Altaic languages, also known as Altaic language family, including Mongolian and Tungusic, as well as our mother tongue Turkish; It covers the languages spoken by the nations living in the Asian steppes. Let’s take a closer look at whether the Altaic language family, which sometimes includes Japanese and Korean, is theoretically correct or still valid.
If you scrutinize your memories in high school Turkish class, “Turkish is a member of the Ural-Altaic language family.” You will surely remember the sentence. It is true, but some experts separate the Uralic and Altaic languages, and even say that the Altaic language family is not as it was claimed. adopted from the same family grammatical and phonetic aspects of all these languages. The claim that they are similar to each other has not been supported much in recent years.
All languages belonging to the Altaic language family are the languages spoken by the nations living in the Asian steppes. Languages in this family, sometimes including Japanese and Korean similar in origin It has been said for many years, but perhaps this similarity is only due to the closeness of the nations. Let’s take a closer look at the Altaic language family and see the theories on the subject.
What is the Altaic language family?
widely spoken in Asia Mongolian, Tungusic and Turkic languages The language group, which sometimes includes Japanese and Korean, is defined as the Altaic language family or Altaic languages. Many studies have been conducted on the grammatical and phonetic similarity of languages in this variative group, which was introduced in the 18th century.
Altaic language family features:
- All languages in the group are additive languages.
- No prefix is used.
- The root does not change even if it takes a production and a shooting attachment.
- They are extremely rich in supplements.
- The complement comes first, the complement comes after.
- The adjective comes before the noun.
- Plural suffixes are not used in number words.
- Sentence structure has a regular hierarchy.
- There is no grammatical gender. (he – she)
- All languages in the group have question suffixes.
- All languages in the group have common suffixes from the same source.
- All languages in the group have vowel harmony.
How did the Altaic language family come about?
The Altaic language family theory was first developed by Philip Johan von Strahlenberg, a geographer who had been captured by the Russian Empire and traveled the eastern region. It was introduced in 1730. Strahlenberg saw the relationship between Turkic, Mongolian and Tungusic languages, albeit roughly, and classified them.
Definitions such as Altaic language and Altaic were first made by Finnish linguist Matthias Castrén in 1844. According to Matthias Castrén, who also conducted detailed studies on Uralic languages, Finno-Ugric and Samoyed languages are also should be considered as the same or a similar language family. Because of this thought of Castrén, the definition of Uralic – Altaic language family has been accepted by scientific circles for many years.
Anton Boller in 1857 JapaneseIn 1920, GJ Ramstedt and ED Polivanov also your korean They claimed that it belongs to the Ural-Altaic language family. In a later work, Ramstedt rejected the definition of Ural – Altaic family and argued that Korean belongs to the Altaic language family.
This work of Ramstedt was revised and republished by Nicholas Poppe in 1960. Between Turkish, Mongolian, Tungusic languages and Korean in the new edition It has been said that no definite link has been found. Different theories have been put forward such as that Korean may be genetically similar to the Altaic language family, may be related, or that it has been separated from these languages before the characteristic features become clear.
What are the Altaic languages and their subgroups?
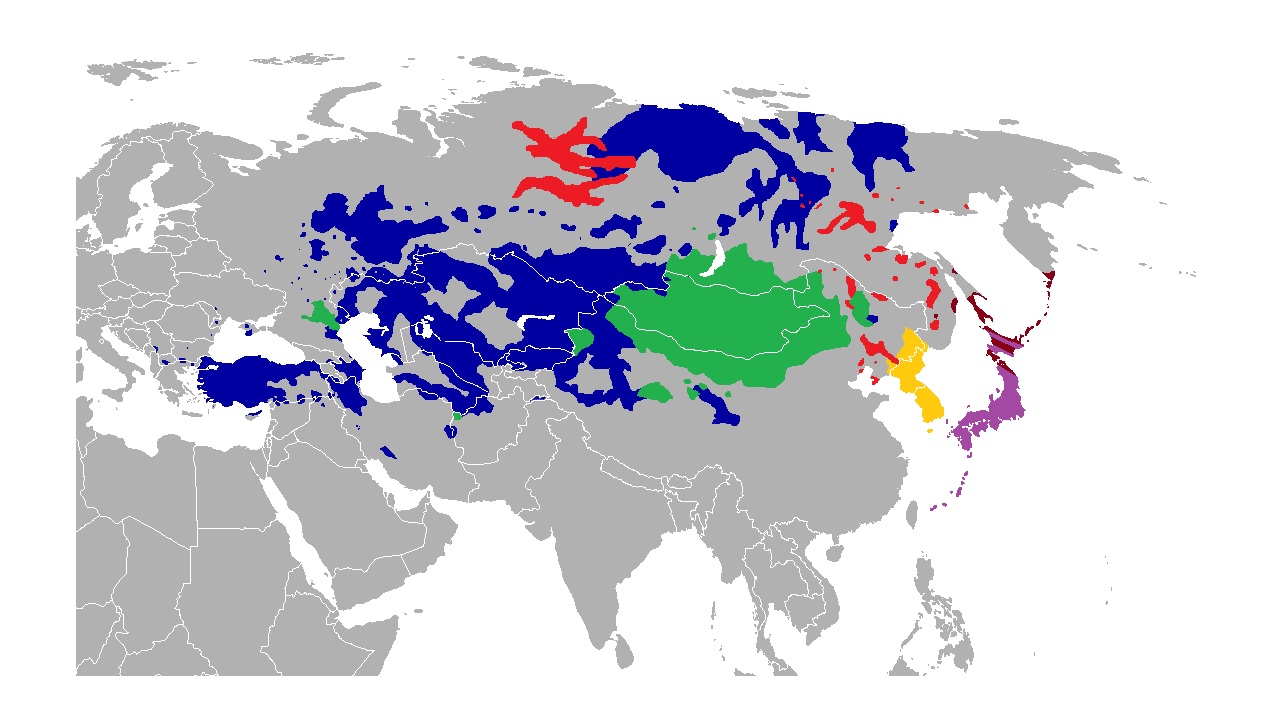
- Japanese
- Korean
- Mongolian languages
- Buryat language
- Kalmyk language
- Mongolian
- Tungusic languages
- Northern Tungusic languages
- Evenki
- manegir
- Negidal
- Oroqen
- solo
- Even (Lamut)
- Evenki
- Southwestern Tungusic languages
- Southeast Tungusic languages
- Akani
- beer
- Bushel
- Nanai (Gold, Goldi, Hezhen)
- oroch
- Orok
- Samaghir
- Udege
- Ulc
- Northern Tungusic languages
- Turkic languages
- Azerbaijani
- Bashkir
- Chuvash
- Gagauz
- Khalaj
- Karachay-Balkarian
- Kazakh
- Kyrgyz
- Uzbek
- Kazan Tatar
- Crimean Tatar
- Khakas Turkish
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Tuvan
- Uigur
- Yakut language
Other known language families:

- Gottologous language families;
- Atlantic-Congo (1,432 languages)
- Austronesian (1,275 languages)
- Indo-European (588 languages)
- Sino-Tibetan (494 languages)
- Afro-Asian (373 languages)
- Nuclear Trans-New Guinea (314 languages)
- Pama–Nyungan (248 languages)
- Auto-Mange (180 languages)
- Austroasian (159 languages)
- Thai–Kaday (94 languages)
- Dravidian (81 languages)
- Arawak (78 languages)
- Mande (75 languages)
- Tupi (71 languages)
- Ethnologue language families;
- Niger-Congo (1,542 languages)
- Austronesian (1,257 languages)
- Trans–New Guinea (482 languages)
- Sino-Tibetan (455 languages)
- Indo-European (448 languages)
- Australia [şüpheli] (381 languages)
- Afro-Asian (377 languages)
- Nilo-Saharan [şüpheli] (206 languages)
- Auto-Mange (178 languages)
- Austroasian (167 languages)
- Thai–Kaday (91 languages)
- Dravidian (86 languages)
- Tupi (76 languages)
Altaic language family, which also includes Turkish, or with its other name We told you about the Altaic languages. and we talked about the theories put forward that this concept might be wrong. Do you think the Altaic languages are similar to each other? You can share your thoughts in the comments.
