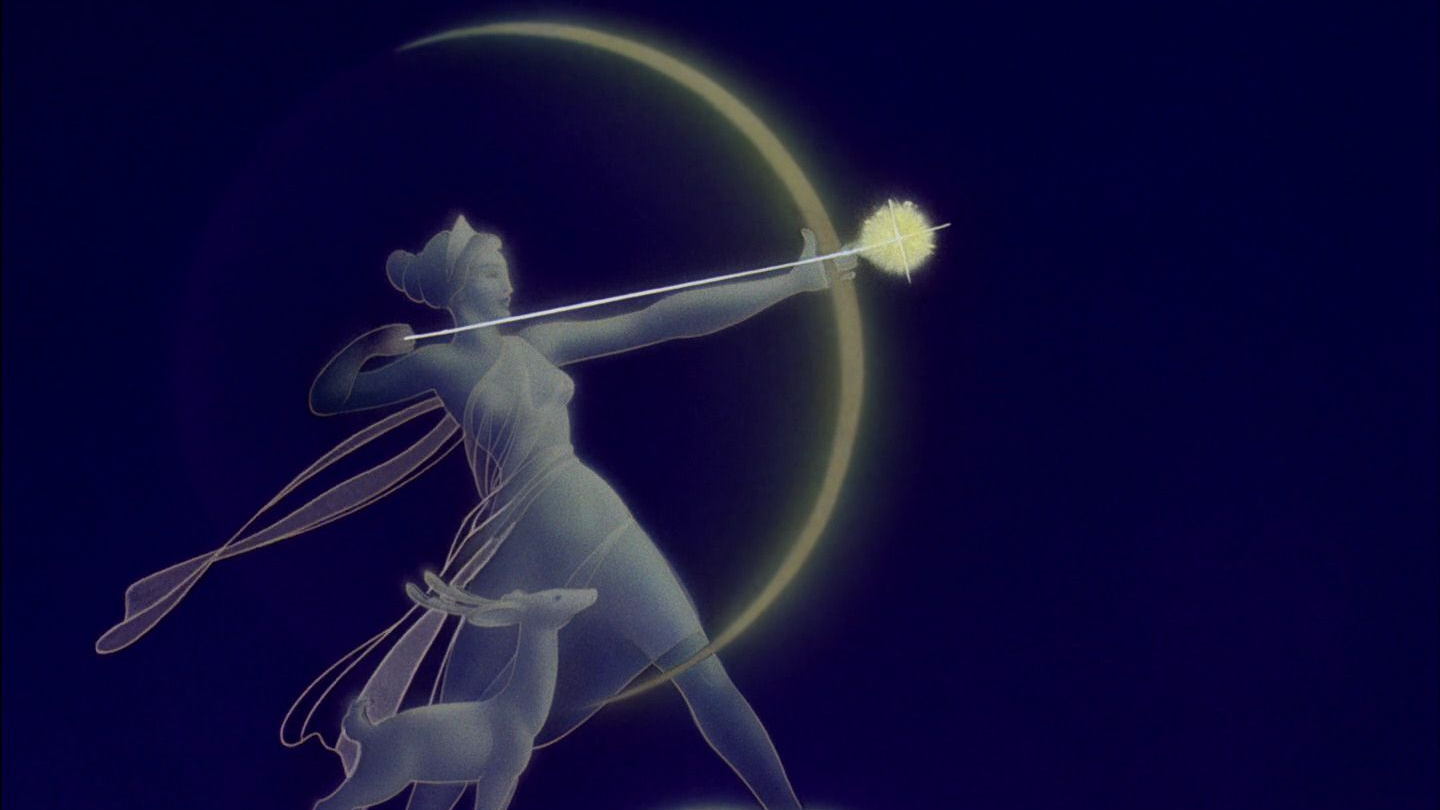
The crescent was likened to a bow because of its shape. Sometimes bow of Artemis can be seen as depicted.
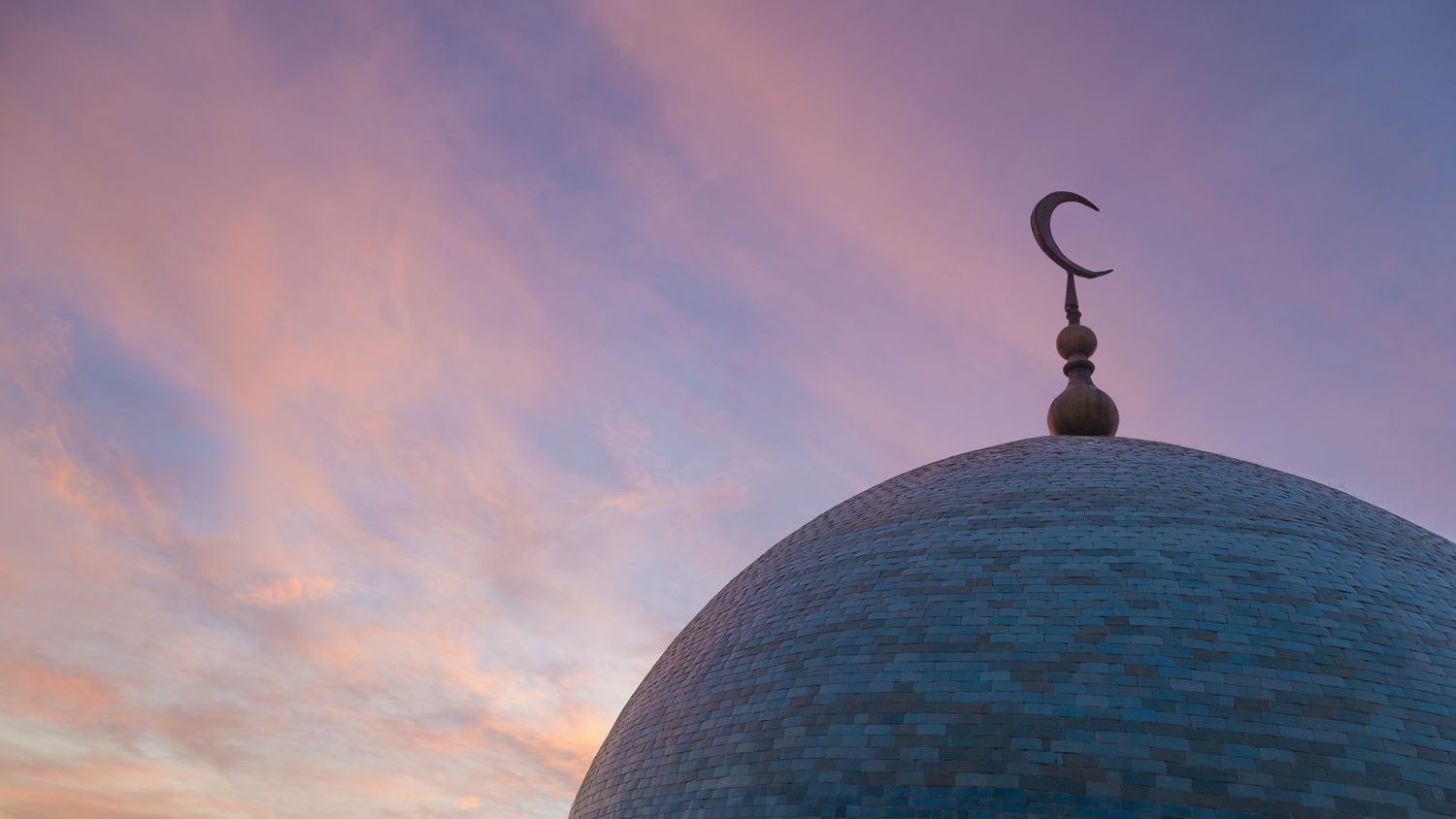

After the conquest of Istanbul in 1453, the crescent began to be used in the flag of the Ottoman Empire. It passed to other Islamic states such as Aceh Sultanate through the Ottoman Empire and in time It became associated with Islam.
That’s enough history. What determines how, how and at what angle the crescent is placed on flags?

Although this fact does not come to our minds, the Moon is especially in the crescent phase. It is not seen from the same angle all over the world. The reasons for this are that the Earth rotates around itself, the Moon rotates around the Earth, and the Moon can be seen in more than one place at the same time at different distances and angles.
The parallel to which the country is located may also play a role in determining the angle of the crescent. Let’s take Pakistan’s flag as an example for this theory.
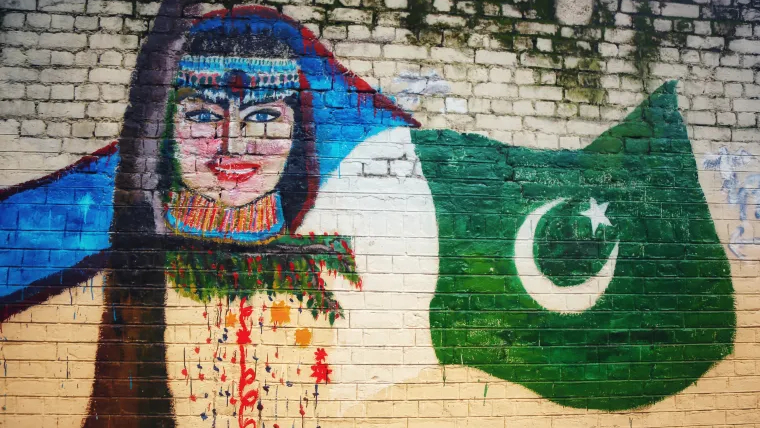

Crescent, to the upper right corner looking. There is a different angle compared to the Turkish flag.
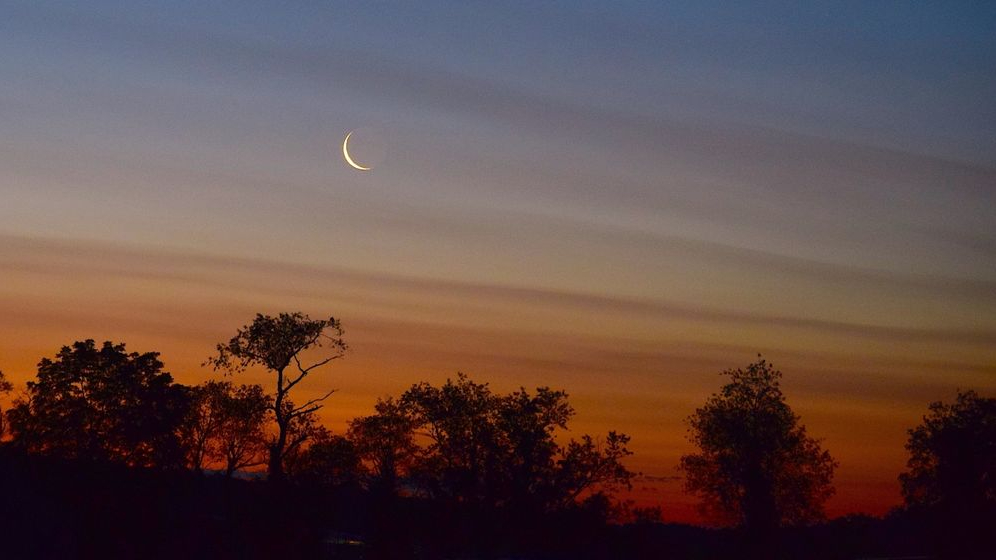

This too Pakistan’s located 30 degrees north A typical crescent phase shot around latitude. Although the angle doesn’t always stay the same when the flag was designed it can be said that they must have benefited from this phase and from this point of view. The landscape is reminiscent of the flag.
The angle almost resembles the angle of the crescent in Turkey, but when planning the Turkish flag, I tried to take the angle into account in time. didn’t need we should be.
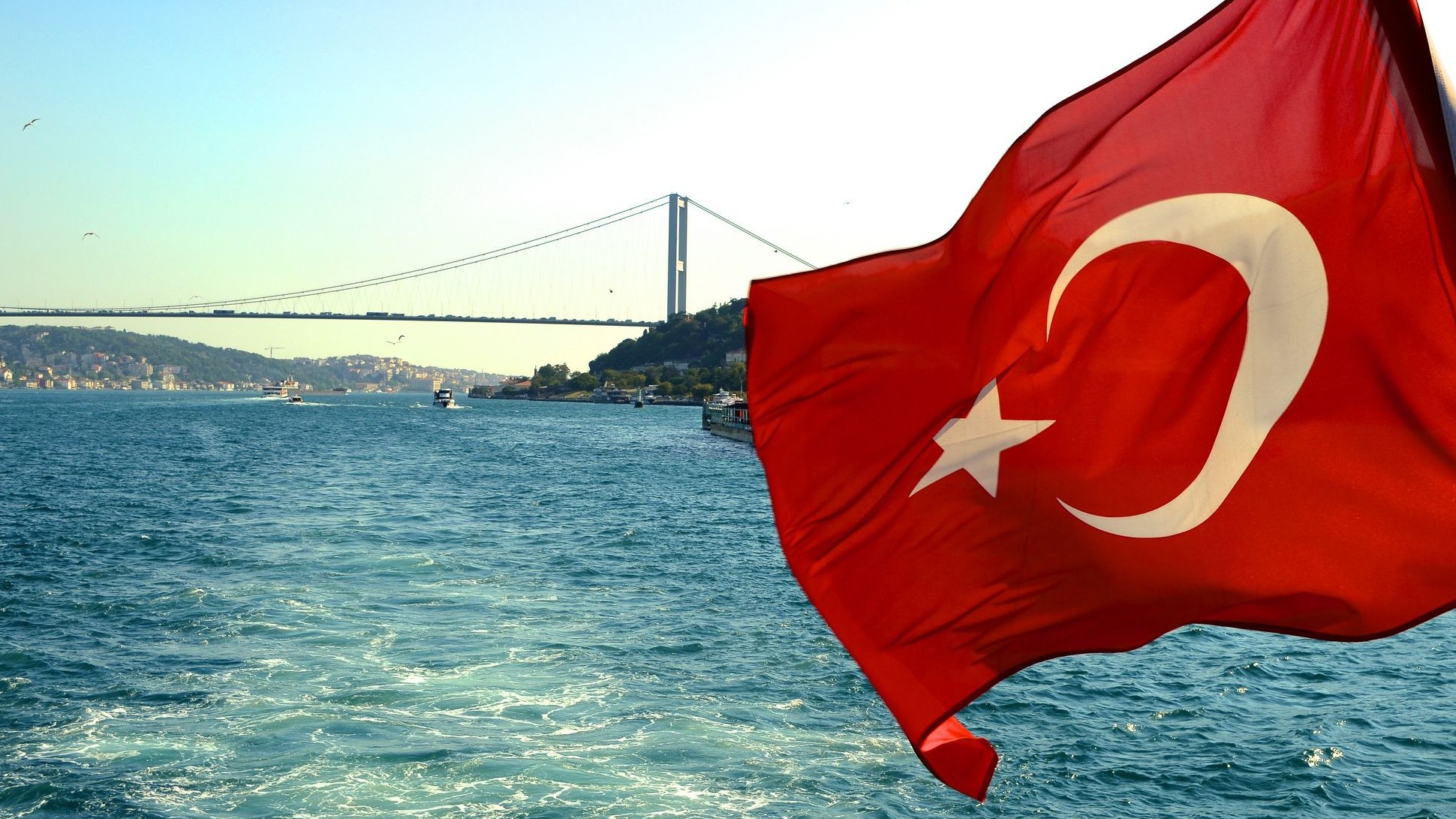

The crescent on the Turkish flag does not have any angles and is always facing right. As a matter of fact, the measurements on the Turkish flag are specific and there is no concern to determine an angle.
As another example, let’s examine the flag of Mauritania. Crescent, towards the top looking.
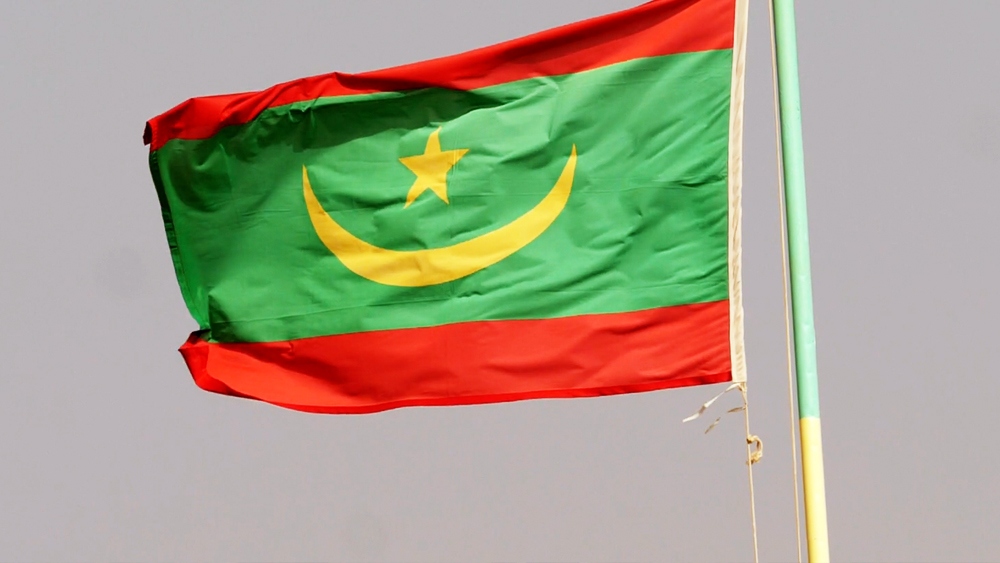

This is where Mauritania is located. 15 degrees north at latitude a crescent phase. The landscape is reminiscent of the flag again.
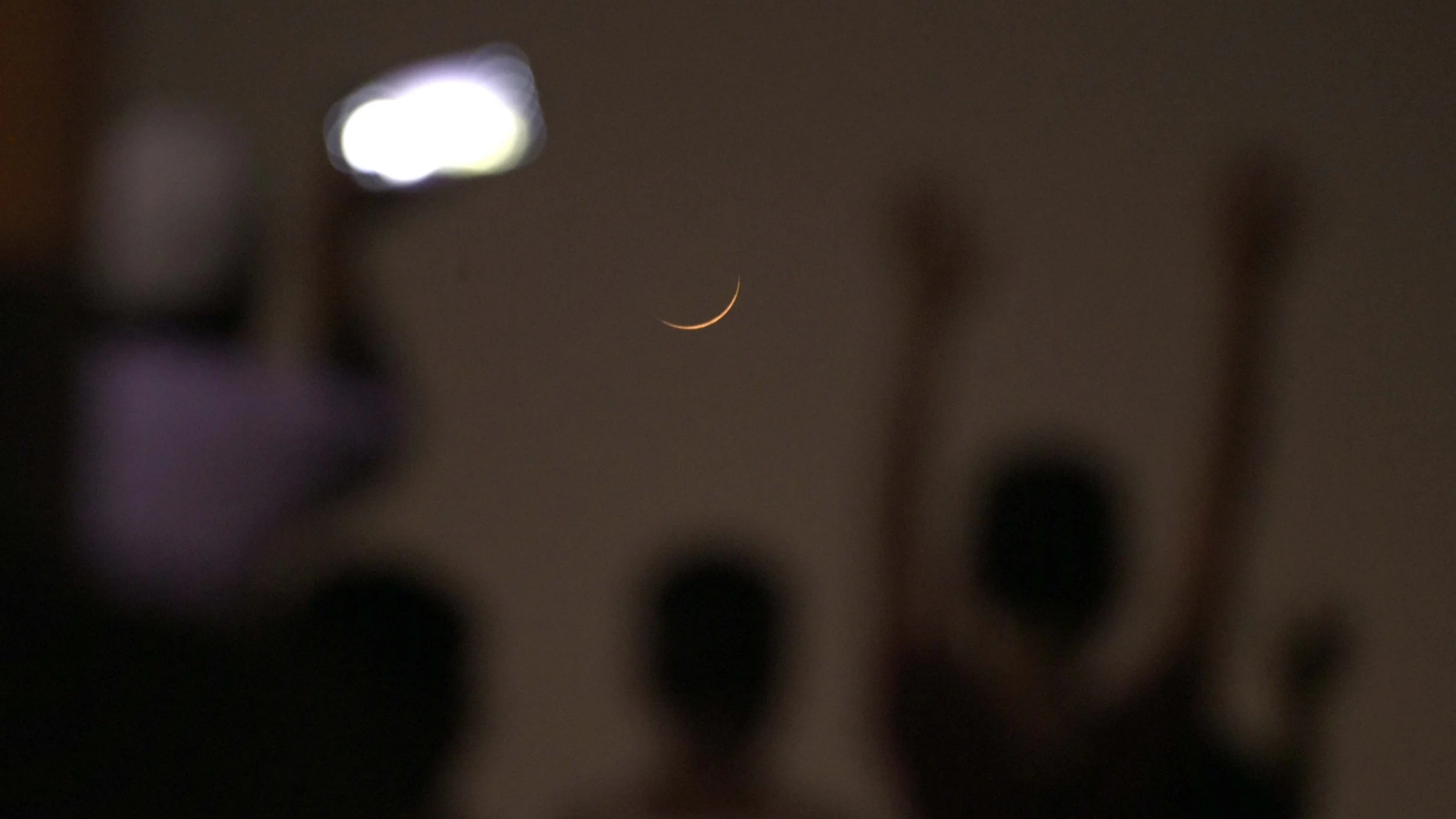

Finally, the US 33 degrees north Let’s look at the state of South Carolina at its latitude.

The landscape resembles the state’s flag.

There are also experiments on whether the Moon is seen from the same angle all over the Earth. Let’s examine the results of four different observation stations at the same time.

On May 11, 2007, the United States Wisconsin And Hawaii states, the capital of Kenya in Nairobi and New Zealand’s Christchurch Moon observations were made in the city at the same time.
The moon, as you may notice, in each at a different angle looks. The fact that the angle changes according to latitude makes it reasonable to claim that the flags were naturally designed by being influenced by this.
RELATED NEWS
Since We’ve Been to the Moon, Why Can’t We See the Flags and Vehicles With a Telescope?
RELATED NEWS
How is it that the Moon can show itself even during the daytime?
RELATED NEWS
Why Does the Moon Always Look Like It’s Following Us When Traveling on the Road?
RELATED NEWS
