The James Webb Space Telescope imaged a galaxy simultaneously in 3 different time zones. In the galaxy, a supernova was seen before and after.
The most advanced space telescope, which started operating in the summer of 2022 James Webb, sent a new frame to Earth that you will get lost in details as you look at it. Spectacular detail was also seen in the image of the RX J2129 galaxy cluster.
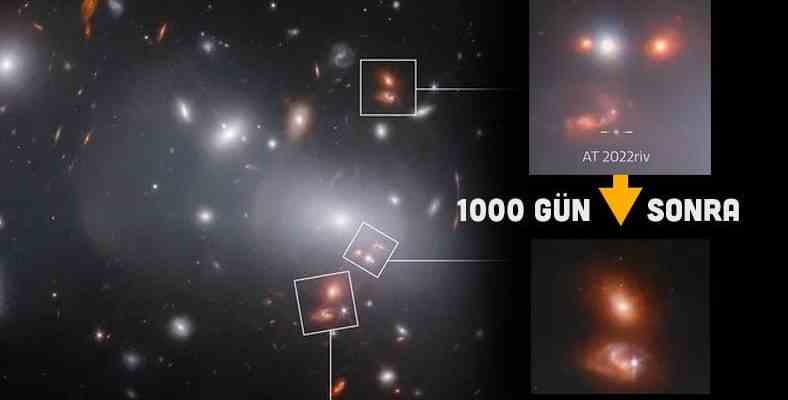
James Webb, thanks to the phenomenon described as “gravitational lensing”, a galaxy with a star experiencing a supernova, in three different time zones viewed simultaneously. That image was like this:
The supernova and its galaxy displayed in different time zones:
The presence of a bright star can be seen in the first image (middle) from the event called “AR 2022riv”. But from the event 320 days and 1000 days later This star is no longer seen in its reflections. The star disappears by experiencing the supernova process.
The European Space Agency announced that the type of supernova was ‘Ia’. Because such supernovas produce the same intensity of brightness, they are easier for scientists to study than other supernovas, so more scientific outputs can be obtained.
So how can we see 3 different times at the same time?

Gravitational lensing occurs when objects in the vacuum of space bend space and time thanks to their mass. This inflection is the result of the objects left behind in our view. bending the light provides.

Thanks to this effect, we get the chance to observe other structures that are behind the massive structures and are at a distance that we cannot normally observe. states in different time periods we can see at the same time.
RELATED NEWS
A Star Dying Observed 3 Different Times Simultaneously (We Are Confused, Too)
RELATED NEWS