The frequency, which we can generally define as the measurement of alternating current at a certain time, is also encountered as sound, radio and light frequency. Let’s take a closer look at the frequently asked questions such as what is the frequency, which also has an international unit of measurement, and what are its types.
When it comes to frequency, we are sure that many people will first think of radio frequency. True, there is such a type, but in general frequency is used to measure alternating current. To make a more general definition, actually Frequency is a measure of how many times an event is repeated. Frequency even has a special unit of measurement and a special measurement formula.
The question of where is frequency used is fundamentally wrong because frequency measures the repetition of an event. So it is not a tool to be used. Of course, we come across as sound, radio and light frequencies, but these are the measurement of the repetition of the event in question, just like current measurement. Come before we confuse any more what is frequency, what are its types Let’s take a closer look at the frequently asked questions.
Let’s start with a basic definition; What is frequency?
Frequency, which we can also call vibration number, in a unit time generally determined as 1 second It can be defined as the measurement of how many times an event is repeated. It can also be defined as the rotational speed of alternating current in one second. Although there are different types, the basic definition is the same.
How to measure frequency?
Frequency is measured by how many times an event is repeated in 1 second. According to the international system of units, hertz is denoted by Hz for short. A current with a frequency of 1 Hz means that it repeats 1 time in 1 second. A current with a frequency of 3 Hz means that it is repeated 3 times in 1 second.
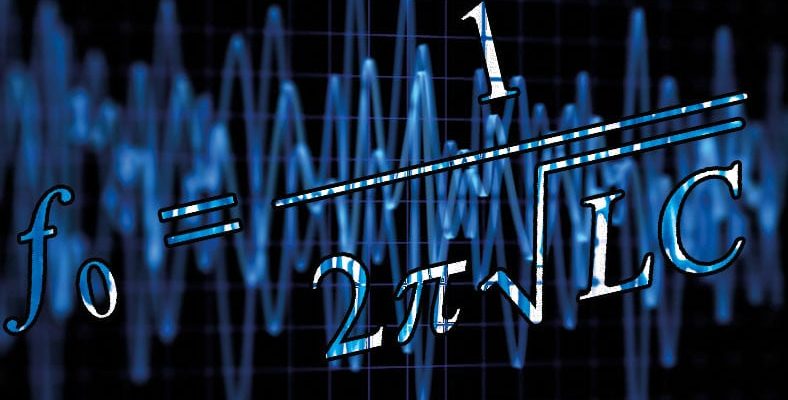
It is also possible to measure the frequency measurement over the period. In this measurement, the time between two repetitions is looked at, not how many times the event repeats per second. with the formula f = 1 / T frequency can be found over the period of the current. The result will be the same in both methods.
Multiples of frequency unit:
- 1 Hz = Hertz
- 1 kHz = 1000 Hz = Kilohertz
- 1 MHz = 1000 kHz = 1000000 Hz = Megahertz
- 1 GHz = 1000 MHz = 1000000 kHz = 1000000000 Hz = Gigahertz
Some of the frequency types are:
- Audio frequency
- Radio frequency
- light frequency
Audio frequency:
Audio frequency, known as AF abbreviation, in Turkish, sound frequency; refers to the range of sound that the human ear can hear. Even if it varies from person to person, a person can hear the sound frequency range is considered to be 20 – 20 thousand Hz. Even if we do not hear sounds below 20 Hz, we can feel them as vibrations. Sounds above 20,000 Hz, that is, 20 kHz, can cause hearing loss.
Radio frequency:
Radio frequency or radio frequency is used to transmit audio and video data in the broadcast and telecommunications world. Terrestrial broadcasting, satellite broadcasting and cable broadcasting are maintained over radio frequency. The frequency range may also vary depending on the type of broadcast. It can be in the range of 30 – 300 MHz, as well as in the range of 300 MHz – 3 GHz. it could be.
Light frequency:
The frequency of light, which we can also define as visible light, refers to the appearance of light that the human eye can perceive. Even if it changes The light frequency that the human eye can see is considered to be in the range of 430 – 750 THz on average. In other words, we can see electromagnetic rays called photons in this frequency range with our eyes.
All known frequency ranges:
- Extremely low frequency, known by the abbreviation ELF, in Turkish extremely low frequency; It has a frequency range of 3 – 30 Hz.
- Super low frequency, known by the abbreviation SLF, in Turkish super low frequency; It has a frequency range of 30 – 300 Hz.
- Ultra low frequency, known as ULF abbreviation, in Turkish ultra low frequency; It has a frequency range of 300 Hz – 3 kHz.
- Very low frequency, known as VLF abbreviation, in Turkish very low frequency; It has a frequency range of 3kHz – 30kHz.
- Low frequency, known as LF abbreviation, in Turkish low frequency; It has a frequency range of 30 kHz – 300 kHz.
- Medium frequency, known by the abbreviation MF, in Turkish medium frequency; It has a frequency range of 300 kHz – 3 MHz.
- High frequency, known by the abbreviation HF, in Turkish high frequency; It has a frequency range of 3 MHz to 30 MHz.
- Very high frequency, known as VHF abbreviation, in Turkish very high frequency; It has a frequency range of 30 MHz – 300 MHz.
- Ultra high frequency, known as UHF abbreviation, in Turkish ultra high frequency; It has a frequency range of 300 MHz to 3 GHz.
- Super high frequency, known by the abbreviation SHF, in Turkish superhigh frequency; It has a frequency range of 3 GHz to 30 GHz.
- Extremely high frequency, known by the abbreviation EHF, in Turkish extremely high frequency; It has a frequency range of 30 GHz to 300 GHz.
There is also something called body frequency:
Frankly, it is not possible to say for sure whether it is a subject accepted by the whole scientific world, but in 1920, a doctor named Royal Rife with a tool called a frequency generator There is a study in which it destroys cancerous cells and some viruses by using currents in different frequency ranges. Later, many new studies were carried out on the vehicle in question.
Dr. Written by Robert O. Becker in 1998 In a book called The Body Electric, A relationship between human health and body electricity has been mentioned. According to this, while the body frequency of a healthy person is between 62 and 72 MHz, it drops to 57 MHz in case of flu, 50 MHz in bacterial infections, and 42 MHz in cancer. Positive thoughts are said to increase this frequency by 10 MHz, while negative thoughts decrease it by 12 MHz.
According to the same book, the frequency range for canned foods or processed products is 0 MHz. Fresh herbs have a frequency range of 20 – 27 MHz, while dried herbs have a frequency range of 12 – 22 MHz. Vegetable oils, on the other hand, have a range of 52 – 320 MHz. The author recommends keeping our frequency range high by staying positive, taking walks in nature and eating healthy.
It is the measurement of how many times per second many events, especially alternating current, are repeated. what is frequency, what are its types We talked about important details you need to know about the subject by answering frequently asked questions.