Ontology, which is accepted as the first philosophy by the Greek philosopher Aristotle and asks questions about the being, which is thought to be the basis of everything, is also known as the philosophy of being. Although its emergence is old, let’s examine in all details the questions such as what is an ontology, which was first defined in the 17th century and later revived and questions the concept of being.
Since the first day of its existence, humanity has tried to understand the world in which it lives, and for this reason, philosophy has emerged. Philosophy is an extremely broad field that is divided into countless sub-branches. However, ontology, also called ontology, is accepted as the first philosophy, as the Greek philosopher Aristotle said. The field that ontology examines is actually considered to be the basis of everything. is the very concept of being.
Ontology, which started its studies with the difficult question of whether there is an existence, then asks many different questions about what the concept of existence is. Although it started with Aristotle, its first definition was made in the 17th century. After being forgotten for a while, it was revived in the following years and countless thoughts were produced on it. Come on so everyone can understand What is ontology, what does it study Let’s examine the most frequently asked questions in detail.
Let’s start with the basics, what is an ontology?
Ontology, also called ontology and philosophy of being, examining the concept of being and it can be defined as a philosophical discipline that asks questions about it. Concepts such as existence, existence, existence of existence and absence of existence constitute the main discussion topics of this discipline. Ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle, who is estimated to have lived between 384 and 322 BC, used the first definition of philosophy for ontology.
So what does ontology study?
Ontology, which Aristotle defines as an ontology, examines the categorization of existence. Looking through the windows of science and philosophy asks questions about the concept of being. Explains the separation of the subject from metaphysics through theories such as the existence of existence with time. In other words, it is a discipline in which the concept of being is examined from different angles and questions are asked to examine what exactly it is.
What questions does ontology ask? Ontological questions:
- What is an asset?
- When does an object disappear or change?
- What is existence?
- Is existence a feature?
- What are physical objects?
- What is true?
- Is it possible to prove the existence of a physical object?
- What is information theory?
- What is the relationship between objects?

Approaches of ontology to existence:
The discipline of ontology approaches from two perspectives, scientific and philosophical. According to science, existence is factual and these are studied. In fact, science has nothing to do with the question of whether there is an existence, because there is existence as a presupposition. Unlike philosophy, science examines the existence in parts, not as a whole.
Philosophy’s approach to existence is quite different. Because besides the question of existence Is it possible to know asks questions like Like science, it does not follow a method to solve these questions and seeks answers through reflection. For philosophy, existence is a whole and it emerged with an effort to understand the universe.
Currents established by answering the questions of ontology:
The first and most basic question of ontology is whether there is an entity and it provides the examination of the concept of being. Of course, existential philosophers do not give a clear answer to this question. but there are philosophical movements established by answering this question.
According to the nihilism movement that emerged in the 19th century and developed in Russia, there is no existence. Same way originated in ancient China Taoism also says that existence actually does not exist. Realism, on the other hand, with the premise that there is existence, argues that it is an independent structure other than reason. Of course, these currents have also been divided into many sub-currents and disciplines over time.
Ontology’s ‘What is Being?’ Answers to the question:
Create entity:
The first person to say that being is a becoming Ancient Greek philosopher Heraclitus and ‘You can’t bathe in the same stream twice.’ explained with an example. Being a becoming means that it is constantly changing and nothing stays the same as before.
Being is the idea:
Those who say that existence is an idea Socrates, Plato, Aristotle and Hegel. There are idealism and dualism movements that support this idea. Being an idea means that it is a thought, that is, there is no mind-independent world.
Entity is matter:
People who say that existence is a substance Democritus, Hobbes, Karl Marx and La Mattire. There is a current of materialism that defends this idea. Being a matter means that the actual reality is physical matter and even consciousness emerges as a result of matter interactions.
Being is both idea and matter:
The person who says that existence is both idea and matter Descartes. Accordingly, mind thinks, matter occupies space. All other ideas of Descartes are based on this idea. Those who advocate this are called Cartesian.
Being is the phenomenon:
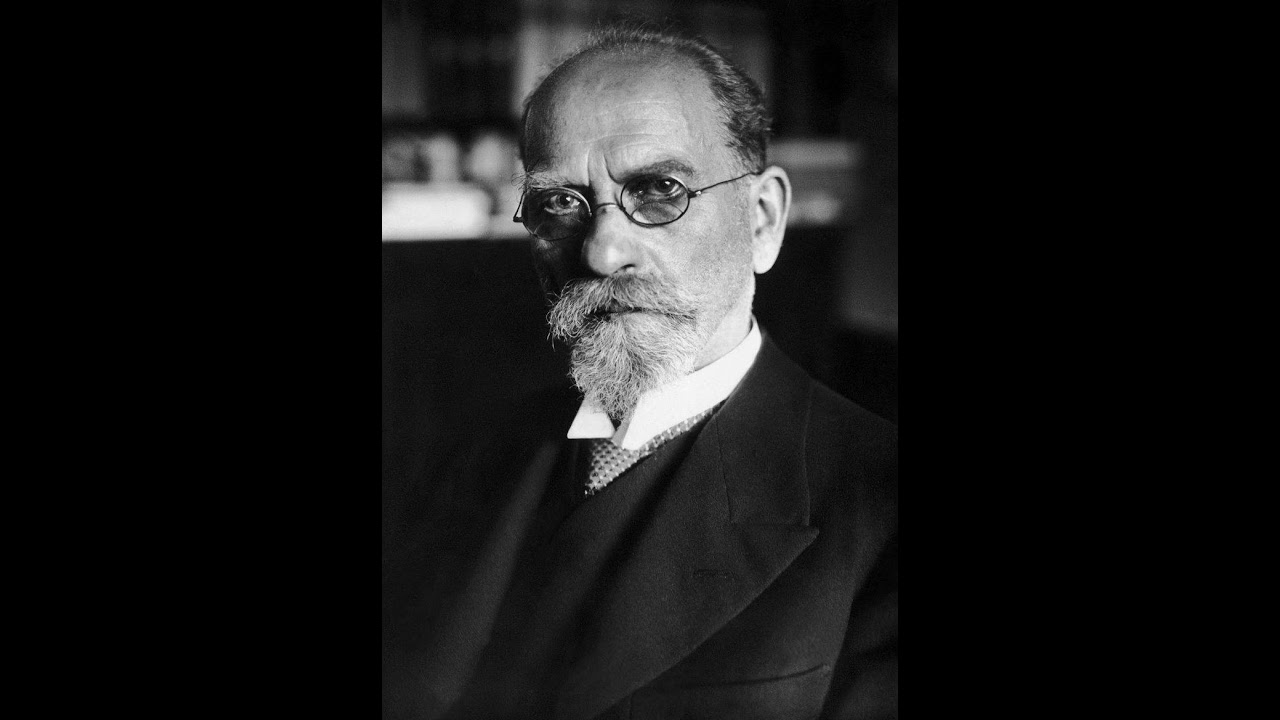
The person who says that existence is a phenomenon lived between 1859 and 1938 and is the founder of the phenomenological school. German philosopher Edmund Husserl. Being a phenomenon means that it is only a phenomenon, that is, something that can be observed and perceived by the senses.

Brief history of ontology:
Although ontology was first put forward by Aristotle, it was defined and named philosophically. It was realized in 1606 by the German philosopher Jacob Lorhardus. This view was harshly criticized by David Hume and Immanuel Kant in the 18th century.
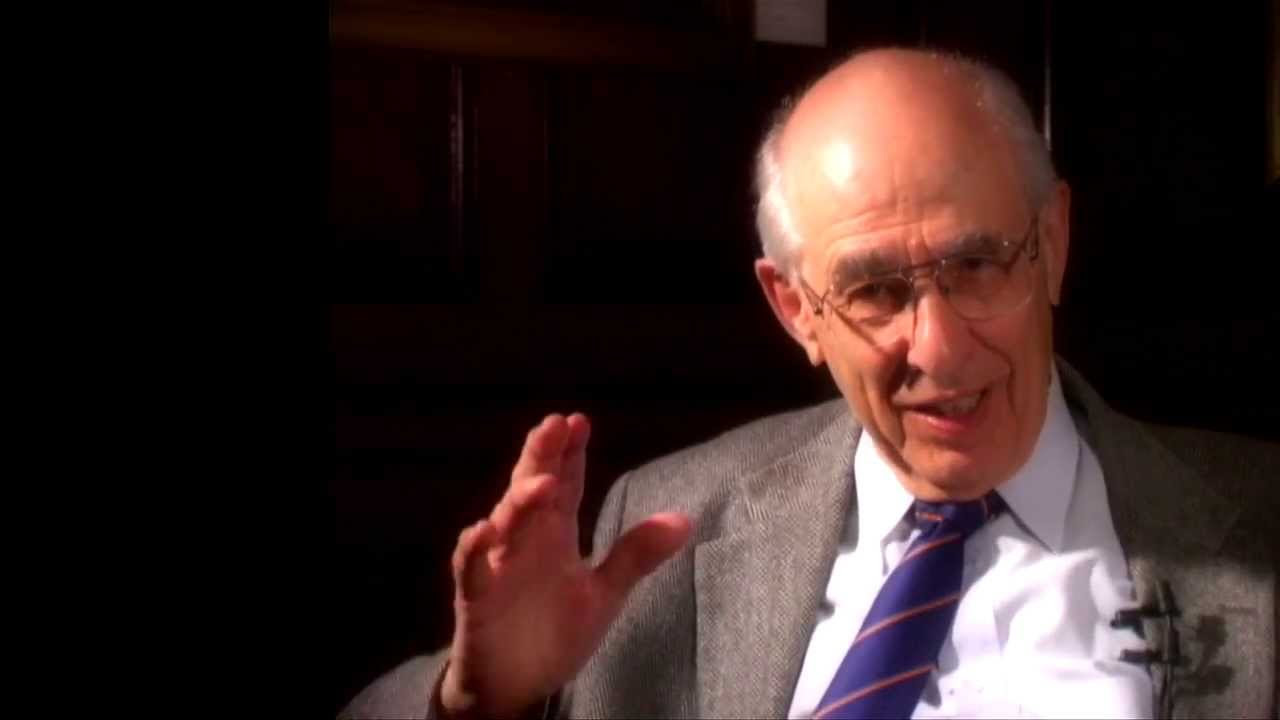
Ontology, which was seen as a general metaphysical subject by Christian Wolff, was evaluated as a phenomenon by Edmund Husserl. Ontology, which has not been studied much for a while, It was brought to the status of a philosophical discipline by the American philosopher Willard Van Orman Quine, who lived between 1908 and 2000.
Philosophers asking and examining ontological questions:
- Aristotle
- David Malet Armstrong
- Kindi
- birûni
- Alain Badiou
- Gustav Bergmann
- Patricia Churchland
- Paul Churchland
- Gilles Deleuze
- René Descartes
- Jean Gebser
- Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
- Martin Heidegger
- Heraclitus
- Edmund Husserl
- Roman Ingarden
- Saul Kripke
- Gottfried Leibniz
- Friedrich Nietzsche
- William of Oakham
- Parmenides
- Plato
- Plotinus
- Hilary Putnam
- W.V. Quine
- Bertrand Russell
- Gilbert Ryle
- Jean-Paul Sartre
- Barry Smith
- Baruch Spinoza
- PF Strawson
- Pierre Teilhard de Chardin
- Ludwig Wittgenstein
- Emmanuel Levinas
- René Descartes
The philosophy of being, which examines the concept of being and asks questions about it, is also known as the philosophy of being. What is ontology, what does it study We talked about the studies of philosophers about this discipline by answering the curious questions. You can share your thoughts on the subject in the comments.
