When it comes to earthquakes, geological facts and conspiracy theories such as fault lines probably come to our minds first, but it is possible to talk about another factor that can be just as effective, even if we don’t think about it.
prof. Dr. Celal Şengör answered some questions about “earthquake weapons” at Teke Tek about 5 years ago. The subject of the publication is the from existing technologies which could cause earthquakes.
Celâl Şengör, who underlined that earthquake weapons are conspiracy theories, most likely to cause an earthquake He mentioned that human invention is dams. Let’s briefly examine the truth of this argument within the framework of the resources that science and scientists offer us.
According to research, dams can seriously increase the risk of earthquakes if the necessary precautions are not taken.
The bases of the water sources on which some dams are built are used to undertake such a task. may not be convenient enough.
Artificial aquifers (the upper part in the image) where water is accumulated, if the bottom is soft, than the earth’s crust normally much more they apply pressure and pressure.
The accumulated water sometimes goes beyond the base. rock layers and fault lines beneath it erodes. These stone layers and fault lines were then displaced. more And faster they start playing. Therefore, fault lines, which normally move more slowly, move more easily as the stone layers in front of them begin to soften, and both the frequency and intensity of earthquakes increase.
The extremely deadly earthquakes that occur periodically in Pakistan confirm this argument and scientific reality.
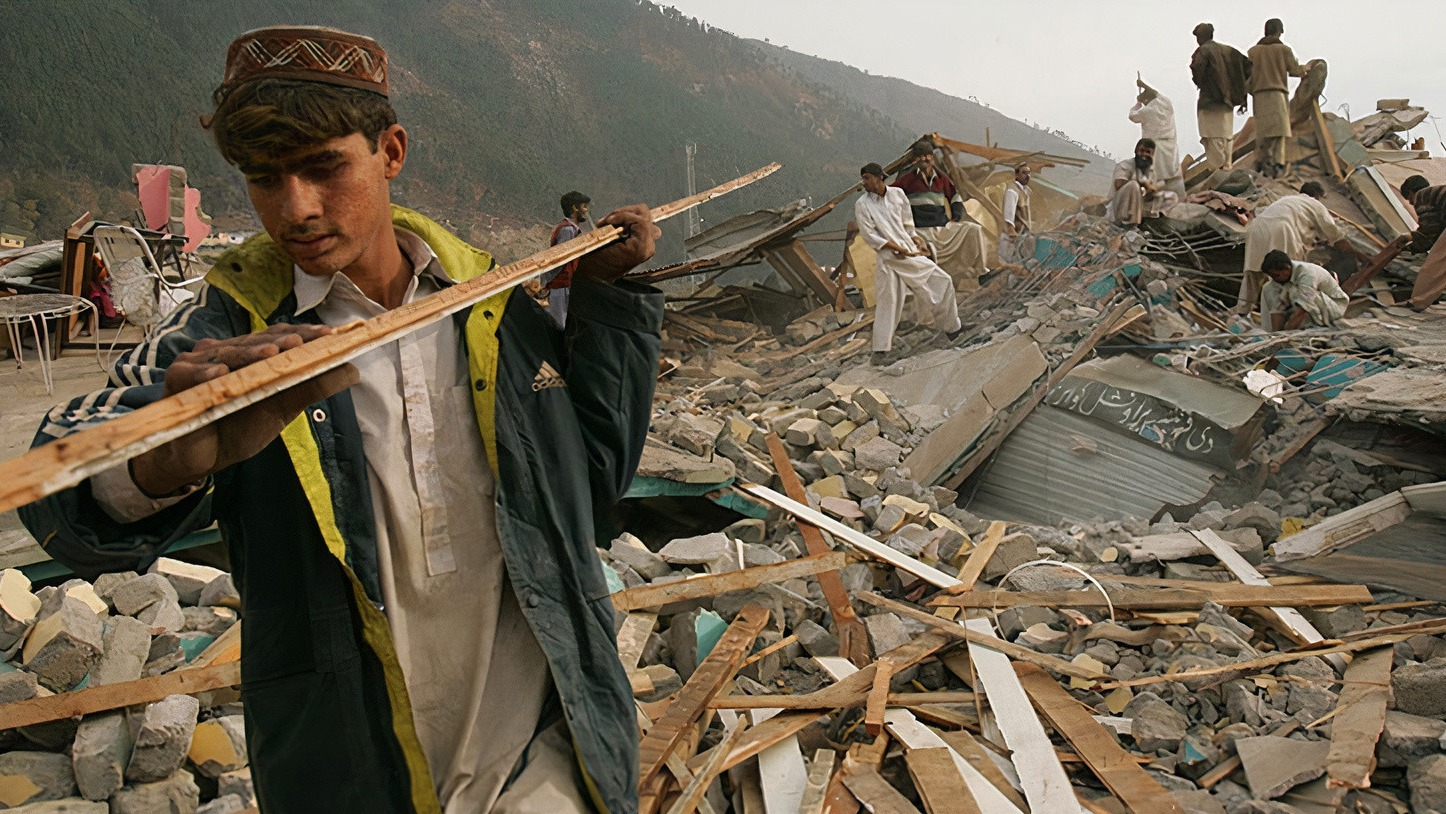

Due to the narrow and mostly arid geography of the country, a large part of Pakistan’s population lives both in the beds of the Indus River and in close to dams have to live. This country, which has a population of more than 230 million, needs just as much energy. For this reason, residential areas, agricultural areas, wells, mines, dams, factories and industrial areas, necessarily to the bottom is being built.
The situation, as you can imagine, is a disaster history full of tragic disasters. The number of people who lost their lives in an earthquake in the Balochistan region in 1935 50-60 thousand was around. The number of people who lost their lives in another earthquake in the Azad Kashmir region in 2005 87 thousand around, the number of injured 75 thousand had found it. Those who were not affected by the earthquake lost their lives due to floods, erosion and similar natural disasters.
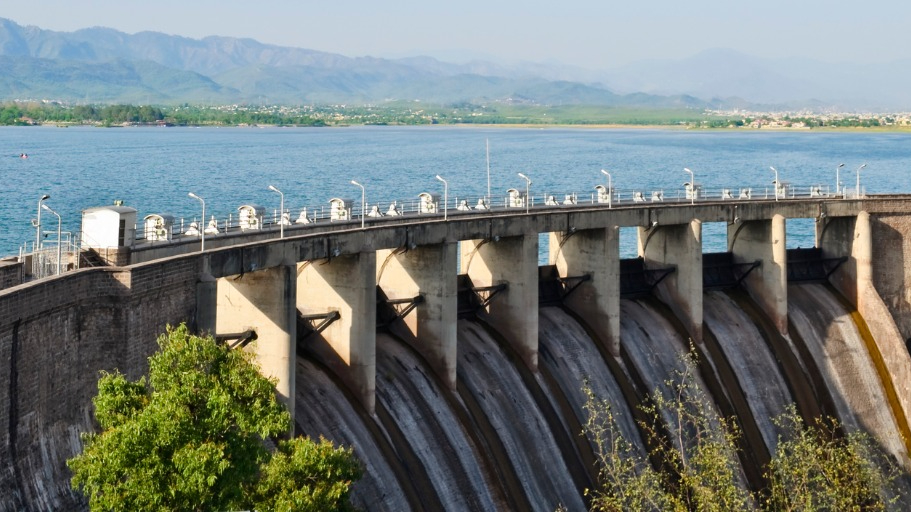

The main source of all these problems is the dams built on the Indus River, one of the rivers of our planet with the highest current strength and intensity. around the river frequency of residential areas and dams regular erosion of river bottoms, It has placed Pakistan in this inevitable cycle of tragedies.
Disasters caused by the disproportionate use or careless storage of water resources are not limited to those caused by dams.
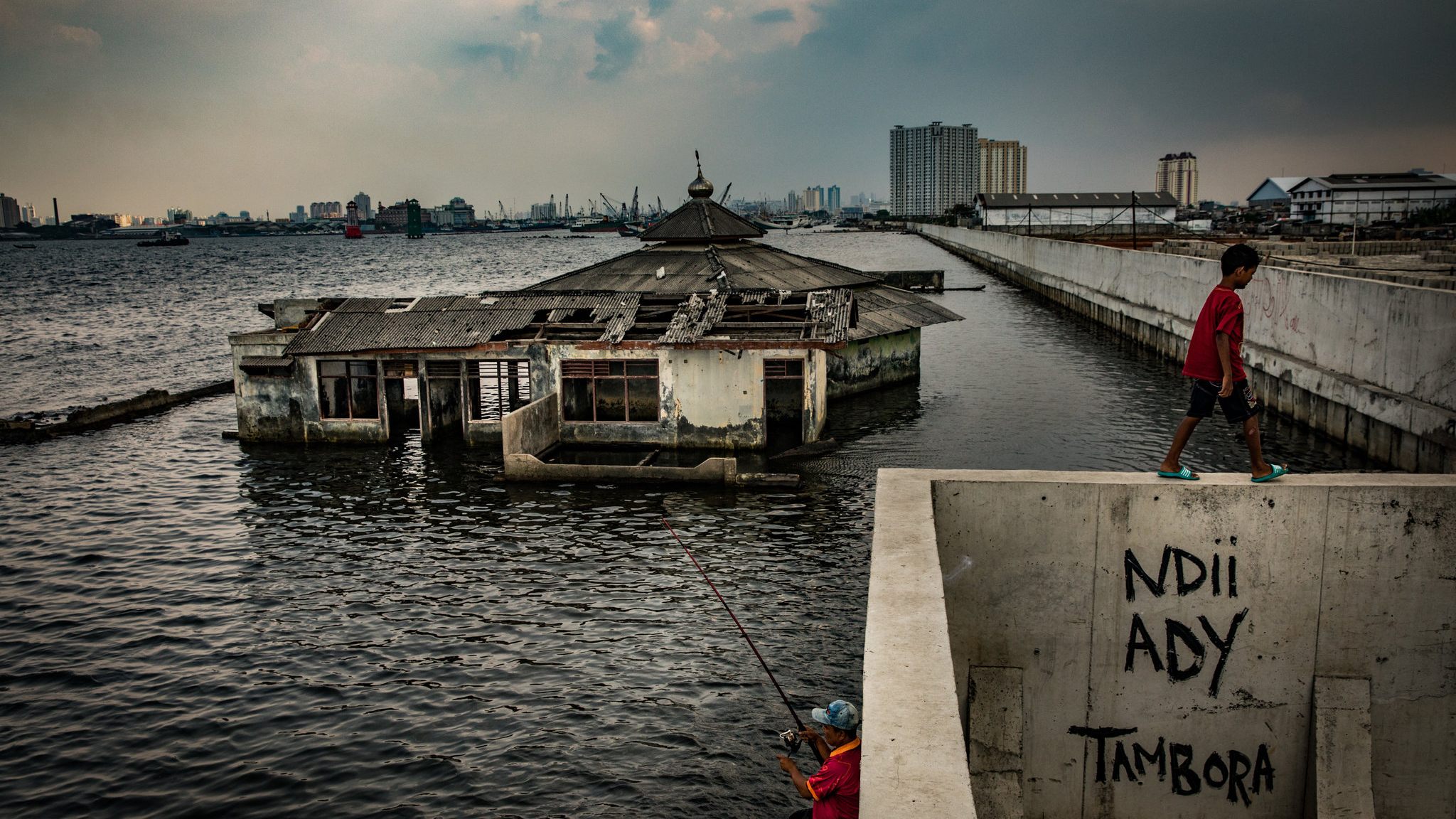

A similar situation occurs inside the earth’s crust. when too much water is pumped And even when settlements were established in river beds it can be lived.
Soils weakened by excessive water pumping are vulnerable to earthquakes and erosion. The best examples of this are Indonesia’s capital, Jakarta, which sinks a few inches into the ground each year, and Mexico’s capital, Mexico City. Jakarta 5 centimeters per year sinking to the ground, Mexico City 50 centimeters per year sinks into the ground.
drinking water in these cities. reach with wells And pump out common practices. As underground water supplies dwindle and water from rivers accumulates in the dam’s aquifers, the floors and river bottoms of these cities are both collapsing and over-softening, respectively.
The first rational solution that comes to mind for all these problems is to establish the settlements as far away from the dams as possible and to take the necessary precautions to prevent the settlements established close to the dams from being affected by the softening ground.

prof. Dr. Celal Şengör has had a clear view on this issue since 2009: “Don’t build dams anymore!”. But given the energy needs of people, the fact that they live close to rivers, and that dams cannot be built on flat areas where there is no risk of earthquakes, it is not difficult to realize that it is not possible not to build new dams or to remove people from the settlements around the dams.
Other scientists and experts also offer different solutions:
- Afforestation should be done in settlements close to dams and buildings should be strengthened.
- The reservoirs of the dams near which settlements are located should not exceed a certain occupancy limit in order to reduce the pressure on the river bed. Unless there is a great demand for water, the dam should not be overloaded.
- The dams on the rivers whose river bed is not very solid should be closed, and new dams should be built in other parts.
- If not many people will be affected, the direction of the river should be changed and a dam should be built on the new river bed.
- The use of dams should continue, but in time alternatives such as nuclear energy should be switched.
Although the status of the dams in Turkey is not yet fully known, it is necessary not to mention that at least some research has been carried out so far.
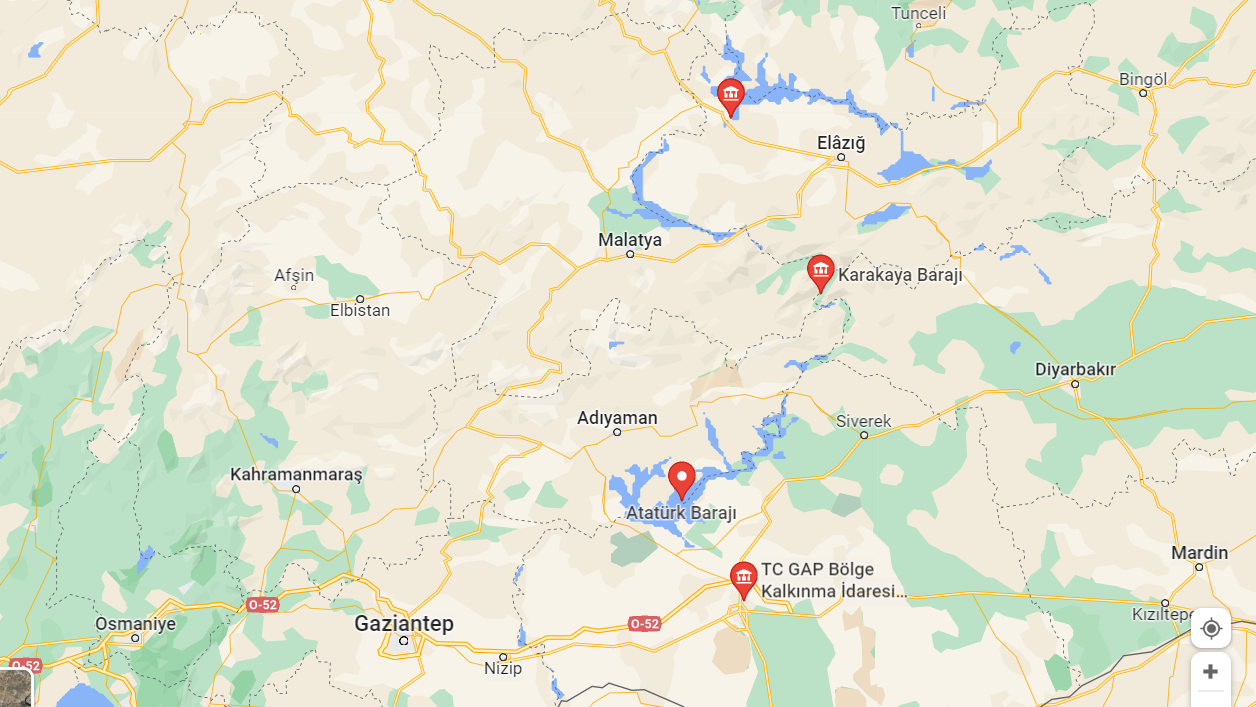
Prof. from Istanbul Technical University. Dr. Haluk Eyidogan, Ataturk Dam in 2017 earthquake triggered or that you can trigger He shared an academic article about it.
Known for his researches in seismology and geophysics and predicting the September 26, 2019 Istanbul earthquake (5.8), Prof. Dr. Haluk Eyidogan made four suggestions in his article, which we can summarize as follows:
- The characteristics of the Samsat Fault, Adıyaman Fault, Lice Fault and Çalgan Fault should be studied for the safety of nearby dams (and therefore the region).
- Especially the Bozova Fault, which is very close to the dam, should be examined in terms of its relationship with the earthquake.
- A seismograph that will measure the 30-kilometer radius of the dam should be installed in order for it to lose its earthquake activity, and its data should be evaluated in seismology.
- Information restrictions on the dam’s water level values should be ended and most of our dams, including the Atatürk Dam, should be used to investigate the relationship of dams to earthquakes.
To summarize, there is some truth to the argument that earthquakes can be triggered by dams, and there is still debate about its solution.
RELATED NEWS
Everything You Need To Know About Famous Geologist Celal Şengör
RELATED NEWS
