Coastlines are not uniform around the world. It differs in shape, size and complexity depending on many factors such as climate, tectonic and erosion. Especially near the poles and in tropical regions.
Have you ever noticed that some coastlines are more meandering and irregular than others? When you pick up a world map and look at it, you can see the coastlines of islands and continents near the poles. more wrinkledwhile those close to the equator more straight You will notice that it has coastlines. So what’s the reason for this?
The answer lies in the different processes that affect land and sea borders over time. These processes glaciation, weathering, erosionsedimentation, sea level change and tectonic movement It contains several natural phenomena such as Depending on the climate, geology, and history of a region, these processes can generate different patterns of shoreline morphology.
Glaciation: Ice cuts the land.
Norway
One of the main factors that creates wrinkled coastlines near the poles is glaciation. Glaciation, ice formation and movement on land; is the process of carving valleys, fjords, lakes and islands.
Glaciers are large sheets of ice that flow under their own weight. They can erode the rock beneath them by plucking and freeze-thaw action. Moreover large amounts of sediment and deposit them as moraines, eskers, and overflow plains.
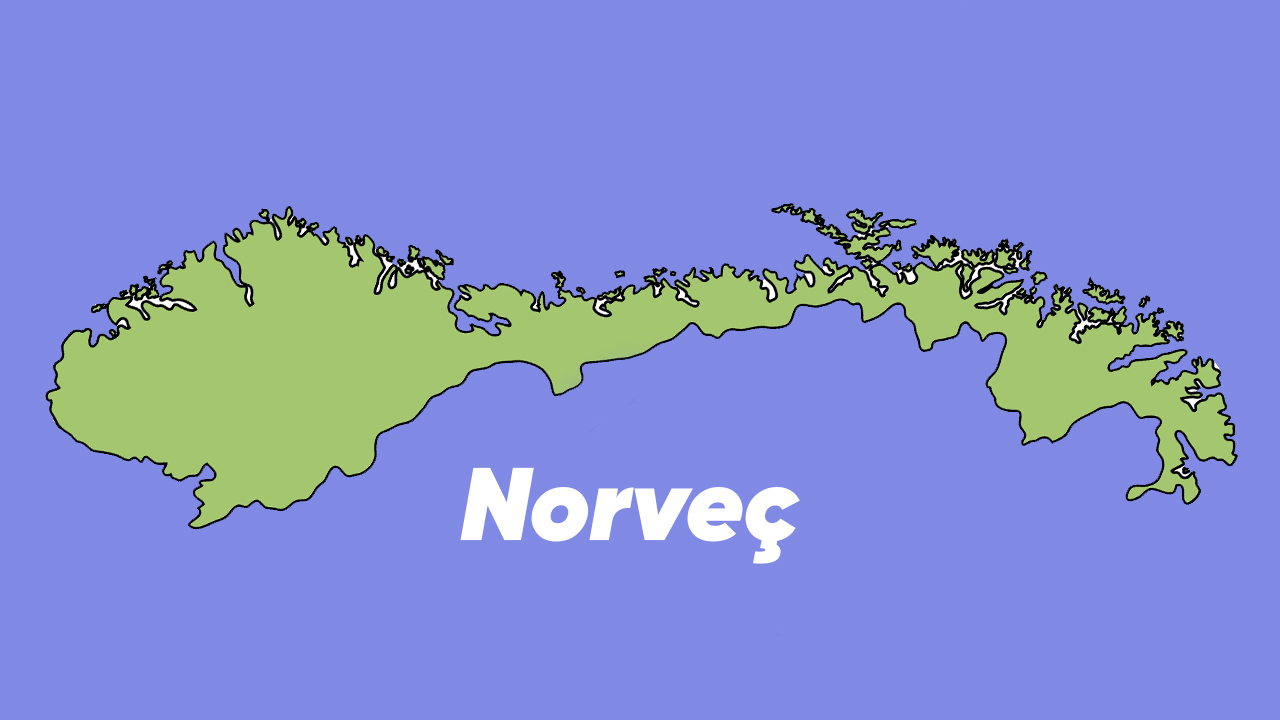
Glaciation has occurred throughout Earth’s history, especially when ice sheets covered most of North America, Europe, and Asia. During the Pleistocene (2.6 million to 11,700 years ago) occurred repeatedly. During this time, the glaciers we see today Norway, Alaska, Greenland and Antarctica shaped many of the wrinkled coastlines such as
Weathering and erosion: Water erodes the soil.
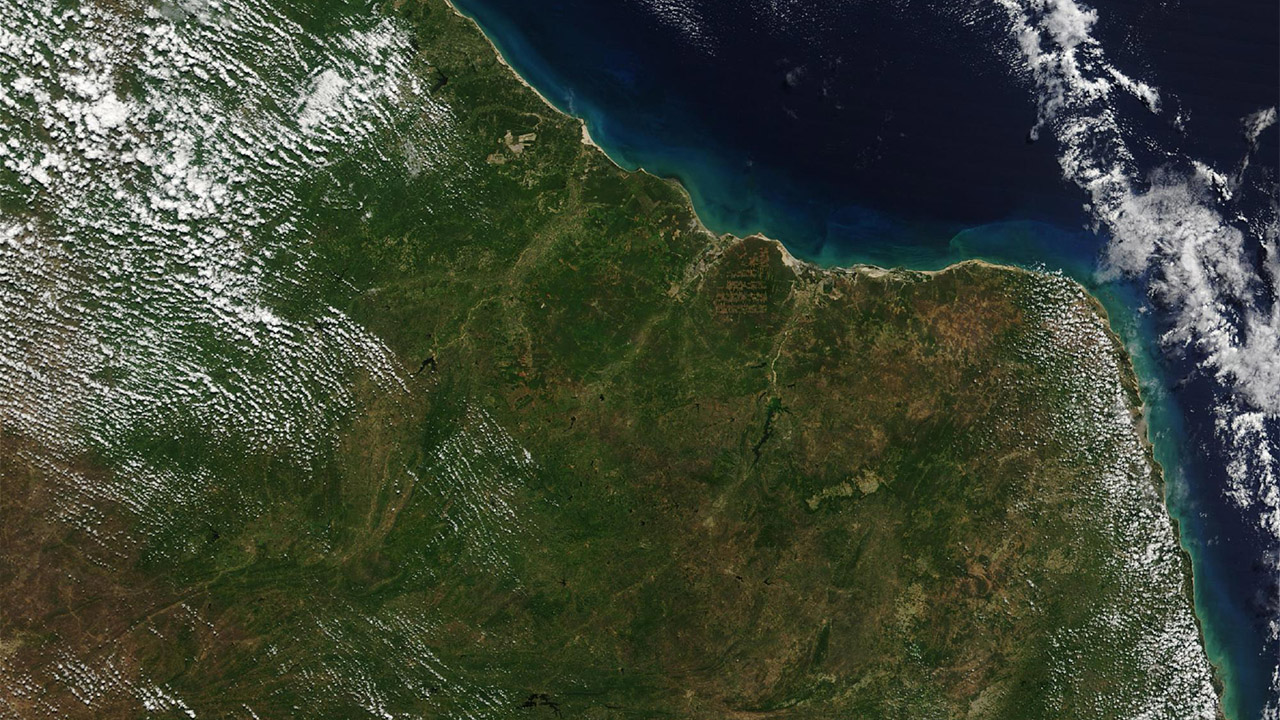

Brazil
The factor that creates smooth coastlines near the equator weathering and erosion. Weathering rocks rocks by physical, chemical or biological means. to the shredding process is the given name. Erosion is when weathered material is blown up by water, wind, or ice. relocation and transport process.
Weathering and erosion; It is more effective in hot, humid climates where precipitation, temperature changes, vegetation, and chemical reactions can weaken and dissolve rocks. These two events; smooth and rounded landforms such as cliffs, beaches, deltas, and coral reefs can create.
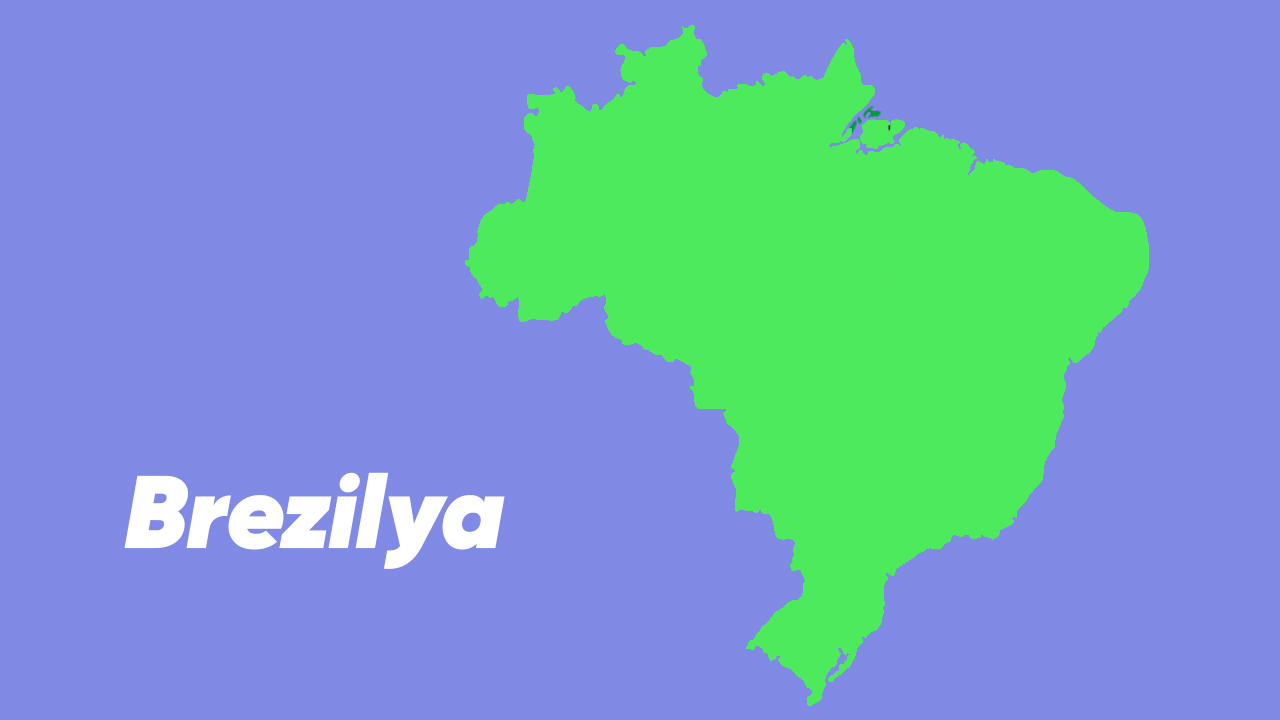
Weathering and erosion have been an ongoing event throughout Earth’s history, but they are more pronounced, especially in areas that have not been affected by glaciation or tectonics. Here are some examples of smooth coastlines formed this way. in Brazil, India, Australia and Hawaii we can see.
Tectonic: Plates move over land and sea.
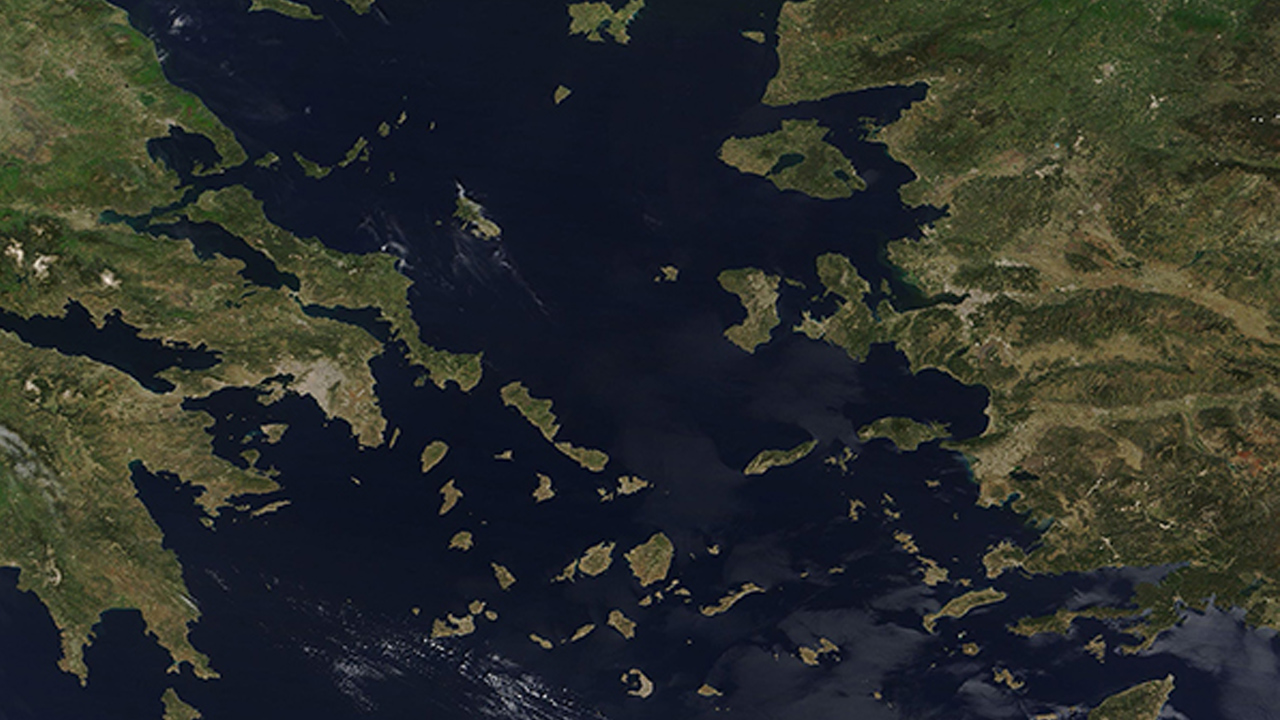

Our Aegean coasts
A third factor influencing the shape of the coastline is is tectonic. Tectonics is the study of how the earth’s crust is divided into plates that move relative to each other. This event; mountains, volcanoes, earthquakes and tsunamis can create various features such as
Tectonics, by changing the relative position of land and sea over time can also affect the shape of the coastline. For example, when plates converge or diverge, they can cause land masses to rise or fall. When plates slide past each other, it can cause lateral displacement or shifting of shorelines.
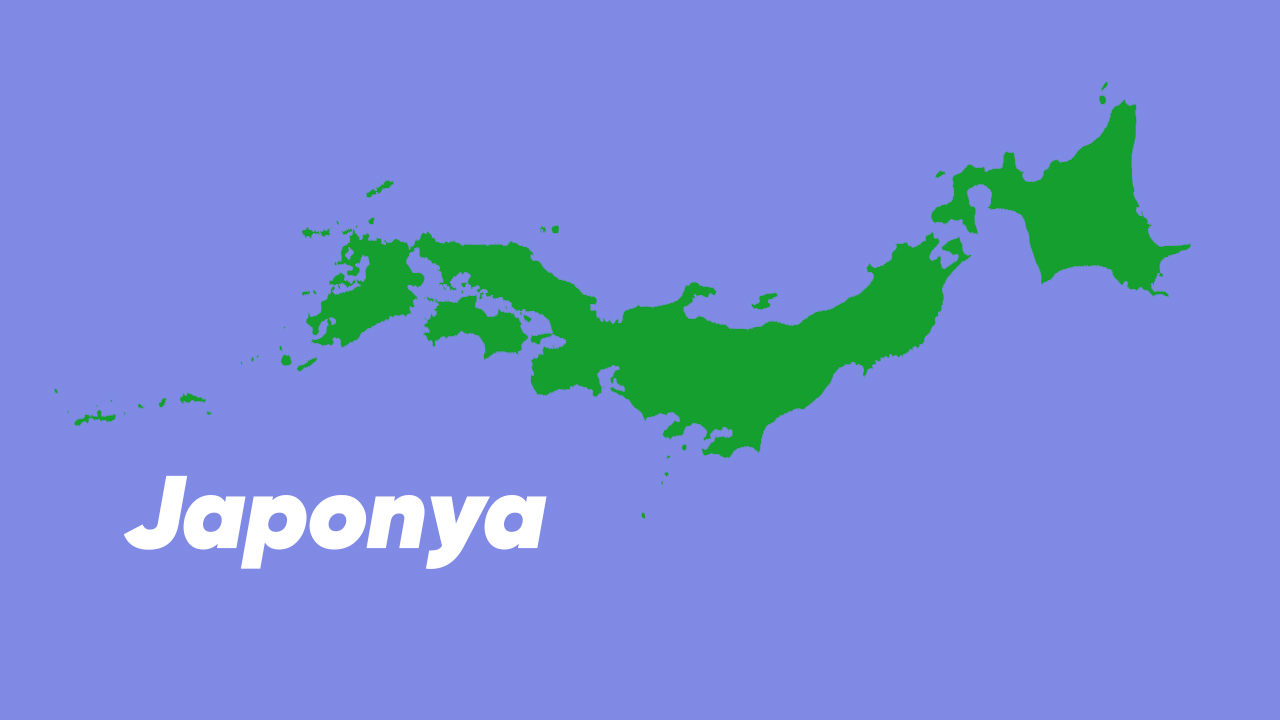

Tectonics can create both wrinkled and smooth coastlines, depending on the type and direction of plate movement. tectonically formed coastlines California, Japan and Iceland we can give.
In summary: the coastline; It is shaped by various processes related to climate, geology and history.
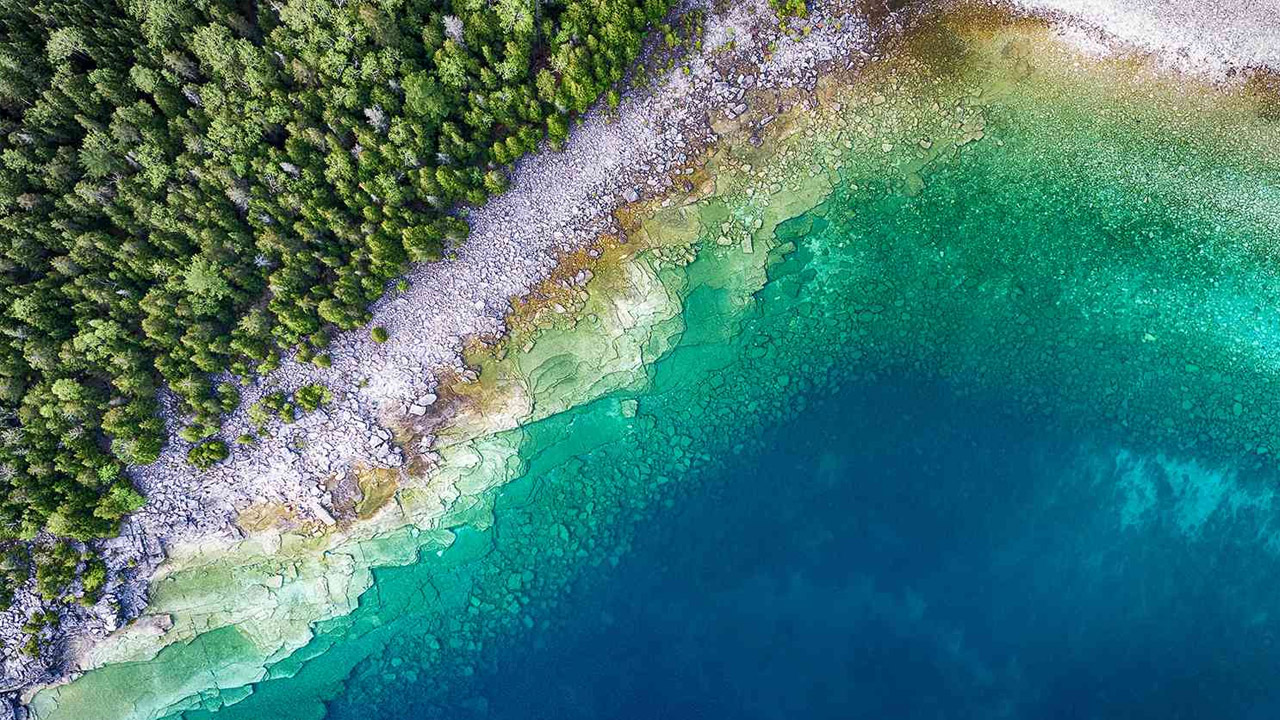

coastlines close to the poles, becoming more wrinkled due to glaciation while tending; coastlines close to the equator, become smoother due to weathering and erosion tends to. Tectonics can create both types of coastlines depending on plate movement. So if you see a near-smooth coastline in Norway or a curved coastline in Hawaii, it’s because of tectonic movements.
The shape of the coastline is not only for aesthetic reasons, but also It is also important for ecological, economic and cultural reasons. It affects biodiversity, natural resources, tourism, trade and human settlement. Therefore, understanding how coastlines form and change is crucial to managing them sustainably and passing them on to future generations.
RELATED NEWS
