The change of gene and trait distributions in a population over generations is called evolution. Even today, there are some situations where we can still see the effects of evolution.
When our distant ancestors left the trees to walk in the savannah, physical changes occurred that are still visible today. Some atrophied and while they are no longer necessary, some hold up as efficiently as ever.
In fact, modern humans for them to survive they can thank many ancient perks, including laughter and eyebrows. Human evolution is far from finished. Here are 10 fascinating facts about human evolution, from changing female voices to genes ruining drinking games!
The nails are much older than we expected.
58 million years Prior to this, primates were introduced to nails. It provided various benefits for the creatures living in the tree. The main goal was to make them better for navigating trees where they were basically limited. The nails strengthened the fingers, allowing them to grip better. Also, unlike other tree animals, primates can grow from the ends of branches. Collect fruit has become superior.
At one point, humans stopped nesting in trees any more because an ancestor realized that the land was more suitable for living. As the lineage evolved, humans ventured into caves and flatter lands. During a radical habitat shift and physical changes over thousands of years, humans kept their claws down. The woodworking skill of nails has evolved into productive crafting and the endless tasks the human hand can perform today.
What is the main purpose of laughing?
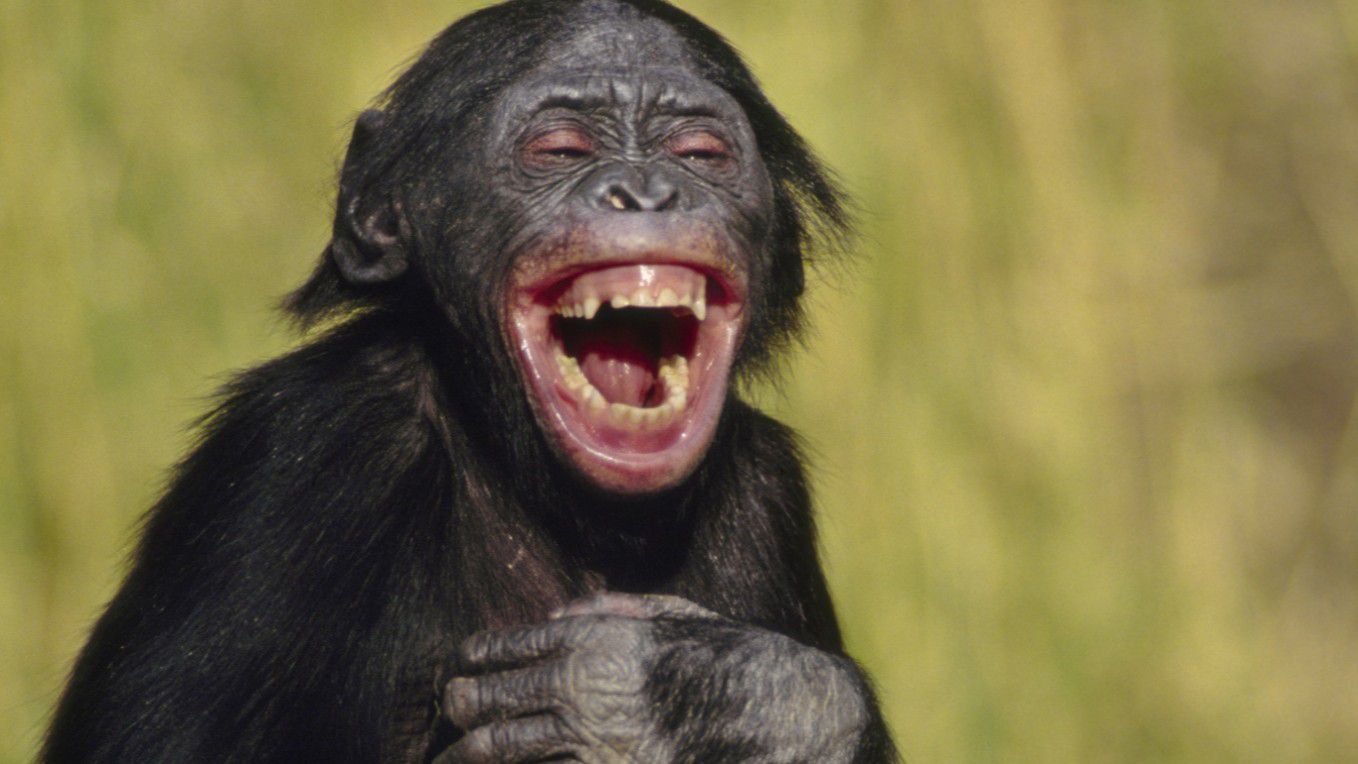

act of laughing seems simple at first. People laugh when they find something funny or pretend it’s something funny. No one wants to meet someone with a killer gaze or an argumentative nature. Research shows that laughter is a powerful social glue has shown that.
The habit of laughing probably evolved in the past as a way to strengthen alliances and reject violence. While our fake laughter seems to remove the same barriers as a real giggle, it may not deceive the people around us.
RELATED NEWS
Solution Found for Alexa Who Keeps Laughing Constantly
Unexpected effect of female friend voice

In one study, men and women were brought together for 30 appointments that would happen quickly. men every six minutes women pass to other tables at the same table left. Each of them had to mark a card indicating whether they liked the other person or not.
When the researchers then listened to the recorded conversations, they were talking to a loved one of both sexes. lowered the tone appeared. It contradicted previous studies that showed men were attracted to louder women because they looked younger and more feminine. However, many find that a quieter conversation is more sincere. When flirting in a room full of people, a woman might lower her voice just for privacy.
Interestingly, it showed that female voice recordings from 1945 were lowered when compared to those taken in the 1990s. This may be because women are trying to convey maturity and dominance in a more equal opportunity world.
Why don’t people have fur?
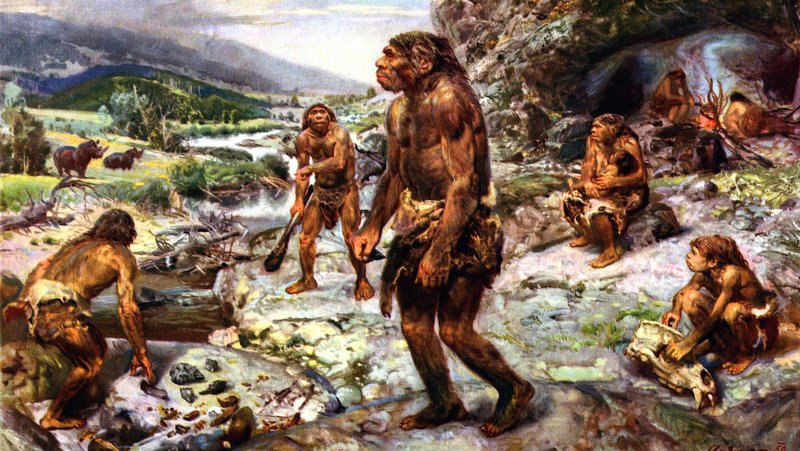

Compared to other animals, humans have a dense hair structure and it has no fur. Fur kept our earliest ancestors warm, protected their skin and provided camouflage. But a circumstance in evolution pressed to delete it.
The strongest theory for the extinction of our fur was that after leaving the trees to live in open savannas, a body covered in fur made it impossible to live and hunt in the heat of the sun, as the new environment was warmer. It is also thought that people’s sweat glands become quite active as the fur becomes thinner. In fact, modern humans are the sweatiest primates.
Why did the big toe change so slowly?
In one study, big toeIt has been described as one of the last foot bones to develop after passing from tree-swinging ancestors to land-dwelling ancestors. It required major overhaul of the feet to walk upright. The big toe was instrumental in this change because it allowed traction during walking.
Despite its importance, the fingers were attached for a long time in primate origin. In the beginning almost one finger It was like, holding branches and working like a tool. For this extremely useful feature to be even more effective, the fingers had to harden, and this happened very slowly over millions of years. But later research proved that the big toe doesn’t really affect the ability to walk efficiently.
Do men’s nipples produce milk?
Male mammals cannot feed their young, but they still have the means to suckle. Some men milk acid It even gives off lactic acid, known as Male nipples are not an evolutionary oddity. They are the result of a biological process that prevents evolution from deleting a useless trait.
A mammalian embryo has the potential to be either sex. Somehow, when the time comes, the chromosome set decides the sex. If there is a male XY pair, SRY A gene called
However, there is another process that takes place before the male genetic switch can be reversed. Mammary glands in mammals begin to develop extremely early, and these glands do not care for any old set of chromosomes. They lay the groundwork for breast tissue and nipples and there is nothing SRY or evolution can do about it.
RELATED NEWS
It Takes a Lifetime to Love, How Many Minutes to Make Love?: Explaining the Evolutionary and Psychologically Ideal Ejaculation Time
A pretty useless tendon
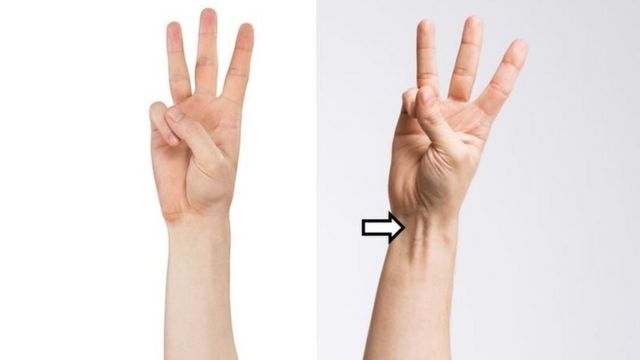
One of the most useless things nature has left in the human body palmaris longus tendon. It appears quite prominently on the wrist. Most people can see this when they touch their thumb and little finger together and tilt the hand slightly towards them. A raised line will appear in the middle of the wrist. If it does not appear born without peoples 10-15% of are among.
The tendon attaches to the palmaris longus muscle but does not make it stronger. The only time it serves a purpose is when surgeons remove and use it elsewhere in the body during plastic and reconstructive surgery. Why do people useless Whether it has tendons remains unclear. It is a relic from a time when the forearms as well as the legs were used to move it, according to a not very valid guess.
Is the function of eyebrows just to protect the eyes?
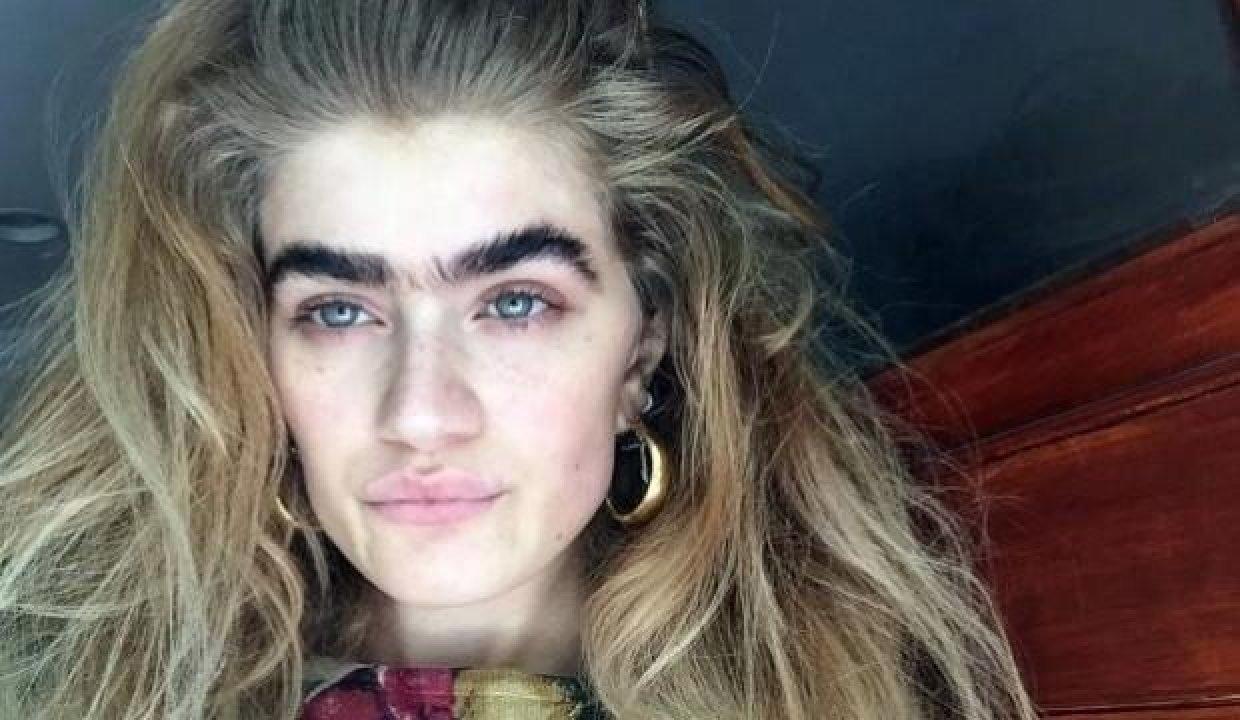

Eyebrows serve an obvious purpose today: for the eyes. protective barrier they serve. Human ancestry would be extinct without eyebrows, according to a surprising study Neanderthals It could be out of stock. Neanderthals and apes had prominent bony prominences above the eyes, much like modern primates. Research has shown that this non-human protrusion has no real purpose other than to look wild.
Returning bone: Fabella
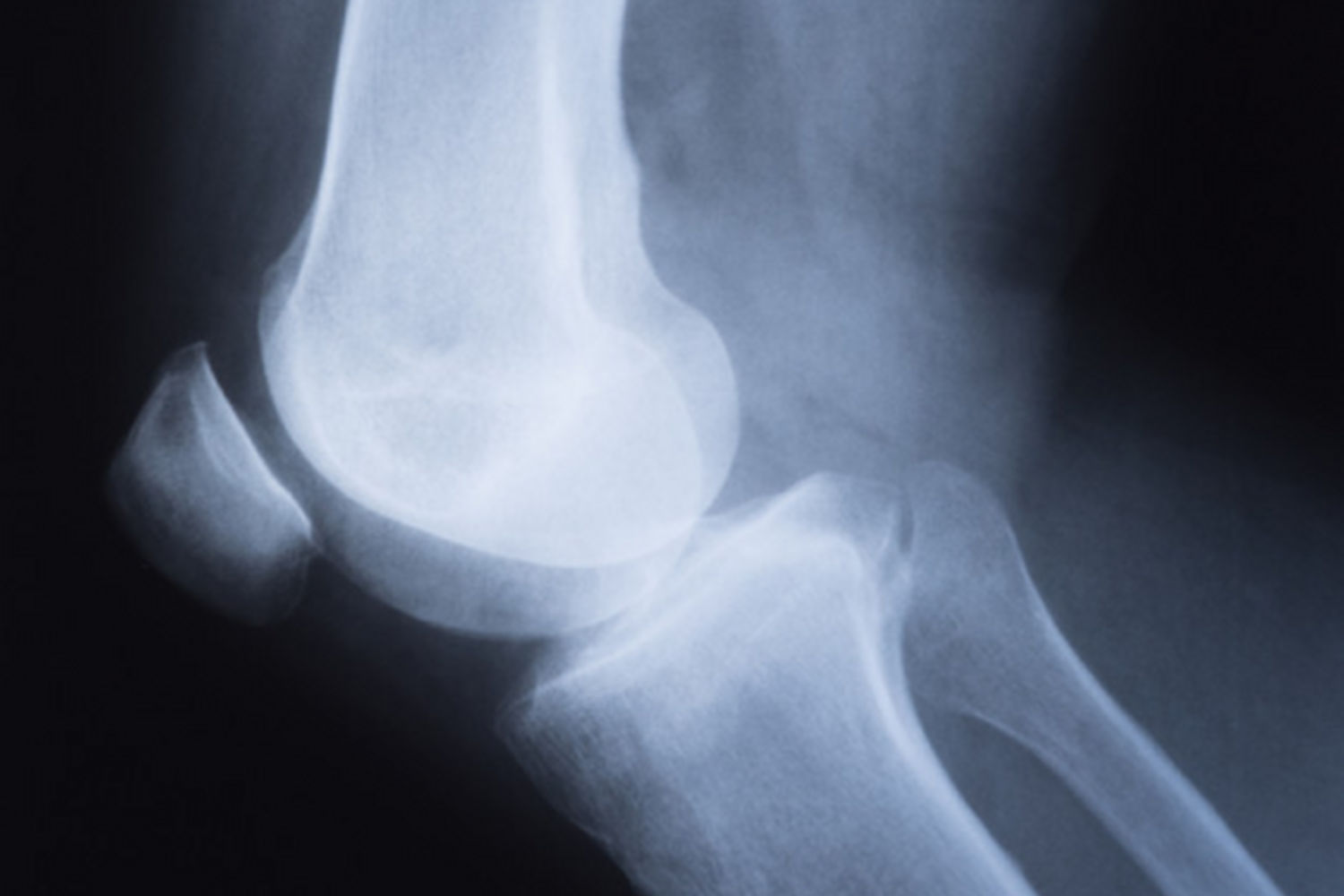
To the human kneecap, once fabella It was accompanied by a small bone called Millions of years ago, it had the same function for monkeys as the modern kneecap. As humans evolve, fabella disappeared and shrank. However, in some people fabella still available It only takes a few kneecap surgeries and scans to realize he has it.
In 2019, researchers conducted an extensive study. They reviewed medical records from 27 countries that included more than 21,000 knees. The results were pretty clear. The tiny bone fabella was returning. Records spanned almost a century, with the earliest showing that in 1875 about 18% of the population had it. In 1918 only 11.2 percent had it. But it’s estimated that about 39 percent of people today have returned remains.
Could your genes be at play if you are prone to hangovers?

One of the weirdest ways humans still evolve is with the alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) gene cluster. Normally, a person one or fifty beers When you drink it, the body breaks down alcohol into poisonous acetaldehyde. When these things accumulate, the drinker no longer feels so cheerful. The face becomes red and the person experiences nausea and rapid heartbeat. Typically, acetaldehyde It is rapidly metabolized to a less irritating acetate that is easily excreted from the body.
Some individuals of East Asian and West African descent have an evolved form of drinking that makes them uncomfortable very quickly. ADH showed the set. This makes it harder to process alcohol and so such people get hit with super hangovers faster. It is not clear how quickly the adaptation spread to other populations or whether the genes were changed to protect people from drunkenness.
Source :
https://listverse.com/2019/05/03/10-fascinating-facts-about-human-evolution/?utm_source=seealso&utm_medium=link&utm_campaign=direct
