A phenomenon based on quantum physics has allowed scientists to develop a lens just three atoms thick. The discovery stands out because it directly transmits most wavelengths of light, and this feature has great potential in devices such as fiber optic communications and augmented reality glasses.
The thinnest lens in history was produced
It is stated that this lens, developed by researchers from the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands and Stanford University in the USA, will advance the research of such lenses and miniature electronic systems.
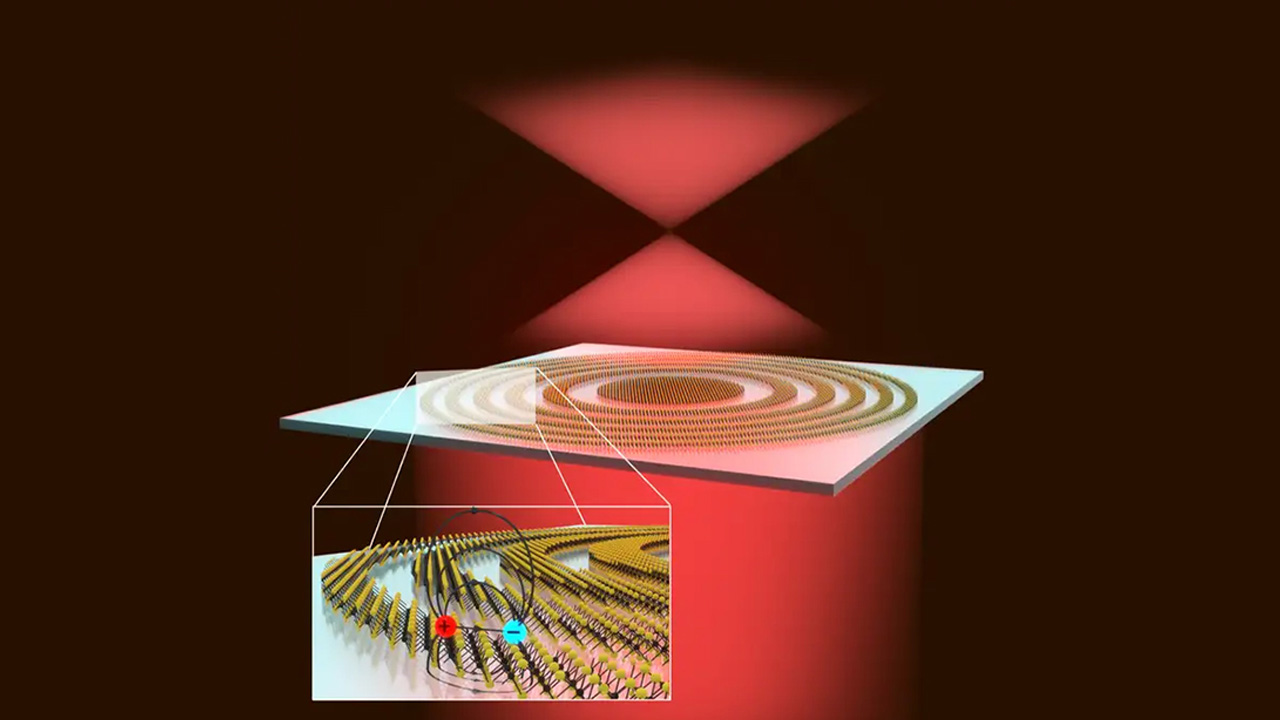
Rather than using the curved surface of a transparent material to refract light, the lens focuses incoming waves using refraction.
The technology, known as Fresnel or zone plate lensing, has been used for centuries in the production of lightweight, thin lenses, such as those used in lighthouses.
To add quantum power to the technology, the research team etched concentric rings into a thin layer of a semiconductor called tungsten disulfide (WS2). When WS2 absorbs light, its electrons move in a certain way, leaving a gap; This space can be thought of as a type of particle.
The electron and the “hole” combine to form an “exciton,” which has properties that help the efficiency of focusing light at certain wavelengths while allowing other wavelengths to pass through unchanged.
The size of the rings and the distance between them allowed the lens to focus red light 1 millimeter away. The research team discovered that the lens works at room temperature, but its focusing abilities become even more efficient at lower temperatures.
The researchers plan to conduct more experiments in the future to see how exciton behavior can be further manipulated and increase the efficiency and capabilities of the lens.
If you wish, you can take a look at the original source where the research was published here. What are you thinking? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section below.

