The story of the discovery of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar and is essential for diabetics, has a fascinating story that goes back to the Nobel Prize.
Diabetes, a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide and occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or use it effectively, predates the discovery of insulin. It definitely resulted in death.
People with diabetes had to follow strict diets that often led to hunger and malnutrition. Because there was no effective treatment, many people with diabetes died within a few years of being diagnosed. However, everything from 100 years ago changed after the work of a group of researchers.
How did scientists discover insulin?
Insulin is a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream and use it for energy. Without insulin, glucose builds up in the blood, causing high blood sugar levels and various complications.
The link between diabetes and the pancreas was first discovered by German researchers in the late 19th century. Oskar Minkowski And Joseph von Mering was founded by They found that removing the pancreas from dogs caused diabetes, suggesting that the organ produces something that regulates blood sugar levels.
But isolating this substance turned out to be very difficult. Many scientists have tried to extract pancreatic juices or tissue and inject them into diabetic animals or humans, but none have been successful. Pancreatic extracts are too small to have any effect. it was too poisonous, too impure, or too unstable.
In fact, we owe insulin medicine to our dear friends, dogs.
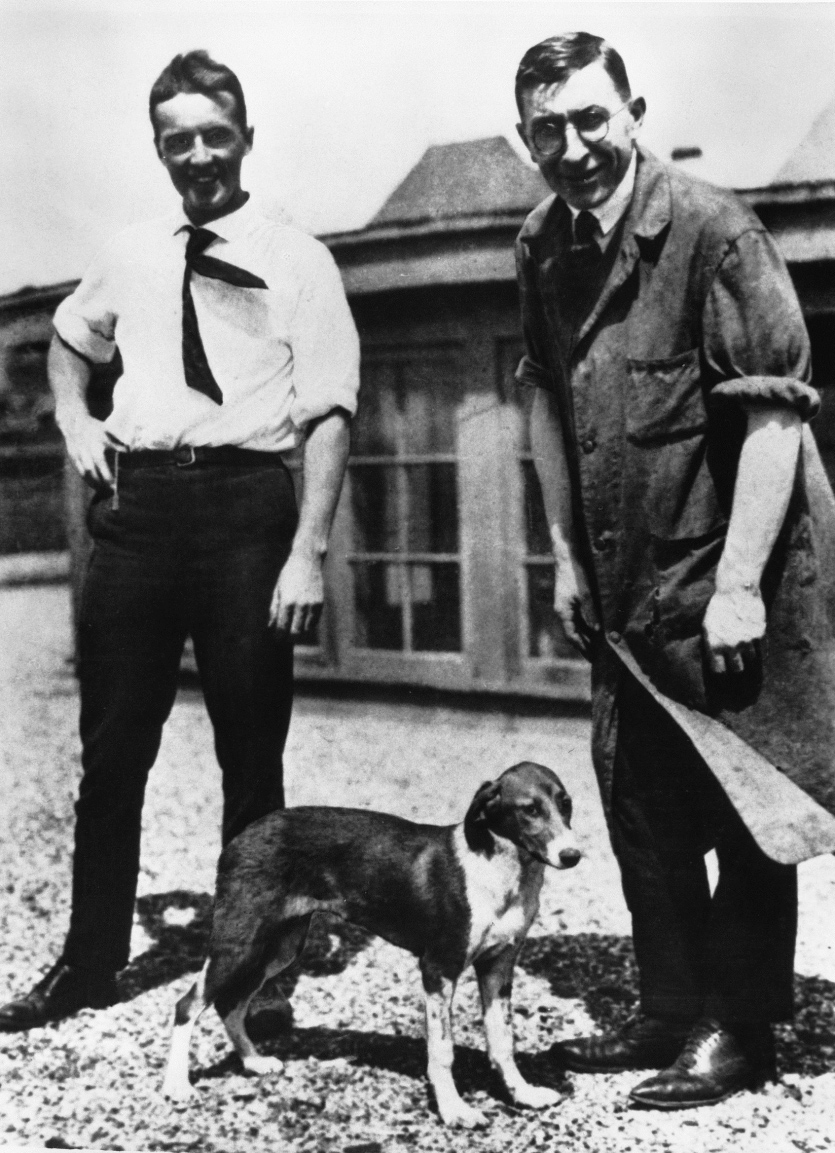

Invention in 1921 Frederick Banting It happened when a young surgeon named John Macleod, professor of physiology at the University of Toronto, gave an idea. Banting uses dogs to stop the flow of digestive enzymes that destroy insulin-producing cells. connect the pancreatic ducts suggested. He hoped this would allow him to get a stronger output from the degenerated pancreas.
Macleod was skeptical, but gave Banting a small lab space and space to test his hypothesis. several dogs agreed to give. Also to her Charles Best appointed a medical student named as assistant.
Banting and Best conducted several experiments on dogs together in the summer of 1921. Producing a crude extract from blunted pancreas and injecting it into diabetic dogs blood sugar levels They were able to lower it and prolong their survival.
The first human injection was not as successful as expected.

Encouraged by these results, Banting and Best developed a method of removing insulin from the pancreas, and “run itThey got a purer output, which they called ‘, and then tested it on a human patient for the first time.
The patient is a 14-year-old boy dying of diabetes at Toronto General Hospital. It was Leonard Thompson. He made the first islet injection on January 11, 1922. The injection caused an allergic reaction and increased blood sugar levels. had little effect.
But Banting and Best did not give up. which improves purification processes and is named “insulina biochemist who produces a more potent extract, which they renamed ” James Collip they collaborated with. On January 23, 1922, Leonard Thompson received his second injection of insulin. This time her blood sugar levels dropped significantly and her symptoms improved significantly. He was the first to be successfully treated with insulin.
A sweet anecdote: the hospital full of children awaiting death turns into a nest of joy filled with hope.
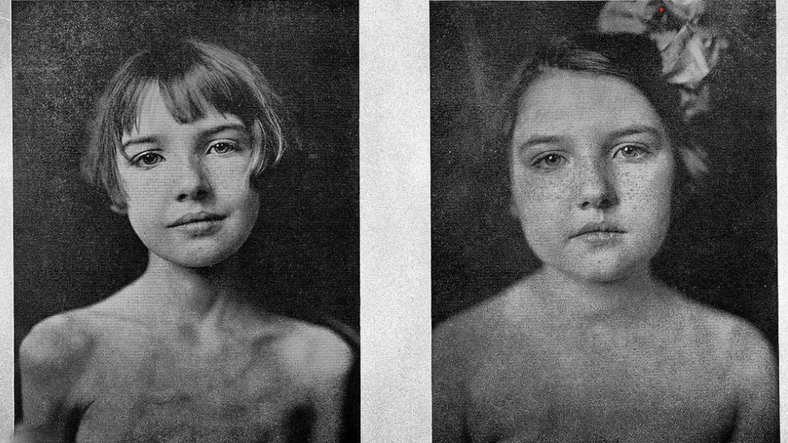
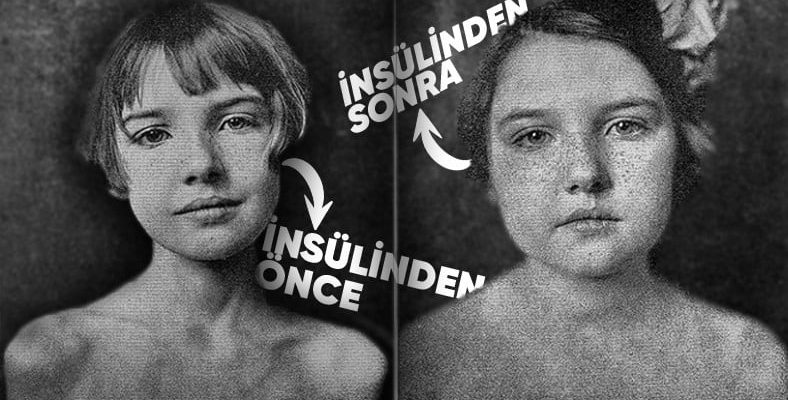
Before insulin injection – 4 months after insulin injection
In 1922, after the discovery of insulin was fully completed and its application on patients, a group of scientists went to Toronto Hospital. in this hospital More than 50 children with diabetes were receiving ‘treatment’.
But many were in coma and dying from diabetic keto-acidosis. If they are not in a coma a strict diet that inevitably ends in death they were subjected. It was hoped this would cure them.
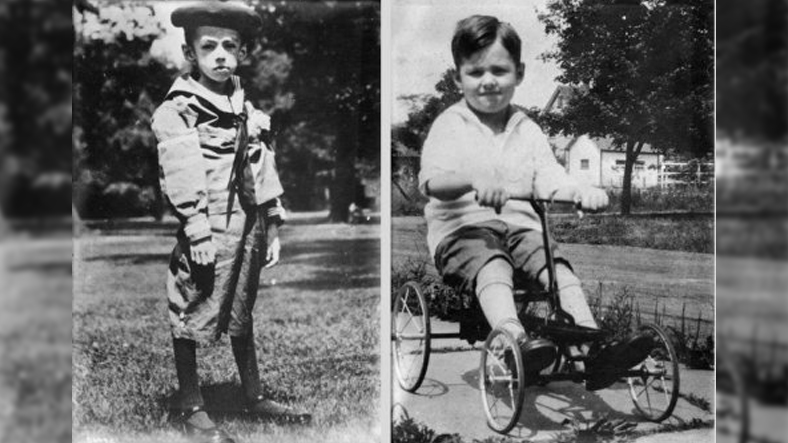
Again, before and after a child’s insulin treatment
These dying children were saved by a group of scientists who came to the hospital with an insulin vaccine. Scientists use this freshly discovered purified they began injecting insulin essence into children.
Of course, the treatment process was not short-lived, it was a period of 4 months. However, while the last child was given insulin, the first children who were vaccinated began to wake up slowly. Children in coma woke up. Those who were not in a coma fully recovered. This hospital, shrouded in death and gloom, suddenly turned into a house overflowing with joy and hope.
However, this success brought with it great ethical debates.

News of the discovery of insulin spread rapidly around the world, and Banting and his colleagues were hailed as heroes. Just two years after their first discovery, in 1923 Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine they were deemed worthy. However, their success came with some controversies and challenges.
One of the biggest controversies was the use of animals in insulin research. Banting and Best conducted their experiments on dogs, and many other scientists used it for insulin production and testing. continued to use animals. Animal rights activists have criticized these practices, arguing that they cause unnecessary suffering and that alternatives such as cell culture or synthetic insulin should be explored.
Another controversy is over insulin. were patent rights. Banting and his team patented the insulin to the University of Toronto. they only sold for 1 dollarThey believed that insulin would be widely available and affordable. However, the university later expanded the insulin market. monopolizing and selling their rights to pharmaceutical companies that set high prices. made it difficult for many patients to access insulin.
Despite these difficulties, insulin saving countless lives and inspiring more research continued. Scientists have discovered different types of insulin, such as rapid-acting, long-acting, and combination insulin, to suit different patient needs. They’ve also developed insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitors, and other devices to help people with diabetes manage their condition more effectively.
Although controversial, insulin is one of the greatest discoveries in the history of medicine.
Today, insulin, along with diet, exercise, and other medications, is available for people with diabetes. a critical treatment continues to be. According to the International Diabetes Federation, around the world, between the ages of 20 and 79 463 million adult diabetics and that number by 2045 reach 700 million Waiting. Insulin research and innovation continues, with the ultimate goal of finding a cure for diabetes.
The discovery of insulin marked a turning point in the history of medicine and It is the first time that a chronic and fatal disease can be treated with a drug. pointed. It was the result of the curiosity, creativity and collaboration of various groups of researchers, who overcame many obstacles and challenges to make insulin a reality.
Insulin has not only changed the lives of people with diabetes, but also in the fields of endocrinology, biochemistry, pharmacology and biotechnology. opened up new avenues of research and innovation. Let’s end our article with the words of Frederick Banting:
“Insulin belongs to the world, not mine.”

RELATED NEWS
Why Do Doctors Write Prescriptions Incomprehensibly?
RELATED NEWS